本文主要是介绍rust ffi bindgen wrapper,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
rust ffi
- rust ffi
- rust 调用c库
- c 调用rust库
- C库封装给rust调用示例
rust ffi
参考
https://github.com/GzhuFlyer/rustLearn/tree/main/ffi
源代码进行文档讲解说明。
rust 调用c库
1,ffi/rust_call_c/use_snappy_lib 示例:
1.1 安装snappy库,在Cargo.toml 文件添加 [dependencies] libc = “0.2.0”
1.2 main.rs里面的 #[link(name = “snappy”)] 表示 需要链接的动态库。
1.3 extern {
fn snappy_max_compressed_length(source_length: size_t) -> size_t;
}
声明作为rust的使用
2,ffi/rust_call_c/use_callback_from_c 示例:
2.1 自己生成使用编写C库,编译后供给rust使用。
gcc -shared -fPIC extern.c -o libext.so 生成libext.so供给rust使用
在use_callback_from_c目录下执行 LIBRARY_PATH=. cargo run,运行rust程序
3, ffi/rust_call_c/show_data_type
3.1:自定义类型的使用
4, ffi/rust_call_c/call_cpp
调用c++接口函数,运行时候用下面命令
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=./target/debug ./call_rust
c 调用rust库
1,ffi/c_call_rust/share_static
执行 make static 或者 make share可以看到生成对应的动态和静态程序
2,使用rust的rust-bindgen工具生成C对应的rust接口
官方参考文档。
如果系统是centos且没有bzlib.h文件,可以执行下面命令
sudo yum whatprovides */bzlib.h
找到有 Libraries and header files for apps which will use bzip2字眼的包
然后安装一下:yum install -y bzip2-devel-1.0.6-13.el7.i686
C库封装给rust调用示例
1,cargo 创建库
cargo new --lib rust_ffi
2修改Cargo.toml文件
[package]
name = "rust_ffi"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
build = "build.rs"[dependencies]
[build-dependencies]
bindgen = "0.60"2,修改rust_ffi/src/lib.rs内容为如下
#![allow(non_upper_case_globals)]
#![allow(non_camel_case_types)]
#![allow(non_snake_case)]#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {use super::*;use std::mem;include!("../bindings.rs");#[test]fn round_trip_compression_decompression() {unsafe {let input = include_str!("../futurama-quotes.txt").as_bytes();let mut compressed_output: Vec<u8> = vec![0; input.len()];let mut decompressed_output: Vec<u8> = vec![0; input.len()];// Construct a compression stream.let mut stream: bz_stream = mem::zeroed();let result = BZ2_bzCompressInit(&mut stream as *mut _,1, // 1 x 100000 block size4, // verbosity (4 = most verbose)0); // default work factormatch result {r if r == (BZ_CONFIG_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_CONFIG_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_PARAM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_PARAM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_MEM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_MEM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_OK as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}// Compress `input` into `compressed_output`.stream.next_in = input.as_ptr() as *mut _;stream.avail_in = input.len() as _;stream.next_out = compressed_output.as_mut_ptr() as *mut _;stream.avail_out = compressed_output.len() as _;let result = BZ2_bzCompress(&mut stream as *mut _, BZ_FINISH as _);match result {r if r == (BZ_RUN_OK as _) => panic!("BZ_RUN_OK"),r if r == (BZ_FLUSH_OK as _) => panic!("BZ_FLUSH_OK"),r if r == (BZ_FINISH_OK as _) => panic!("BZ_FINISH_OK"),r if r == (BZ_SEQUENCE_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_SEQUENCE_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_STREAM_END as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}// Finish the compression stream.let result = BZ2_bzCompressEnd(&mut stream as *mut _);match result {r if r == (BZ_PARAM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_PARAM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_OK as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}// Construct a decompression stream.let mut stream: bz_stream = mem::zeroed();let result = BZ2_bzDecompressInit(&mut stream as *mut _,4, // verbosity (4 = most verbose)0); // default small factormatch result {r if r == (BZ_CONFIG_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_CONFIG_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_PARAM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_PARAM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_MEM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_MEM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_OK as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}// Decompress `compressed_output` into `decompressed_output`.stream.next_in = compressed_output.as_ptr() as *mut _;stream.avail_in = compressed_output.len() as _;stream.next_out = decompressed_output.as_mut_ptr() as *mut _;stream.avail_out = decompressed_output.len() as _;let result = BZ2_bzDecompress(&mut stream as *mut _);match result {r if r == (BZ_PARAM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_PARAM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_DATA_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_DATA_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_DATA_ERROR_MAGIC as _) => panic!("BZ_DATA_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_MEM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_MEM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_OK as _) => panic!("BZ_OK"),r if r == (BZ_STREAM_END as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}// Close the decompression stream.let result = BZ2_bzDecompressEnd(&mut stream as *mut _);match result {r if r == (BZ_PARAM_ERROR as _) => panic!("BZ_PARAM_ERROR"),r if r == (BZ_OK as _) => {},r => panic!("Unknown return value = {}", r),}assert_eq!(input, &decompressed_output[..]);}}
}3,创建wrapper.h文件
touch wrapper.h,并写入希望封装给rust使用的函数头文件
#include <bzlib.h>
4,在rust_ffi目录下,创建build.rs文件
touch build.rs
将下面内容复制到build.rs里面
extern crate bindgen;use std::env;
use std::path::PathBuf;fn main() {// Tell cargo to tell rustc to link the system bzip2// shared library.println!("cargo:rustc-link-lib=bz2");// The bindgen::Builder is the main entry point// to bindgen, and lets you build up options for// the resulting bindings.let bindings = bindgen::Builder::default()// Do not generate unstable Rust code that// requires a nightly rustc and enabling// unstable features.// .no_unstable_rust()// The input header we would like to generate// bindings for..header("wrapper.h")// Finish the builder and generate the bindings..generate()// Unwrap the Result and panic on failure..expect("Unable to generate bindings");// Write the bindings to the $OUT_DIR/bindings.rs file.// let out_path = PathBuf::from(env::var("OUT_DIR").unwrap());let out_path = PathBuf::from(".");bindings.write_to_file(out_path.join("bindings.rs")).expect("Couldn't write bindings!");
}
5,编译生成rust接口文件
cargo b
在rust_ffi目录下可以查看到生成bindgens.rs文件,bindgens.rs文件的路径由下面函数指定。
//.表示当前目录
let out_path = PathBuf::from(".");
6,bindgens.rs测试
新增self.txt文件,在文件中加入以下内容
《尘曲》凡心所向,素履所往,生如逆旅,一苇以航。三月桃花,四月欢唱,两人一马,明日故乡。流浪陌路,暖然绯凉,写意人生,相识一场。不关此世,不负己心,我自倾杯,且君随意。
运行命令 cargo test 可以查看到所有测试都已通过。
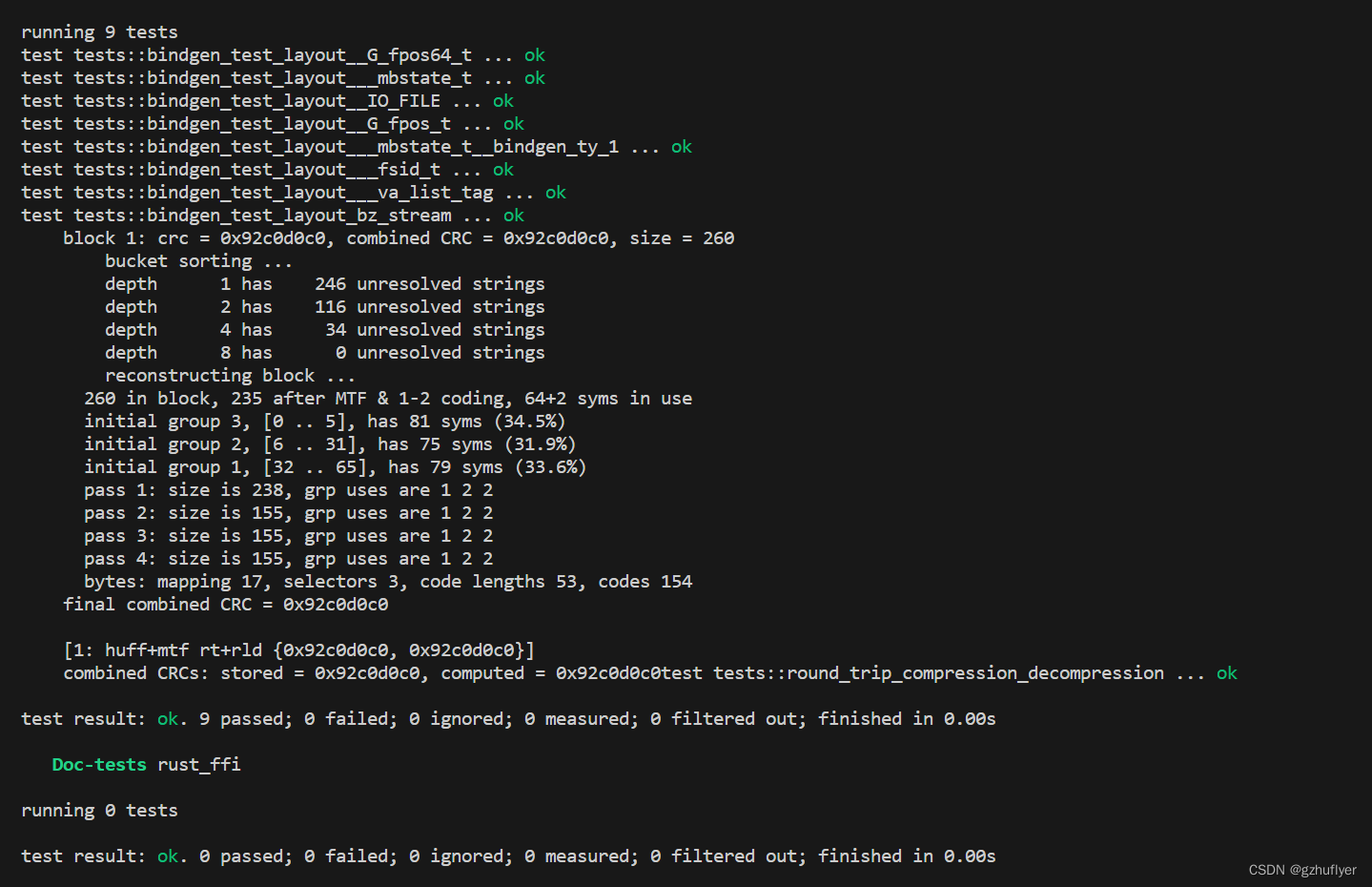
这篇关于rust ffi bindgen wrapper的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



