本文主要是介绍AOP理解——模拟带有横切逻辑的实例,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Spring使用动态代理技术在运行期间织入增强的代码。Spring AOP 使用两种动态代理机制:一种是基于JDK的动态代理;另一种是基于CGLib的动态代理。之所以需要两种代理机制,很大程度上是因为JDK本身只提供接口的代理,而不支持类的代理。
带有横切逻辑的实例
package com.hegx.spring.aop.service.impl; import com.hegx.spring.aop.Forum; import com.hegx.spring.aop.PerformanceMonitor; import com.hegx.spring.aop.dao.ForumDao; import com.hegx.spring.aop.dao.impl.ForumDaoImpl; import com.hegx.spring.aop.service.ForumService; /** * @Author: hegx * @Description: * @Date: 14:25 2017/7/16 */ public class ForumServiceImpl implements ForumService {private ForumDao forumDao = new ForumDaoImpl(); @Override public void remove(Integer forumId) {//开始对方法进行性能监视 PerformanceMonitor.begin("com.hegx.spring.aop.service.impl.ForumServiceImpl.remove"); forumDao.remove(forumId); try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(20); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }//结束对方法进行性能监视 PerformanceMonitor.end(); }@Override public void create(Forum forum) {//开始对方法进行性能监视 PerformanceMonitor.begin("com.hegx.spring.aop.service.impl.ForumServiceImpl.remove"); forumDao.create(forum); try {Thread.currentThread().sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }//结束对方法进行性能监视 PerformanceMonitor.end(); } }
上面带绿色的代码就是具有横切逻辑的代码,每个dao的实现前后都要执行先后的代码,也就是相同的逻辑。
上面的PerformanceMonitor是性能监视的类,我们给出一个非常简单的实现版本,期待吗如下:
package com.hegx.spring.aop; /** * @Author: hegx * @Description: * @Date: 14:33 2017/7/16 */ public class PerformanceMonitor {//通过一个ThreadLocal保存调用线程先关的性能监视信息 private static ThreadLocal<MethodPerformance> performanceRecord = new ThreadLocal<>(); //启动对某一个方法的性能监视 public static void begin(String method){System.out.println("begin Monitor..."); MethodPerformance mp = new MethodPerformance(method); performanceRecord.set(mp); }//启动对某一个方法的性能监视 public static void end(){System.out.println("end Monitor..."); MethodPerformance mp = performanceRecord.get(); //打印出方法性能监视的结果信息 mp.printPerformance(); }}
ThreadLoacl是将非线程安全类改造成线程安全类的法宝。PerformanceMonitor提供两个方法:通过调用begin(String method)方法开始对目标类方法的监视,method是目标类全限定名;而end()方法结束对目标类方法性能监视,并给出性能监视信息。这两个方法必须配套使用。
用于记录性能类的信息MethodPerformance类的代码如下:
package com.hegx.spring.aop; /** * @Author: hegx * @Description:用于记录性能监视信息的类 * @Date: 14:36 2017/7/16 */ public class MethodPerformance {private Long begin; private Long end; private String serviceMethod; public MethodPerformance(String serviceMethod) {this.serviceMethod = serviceMethod; this.begin = System.currentTimeMillis();//记录目标类方法的开始执行点的时间 }public void printPerformance(){end = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取目标类方法执行完成后的系统时间,并进而计算出目标类方法执行时间 Long elapse = end - begin; System.out.println(serviceMethod+"花费了"+elapse+"毫秒");//打印目标类方法执行的时间 System.out.println(); }}
通过下面的代码测试性能监视能力的ForumServiceImpl业务方法:
package com.hegx.spring.aop.test; import com.hegx.spring.aop.Forum; import com.hegx.spring.aop.service.ForumService; import com.hegx.spring.aop.service.impl.ForumServiceImpl; /** * @Author: hegx * @Description:测试拥有性能监视能力的TestForumServiceImpl业务方法 * @Date: 15:10 2017/7/16 */ public class TestForumService {public static void main(String[] args) {ForumService forumService = new ForumServiceImpl(); forumService.remove(10); forumService.create(new Forum()); }}
程序执行的结果:
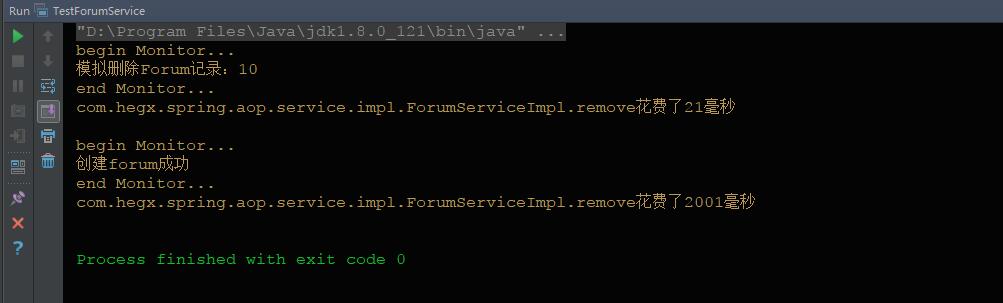
如上图和代码所示,当某个方法在进行性能监视,就必须调整方法的代码,在方法体前后分别添加上开启性能和结束性能监视的代码,这些非业务逻辑的性能监视代码破坏了ForumServiceImpl业务逻辑的纯碎性。我们希望通过代理的方式,将业务类方法中开启和结束性能的这些横切代码从业务类中完全移除。并通过JDK动态代理技术或CGLib动态代理技术奖横切代码动态织入到目标方法的位置。
这篇关于AOP理解——模拟带有横切逻辑的实例的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






