本文主要是介绍笛卡尔树 - HDU 1506,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
转至:https://cs.v8cloud.cn/article.html?blog_id=225
笛卡尔树是一个很有意思的树形结构,因为它同时满足两个性质,从key(key就是索引位置,如下图中9的key为1,3的key为2......)来看,满足二叉搜索树的特性,从value来看,满足堆的性质。
重点参考下图,图片来自维基百科,还算是能够比较形象的说明这两点。

笛卡尔树拥有这两种特性,那么它有什么用途呢?
对于HDU 1506,我们需要计算最大矩形区域,正好是笛卡尔树最典型的用途,从上图中,我们以任意节点K开始,K所在的最大矩形必定是K的value为高,K的右子树最大key值减去K的key值为宽。
笛卡尔树比较难的地方在于构造,小编我是看了好久才把这个思路理清,这里给出大概的思路,不懂得童鞋留言讨论。
1、笛卡尔树的构造:
(1)从第一个元素开始,从左往右遍历数组L
(2)将元素L[0]作为树的根节点R
(3)for i in [a[1], a[2]...a[n]]
(4)如果a[i]小于根节点R,则将a[i]作为根节点R的父节点
(5)如果a[i]大于根节点R,则将a[i]从根节点的右节点开始寻找位置
(6)从右寻找的逻辑同根节点的对比方法
2、特性
对于树上的每个节点,以它作为高的新矩形的面积就是以该节点为根的子树大小乘以它的高
构造源代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct node_s
{struct node_s * l;struct node_s * r;struct node_s * p;int v;
}node_t;typedef struct tree_s
{node_t * root;
}tree_t;node_t * node_create(node_t * p, int v)
{node_t * n = (node_t*)malloc(sizeof(node_t));memset(n, 0, sizeof(node_t));n->v = v;n->p = p;return n;
}tree_t * tree_create()
{tree_t * t = (tree_t*)malloc(sizeof(tree_t));memset(t, 0, sizeof(tree_t));return t;
}void tree_insert_n(node_t * root, int v)
{//当前节点比根节点小,则转换为根节点if(v < root->v){node_t * n = node_create(root->p, v);root->p->r = n;root->p = n;n->l = root;}else{//如果右子树不存在,直接放置if(root->r == 0){root->r = node_create(root, v);return;}//当前的节点比根节点大,则从根节点的右子树开始查找tree_insert_n(root->r, v);}
}void tree_insert(tree_t * t, int v)
{if(t->root == 0){t->root = node_create(0, v);return;}//当前节点比根节点小,则转换为根节点if(v < t->root->v){node_t * n = node_create(0, v);t->root->p = n;n->l = t->root;t->root = n;}else{//如果右子树不存在,直接放置if(t->root->r == 0){t->root->r = node_create(t->root, v);return;}//当前的节点比根节点大,则从根节点的右子树开始查找tree_insert_n(t->root->r, v);}
}void tree_print_n(node_t * n, int level, char dir)
{if(!n){return;}for(int i=0; i<level; ++i){printf("---");}printf("%c--%d\n", dir, n->v);tree_print_n(n->l, level+1, 'L');tree_print_n(n->r, level+1, 'R');
}void tree_print(tree_t * tree)
{tree_print_n(tree->root, 0, 'C');printf("\n");
}void tree_free(tree_t * t)
{}int main()
{freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);int n, height;while (scanf("%d", &n), n){int arr[n];tree_t * tree = tree_create();for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){scanf("%d", &arr[i]);}for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i){tree_insert(tree, arr[i]);tree_print(tree);}tree_free(tree);printf("\n");}return 0;
}C++
Copy
在理解了笛卡尔树的构造之后,HDU 1506这道题就很容易理解了。具体的解题思路就不细讲了,只不过在构造笛卡尔树的时候用了数组形式,如果一时理解不了以后再看也行,重点是把上面的代码弄清楚。
来看题~~翻译看不懂直接看图!
Problem Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
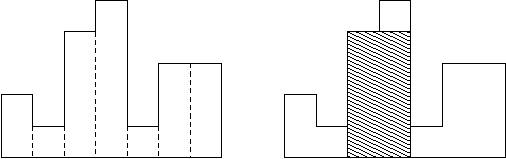
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
Sample Output
8 4000
解题思路:
参考以上。
解题代码:G++
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>using namespace std;typedef long long ll;
const int N = 100000 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;struct node
{int index;int value;int parent;int child[2];friend bool operator< (node a, node b){return a.index < b.index;}void init(int _index, int _value, int _parent){index = _index;value = _value;parent = _parent;child[0] = child[1] = 0;}} tree[N];int root;
int top, stk[N];
ll ans;//创建笛卡尔树
int cartesian_build(int n)
{for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){int k = i - 1;//一直找到比i位置小的位置kwhile (tree[k].value > tree[i].value)k = tree[k].parent;//printf("i(%d - %d) k(%d - %d)\n", i, tree[i].value, k, tree[k].value);//将父节点的右子树放到自己的左子树上tree[i].child[0] = tree[k].child[1];//父节点的右子树重新指向tree[k].child[1] = i;//设置i的父节点tree[i].parent = k;//很多人没加这句,父节点关系就会乱掉tree[tree[i].child[0]].parent = i;}return tree[0].child[1];
}int dfs(int x)
{if (!x)return 0;//计算最大值int sz = dfs(tree[x].child[0]);sz += dfs(tree[x].child[1]);ans = max(ans, (ll)(sz + 1) * tree[x].value);return sz + 1;
}int main()
{int n, height;//freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin);while (scanf("%d", &n), n){tree[0].init(0, 0, 0);for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){scanf("%d", &height);//初始化每个节点tree[i].init(i, height, 0);}//创建笛卡尔树root = cartesian_build(n);//ans = 0;dfs(root);printf("%lld\n", ans);}return 0;
}这篇关于笛卡尔树 - HDU 1506的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



