本文主要是介绍遥感LAI一些记录,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
(一)遥感数据
(二)文献
(一)数据
1.全球十九大主流卫星遥感数据下载平台
2.国家遥感中心
3.美国对地观测系统卫星资料产品及服务
NASA EOS分布式数据存档中心包括:
- 阿拉斯加卫星研究室分布式数据存档中心(ASF DAAC)
- GSFC地球科学数据信息服务中心分布式数据存档中心(GESDISCDACC)
- 全球水资源中心分布式数据存档中心(GHRC DAAC)
- 陆面过程资料分布式数据存档中心(LP DAAC)
- 兰利大气科学资料分布式数据存档中心(LaRC DAAC)
- 国家冰雪资料中心分布式数据存档中心(NSIDC DAAC)
- 橡树岭国家实验室分布式数据存档中心(ORNL DAAC)
- 海洋物理学分布式数据存档中心(PO DAAC)
- 社会经济学数据与应用中心(SEDAC)
3.1 ORNL DAAC Americanflux site modis LAI产品下载网址
-
数据格式说明
(1) MCD14A3H-4day数据产品质量说明
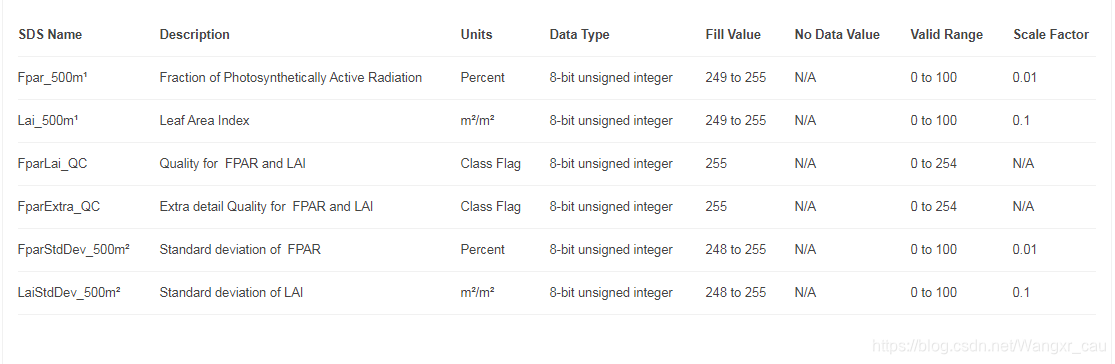
(2) MOD09A1产品说明
(3) NASA MODIS (MCD15A3H v6)反演算法The radiative transfer model is based on photon transfer theory and takes into account clumping at plant and canopy level (but not shoot clumping for pines). This makes the retrieved values more comparable to ‘true LAI’ rather than ‘effective LAI’.
3.2 常用遥感LAI产品及其反演算法
[1] 《Xie, Xinyao, et al. “Assessment of five satellite-derived LAI datasets for GPP estimations through ecosystem models.” Science of The Total Environment 690 (2019): 1120-1130.》
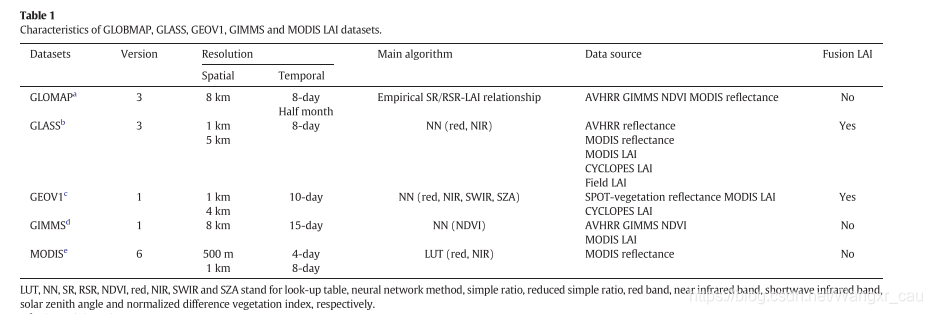
[2] 《叶面积指数的遥感定量方法综述》link
-
统计模型法
利用遥感定向统计分析叶面积指数的依据是植被冠层的光谱特征。(1)绿色植物叶片的叶绿素在光照条件下发生光合作用,强烈吸收可见光,尤其是红光。因此,红光波段反射率包含了植被顶层叶片的大量信息。(2)在近红外波段名植被有很高的反射率、透色率和很低的吸收率,因此,近红外反射率包含了冠层内叶片的很多信息。这就是LAI遥感定量统计分析的理论依据。统计分析法是以LAI为因变量,以光谱数据或其他变换形式(如植被指数)作为自变量建立的估算模型,即LAI=f(x),其中x为光谱反射率或植被指数。
-
光学模型法
光学模型建立的基础是植被的非朗伯体特性,即植被对太阳光短波辐射的散射具有各项异性,反映在遥感上就是从地表反射回天空的太阳辐射和卫星观测的结果很大程度上依赖于太阳角和卫星观测角的关系,这种双向反射特性可以用双向反射率分布函数(BI-DIRECTIOAL REFLECTANCE DISTRIBUTION FUNCTION,BRDF)来定量表示,这就给LAI定向模型的创造提供了理论契机。光学模型就是基于植被的BRDF,它是建立在辐射传输模型基础上的一种模型,具有物理基础,不依赖植被的具体类型或背景环境的变化,因此具有普适性。
辐射传输模型是模拟光辐射在一定介质(如大气和植被)中的传输过程,最初用于研究光辐射在大气中传输的规律,后来被移植到植被对太阳光辐射的吸收和散射规律研究中。对于某一特定时间的植被冠层而言,一般的辐射传输模型为:
S=F(λ,Θs,Ψs,Θv,Ψv,C)
其中,S为叶子或冠层的反射率或透射率,λ为波长,Θs,Ψs为太阳天顶角和方位角,Θv,Ψv为观测天顶角和方位角,C为一组关于植被冠层的物理参数,如植被LAI,叶面分布等。
一般辐射传输模型以LAI等生物物理、生物化学参数作为输入值,得到的输出值是S。从数学角度看,要求得LAI,只需要得到上述函数的反函数,以S为自变量反求LAI,这就是光学模型反演LAI的基本原理。
(二)文献
- 王培娟 link
- 戴永久PPT link
- 梁顺林
[1] LAI的定义和测量方法《Use of General Regression Neural Networks for Generating the GLASS Leaf Area Index Product From Time-Series MODIS Surface Reflectance》
1.1 真实叶面积和有效叶面积
Leaf area index (LAI), defined as one half of the total green leaf area per unit of horizontal ground surface area [1], is often called true LAI. The true LAI multiplied by the clumping index is termed effective LAI [2].
1.2 测量方法
-There are currently two main types of methods for retrieving LAI from satellite data: empirical methods and physical methods.
1.3 方法1 经验法
The empirical methods are based on statistical relationships between LAI and spectral vegetation indexes, which are calibrated for distinct vegetation types using field measurements of LAI and reflectance data recorded by a remote sensor or simulations from canopy radiation models [3].
Sellers et al. [4] retrieved LAI from Fourier Adjusted, Solar zenith angle correction, Interpolation, and Reconstruction of Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) data using empirical relationships derived from available field surveys.
Based on radiative transfer simulations and field surveys, Myneni et al. [5] derived biome-specific LAI–NDVI relationships and generated the corresponding LAI data sets from Pathfinder AVHRR Land and Global Inventory Modeling and Mapping Studies NDVI data.
Chen et al. [6] derived Canada-wide time series of LAI from AVHRR and SPOT-Vegetation data using the land-cover-specific SR–LAI and RSR–LAI relationships.
These empirical methods are computationally efficient in operating with a large amount of data, but they do not exploit the full spectral-directional information conveyed by the radiometric signal [7].
1.4 方法2 物理法
The physical methods are based on the inversion of canopy radiative transfer models through iterative minimization of a cost function [8], [9] or other methods.
Because the model-inversion methods can be adjusted for a wide range of situations [10], radiative transfer models are increasingly used in the inverse mode to estimate LAI from remotely sensed data. However, inversion techniques based on iterative minimization of a cost function require hundreds of runs of the canopy radiative transfer model for each pixel; therefore, they are computationally too demanding [10].
- (1)For operational applications, look-up tables (LUTs) and artificial neural networks (ANNs) are two popular inversion techniques that are based on a pre-computed reflectance database.
(2)The LUT methods consist of determining the distribution of pre-computed canopy realizations that minimize a given misfit function with respect to the observations. Based on the radiative-transfer-model-based LUT, Myneni et al. [11] developed an operational algorithm to retrieve LAI from Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data, and global LAI products have been generated from Terra and Aqua MODIS data with this algorithm since 2000.
(3) ANNs are well known for their good performance in classification and function approximation. They are very efficient from a computational point of view, which is particularly important for operational applications with a long time series of global data. Currently, neural networks are increasingly being used for the estimation of LAI from remotely sensed data [3], [12]. Fang and Liang [13] demonstrated a neural network algorithm for retrieving LAI from the Landsat-7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus surface reflectance and TOA radiance. Bacour et al. [8] developed an operational algorithm based on neural networks to estimate LAI, fAPAR, fCover, and LAI ×Cab from MERIS top-of-canopy observations. Baret et al. [14] developed an algorithm for generating LAI, fAPAR, and fCover estimates from VEGETATION observations based on training neural networks with SAIL +PROSPECT radiative transfer model simulations for each biophysical variable. Verger et al. [15] evaluated the performance of a neural network approach to estimating LAI from CYCLOPES and MODIS nadir-normalized reflectance and LAI products. The neural networks were trained with the LAI products from one sensor and the reflectance from another.
1.5 MODIS LAI反演算法
(1)主要算法和备用算法 The MODIS LAI retrieval algorithm includes a main algorithm and a backup algorithm. When the main algorithm fails, the backup algorithm is used to estimate LAI from biome-specific LAI–NDVI relationship.
(2)MODISLAI是真实叶面积 The MODIS LAI retrieval algorithm accounts for vegetation clumping at the canopy and plant (shoot) scales through 3-D radiative transfer formulations. Since the clumping values at landscape scale is not gathered as a function of biomes, it is partly addressed via mechanisms based on the radiative transfer theory of canopy spectral invariants in the MODIS LAI retrieval algorithm [22], [25]. Therefore, the MODIS LAI retrieval algorithm provides a true LAI.
- 陈镜明
[1] 《Leaf area index of boreal forests: Theory, techniques, and measurements》
这篇关于遥感LAI一些记录的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






