本文主要是介绍一种IPC通信机制Gdbus详解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、DBus介绍
常规进程间通信有管道,消息队列,共享内存,以及socket等,每个都有优劣,这次我们介绍一种高阶的进程间通信方式DBus。
DBus通信是IPC通信机制的一种方式,本身是建立在socket机制之上,它支持远程函数调用和信号传递。
它有两种模式,分别为:session(会话模式)、system(总线模式)
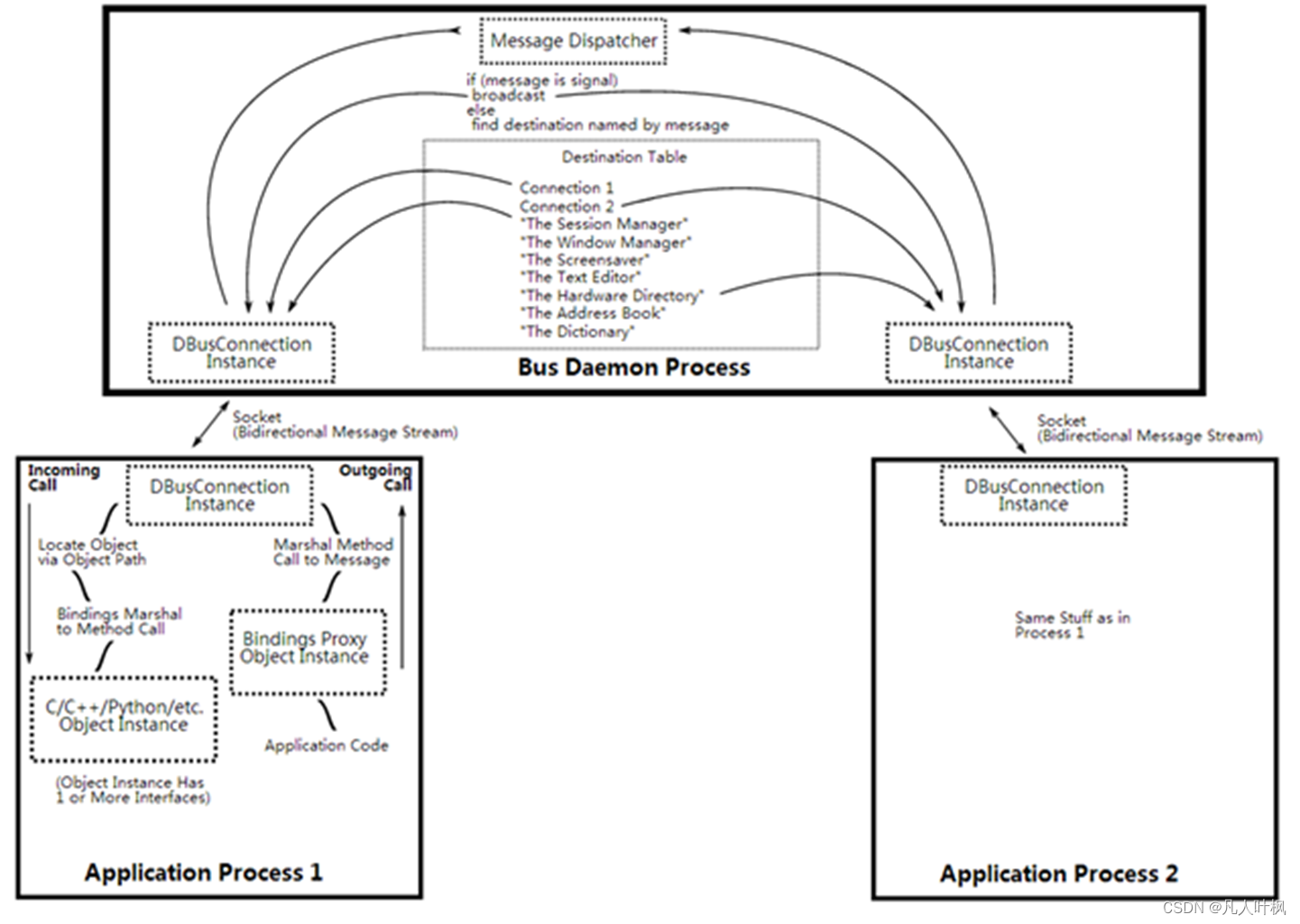
总线模式(system bus):采用总线模式时,系统需要维护一个DBus Daemon,每个DBus的请求通过DBus Daemon转发。这种模式Server只需要维护一个与DBus Daemon的链接,结构清晰,可以通过广播的方式发送消息到各个Client。
会话模式(session bus):这种模式一般称之为点对点的星型结构,Client与Server之间是直接的Peer2Peer的连接,少了DBus Daemon的中转,因此性能较好。
二、DBus API
glib API中有两种可以用的,分别是dbus-glib和gdbus,dbus-glib是一种老的API,现在不推荐使用了,gdbus是从glib2.26开始添加的,目前推荐使用。gdbus和glib-dbus都是GNU组织开发的,gdbus可以认为是dbus-glib的升级版,其编程过程比起dbus-glib来要简单得多。
三、DBus 开发
多进程之间需要通信,可能有一对一,可能有一对多,多对多的通信方式。为简单起见,我们假设某个系统中就只有两个进程需要通信——我们称之为Server和Client。基于GDBus的进程间通信,首先就是要定义好Server和Client之间的通信接口。在GDBus编程框架下,我们使用xml文件来描述接口,然后通过GDbus提供的工具生成对应的C/C++代码。
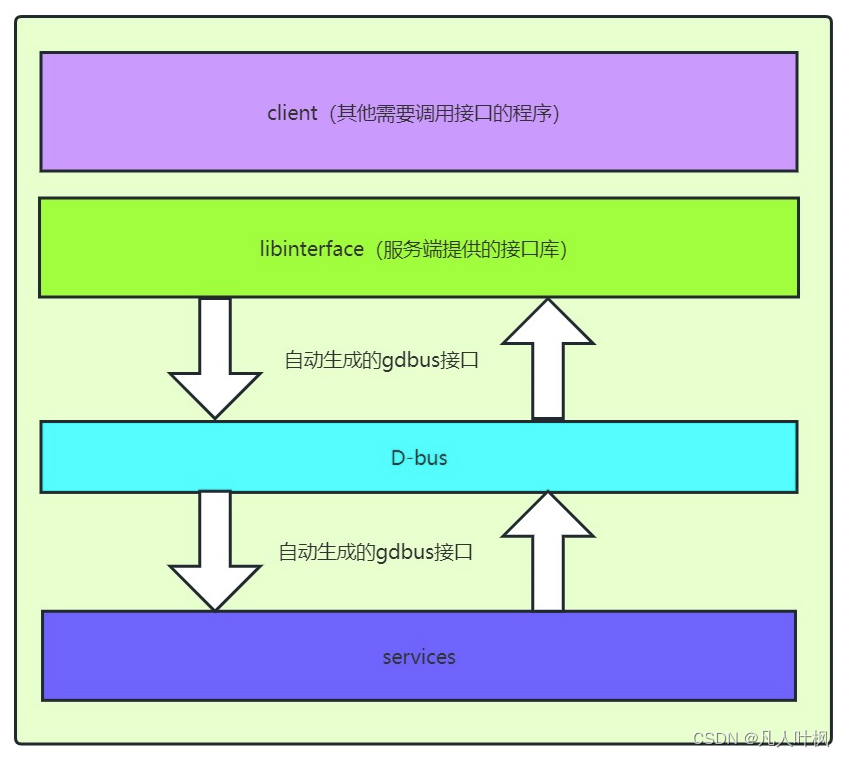
通常应用的组织形式如下,服务端发布的时候同时提供接口库供其他客户端程序调用,客户端连接接口库即可,像正常的接口调用,如下图,下面我们通过一个设置、获取一个人姓名和年龄,并且设置完姓名和年龄后会广播给所有客户端的程序来学习一下GDBus。
interface_people.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<node><interface name="gdbus.demo.people"><method name="set_name"><arg name="name" type="s" direction="in"/><arg name="ret" type="b" direction="out"/></method><method name="get_name"><arg name="name" type="s" direction="out"/></method><method name="set_age"><arg name="age" type="i" direction="in"/><arg name="ret" type="b" direction="out"/></method><method name="get_age"><arg name="age" type="i" direction="out"/></method><signal name="send_info"><arg name="name" type="s"/><arg name="age" type="i"/></signal></interface>
</node>
四、数据类型介绍
上面XML中使用了一些数据类型,对应关系如下表。
1、基本数据类型
| Name | Code in D-Bus | Data Type in glib | Data Type in libdbus-C++ |
|---|---|---|---|
| BYTE | ‘y’ | guchar | unsigned char |
| BOOLEAN | ‘b’ | gboolean | bool |
| INT16 | ‘n’ | gint16 | signed short |
| UINT16 | ‘q’ | guint16 | unsigned short |
| INT32 | ‘i’ | gint | int |
| UINT32 | ‘u’ | guint | unsigned int |
| INT64 | ‘x’ | gint64 | signed long long |
| UINT64 | ‘t’ | guint64 | unsigned long long |
| DOUBLE | ‘d’ | gdouble | double |
| STRING | ‘s’ | const gchar * | std::string |
| OBJECT_PATH | ‘o’ | const gchar * | DBus::Path :public std::string |
| UNIX_FD | ‘h’ | GVariant * | int |
| SIGNATURE | ‘g’ | const gchar * | DBus::Signature :public std::string |
2、复杂数据类型
| Name | Code in D-Bus | Data Type in glib | Data Type in libdbus-C++ |
|---|---|---|---|
| STRUCT | ‘(‘ and ‘)’ | Gvariant | DBus::Struct<> |
| ARRAY | ‘a’ | Gvariant | std::vector<> |
| VARIANT | ‘v’ | Gvariant | DBus::Variant |
| DICT_ENTRY | ‘{’ and ‘}’(Only appear after ‘a’) | Gvariant | When it is used together with ‘a’,it is representedby std::map<> |
五、程序运行
gdbus运行需要先运行deamon和环境变量
方法一:
1、运行下面脚本,生成地址,同时这个daemon要跑着
dbus-daemon --config-file=/etc/dbus-1/session.conf --print-address
2、生成的地址替换掉下面的地址部分
export DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-4z6nMwqewd,guid=e6359f4ef81d07fc7185fb8b6059d267
3、在需要运行程序的终端中设置上面的环境变量
方法二:
1、执行完下面脚本,然后在同一终端运行Server和Client
eval dbus-launch --auto-syntax
方法三:
export DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS="unix:abstract=/tmp/dbus-cwrMdqoyqU,guid=4780330fcb5755ab1492ce8800000024"
dbus-daemon --config-file=/etc/dbus-1/session.conf --address=$DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS
六、代码附录
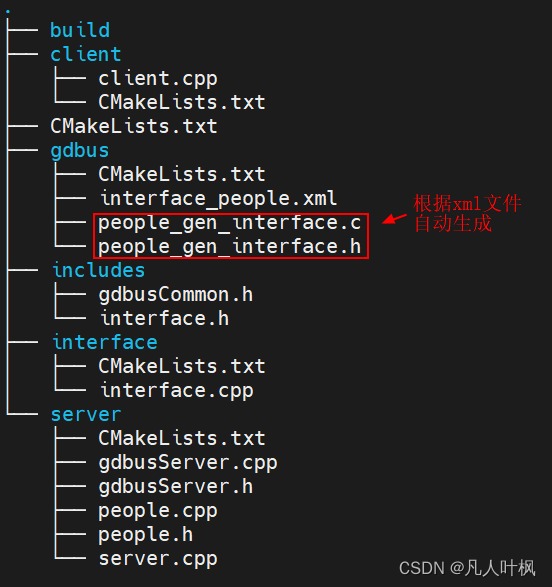
文件结构如下
重点代码
client.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#include "interface.h"using namespace std;int main(void)
{string name = "";int age = 0;interface iface;iface.initDBusCommunication();name = "dongdong.fan";iface.set_name(name);iface.set_age(30);name = iface.get_name();age = iface.get_age();cout << "Have a people name:" << name << "age:" << age;while (1){sleep(10);}return 0;
}
service.cpp
#include <unistd.h>#include "people.h"
#include "gdbusServer.h"int main()
{initDBusCommunication();while (1){sleep(10);}return 0;
}
gdbusServer.cpp
#include "gdbusServer.h"#include <ctype.h>
#include <gio/gio.h>
#include <glib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>#include "gdbusCommon.h"
#include "people.h"
#include "people_gen_interface.h"static guint g_own_id = 0;
static GMainLoop *g_pLoop = NULL;
static GdbusDemoPeople *g_pSkeleton = NULL;
static people g_people;// start
static gboolean set_name_method(GdbusDemoPeople *object,GDBusMethodInvocation *invocation,const gchar *in_arg,gpointer user_data) {my_printf("Server set_name_method is call, arg is : %s.\n", in_arg);bool ret = 0;string strTemp = in_arg;ret = g_people.set_name(strTemp);gdbus_demo_people_complete_set_name(object, invocation, ret);// 同时广播gdbus_demo_people_emit_send_info(object,g_people.get_name().c_str(),g_people.get_age());return TRUE;
}static gboolean get_name_method(GdbusDemoPeople *object,GDBusMethodInvocation *invocation,const gchar *in_arg,gpointer user_data) {my_printf("Server get_name_method is call.\n");string strTemp = g_people.get_name();gdbus_demo_people_complete_get_name(object, invocation, strTemp.c_str());return TRUE;
}static gboolean set_age_method(GdbusDemoPeople *object,GDBusMethodInvocation *invocation,gint in_arg,gpointer user_data) {my_printf("Server set_age_method is call, arg is : %d.\n", in_arg);bool ret = 0;ret = g_people.set_age(in_arg);gdbus_demo_people_complete_set_age(object, invocation, ret);// 同时广播gdbus_demo_people_emit_send_info(object,g_people.get_name().c_str(),g_people.get_age());return TRUE;
}static gboolean get_age_method(GdbusDemoPeople *object,GDBusMethodInvocation *invocation,gpointer user_data) {my_printf("Server get_age_method is call.\n");int age = g_people.get_age();gdbus_demo_people_complete_get_age(object, invocation, age);return TRUE;
}
// endstatic void GBusAcquired_Callback(GDBusConnection *connection,const gchar *name,gpointer user_data) {GError *pError = NULL;g_pSkeleton = gdbus_demo_people_skeleton_new();// Attach to dbus signals// start(void)g_signal_connect(g_pSkeleton, "handle-set-name", G_CALLBACK(set_name_method), NULL);(void)g_signal_connect(g_pSkeleton, "handle-get-name", G_CALLBACK(get_name_method), NULL);(void)g_signal_connect(g_pSkeleton, "handle-set-age", G_CALLBACK(set_age_method), NULL);(void)g_signal_connect(g_pSkeleton, "handle-get-age", G_CALLBACK(get_age_method), NULL);// end(void)g_dbus_interface_skeleton_export(G_DBUS_INTERFACE_SKELETON(g_pSkeleton),connection,GDBUS_DEMO_PEOPLE_OBJECT_PATH,&pError);if (pError == 0) {my_printf("skeleton export successfully. \n");} else {my_printf("Error: Failed to export object. Reason: %s.\n", pError->message);g_error_free(pError);g_main_loop_quit(g_pLoop);return;}
}static void GBusNameAcquired_Callback(GDBusConnection *connection,const gchar *name,gpointer user_data) {my_printf("GBusNameAcquired_Callback, Acquired bus name: %s \n", GDBUS_DEMO_PEOPLE_NAME);
}static void GBusNameLost_Callback(GDBusConnection *connection,const gchar *name,gpointer user_data) {if (connection == NULL) {my_printf("GBusNameLost_Callback, Error: Failed to connect to dbus. \n");} else {my_printf("GBusNameLost_Callback, Error: Failed to get dbus name : %s\n", GDBUS_DEMO_PEOPLE_NAME);}g_main_loop_quit(g_pLoop);
}static void *run_callback(void *arg) {g_main_loop_run(g_pLoop);return NULL;
}bool initDBusCommunication(void) {bool ret = false;pthread_t tid;g_pLoop = g_main_loop_new(NULL, FALSE);if (NULL == g_pLoop) {my_printf("g_pLoop is NULL\n");goto LEAVE;}g_own_id = g_bus_own_name(G_BUS_TYPE_SESSION,GDBUS_DEMO_PEOPLE_NAME,G_BUS_NAME_OWNER_FLAGS_NONE,&GBusAcquired_Callback,&GBusNameAcquired_Callback,&GBusNameLost_Callback,NULL,NULL);pthread_create(&tid, NULL, run_callback, NULL);ret = true;
LEAVE:return ret;
}bool uinitDBusCommunication(void) {g_bus_unown_name(g_own_id);g_main_loop_unref(g_pLoop);return true;
}
gdbusServer.cpp
#ifndef _GDBUS_SERVER_H_
#define _GDBUS_SERVER_H_bool initDBusCommunication(void);
bool uinitDBusCommunication(void);#endif
people.cpp
#include "people.h"people::people()
{m_name = "default";m_age = 20;
}people::~people()
{//todo
}bool people::set_name(string &name)
{m_name = name;return true;
}string people::get_name()
{return m_name;
}bool people::set_age(int age)
{m_age = age;return true;
}int people::get_age()
{return m_age;
}
people.hpp
#ifndef _PEOPLE_H_
#define _PEOPLE_H_#include <string>using namespace std;class people
{public:people();~people();bool set_name(string &name);string get_name();bool set_age(int age);int get_age();private:string m_name; // 姓名int m_age; // 年龄
};#endif
interface.hpp
#ifndef _INTERFACE_H_
#define _INTERFACE_H_#include <string>class interface
{public:interface();virtual ~interface();bool initDBusCommunication(void);//peoplebool set_name(std::string &name);std::string get_name();bool set_age(int age);int get_age();
};#endif
这篇关于一种IPC通信机制Gdbus详解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





