本文主要是介绍努力的方向 之一 NIO 续二,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
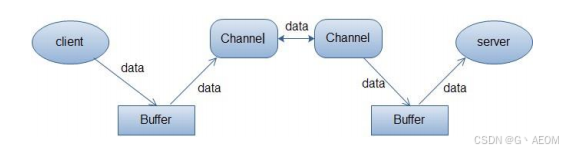
读取文件涉及三个步骤:(1) 从 FileInputStream 获取 Channel,(2) 创建 Buffer,(3) 将数据从 Channel 读到 Buffer 中。FileInputStream fin = new FileInputStream( "readandshow.txt" );
FileChannel fc = fin.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate( 1024 );
fc.read( buffer );
在 NIO 中写入文件类似于从文件中读取。
FileOutputStream fout = new FileOutputStream( "writesomebytes.txt" );
FileChannel fc = fout.getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate( 1024 );
for (int i=0; i<message.length; ++i) {
buffer.put( message[i] );
}
buffer.flip();
fc.write( buffer );缓冲区内部细节
NIO 中两个重要的缓冲区组件:状态变量和访问方法 (accessor)
状态变量
position
变量跟踪已经写了多少数据。更准确地说,它指定了下一个字节将放到数组的哪一个元素中。
limit
变量表明还有多少数据需要取出(在从缓冲区写入通道时),或者还有多少空间可以放入数据(在从通道读入缓冲区时)。 position 总是小于或者等于 limit。
capacity
缓冲区的 capacity 表明可以储存在缓冲区中的最大数据容量。limit 决不能大于 capacity。
flip() 方法
1.它将 limit 设置为当前 position。
2.它将 position 设置为 0。
clear() 方法
1.它将 limit 设置为与 capacity 相同。
2.它设置 position 为 0。
这篇关于努力的方向 之一 NIO 续二的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



![[SWPUCTF 2021 新生赛]web方向(一到六题) 解题思路,实操解析,解题软件使用,解题方法教程](https://i-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/bcfaab8e5a68426b8abfa71b5124a20d.png)
![[置顶] 你必须非常努力,才能看起来毫不费力!(愿与君共勉)](https://img-blog.csdn.net/20140814202330668?watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvdTAxMjg2MDA2Mw==/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/400/fill/I0JBQkFCMA==/dissolve/70/gravity/SouthEast)