本文主要是介绍利用ArcGIS和Python计算路网密度,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ArcGIS
相交
利用ArcGIS里面的相交工具,每个省把路标识了。
计算几何
分别计算路网的长度和各省的面积。
Python
利用Python对属性数据进行处理
导入相关模块
## 导入相关模块
import pandas as pd
import geopandas as gpd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt%matplotlib inline
解决中文乱码
plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['sans-serif']
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']# 替换sans-serif字体为黑体
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决坐标轴负数的负号显示问题
数据读取
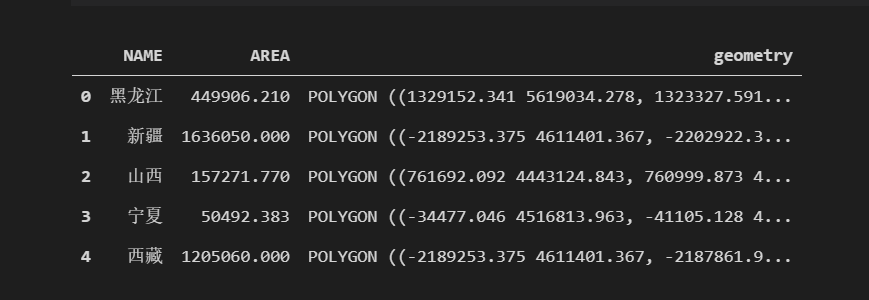
regibns = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file("省级行政区.shp")
regibns = regibns[["NAME","AREA","geometry"]]
regibns["AREA"] = regibns["AREA"]/1000000
regibns.head()
regibns.plot()

road = gpd.GeoDataFrame.from_file("道路密度.shp")
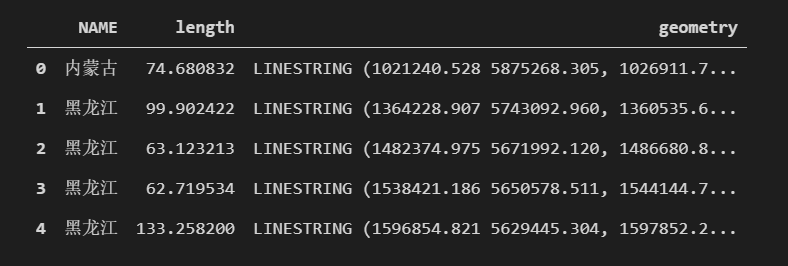
road.head()
road = road[["NAME", "length", "geometry"]]
road.plot()

数据透视
pivot = pd.pivot_table(road, index="NAME",values="length",aggfunc=sum)
pivot.head()
数据连接
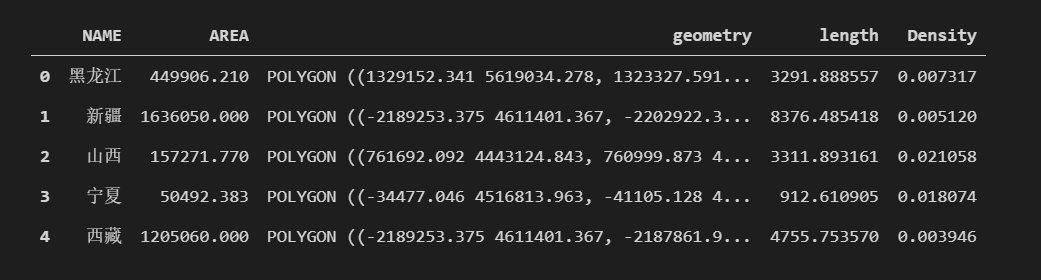
results = pd.merge(regibns, pivot, on="NAME")
results["Density"] = results["length"] / results["AREA"]
results.head()
数据可视化
data_geod = gpd.GeoDataFrame(results)data_geod['coords'] = data_geod['geometry'].apply(lambda x: x.representative_point().coords[0])
data_geod.plot(figsize=(12, 12), column='Density', scheme='quantiles', legend=True, cmap='Reds', edgecolor='k')
for n, i in enumerate(data_geod['coords']):plt.text(i[0], i[1], data_geod['NAME'][n], size=12)plt.title('中国各省主要公路密度图', size=25)
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)

总结和反思
因为arcpy只支持python2,我用ArcGIS Pro的python3,也没有geopandas模块,所以在两个软件切换了。在ArcGIS中注意坐标系,我们计算面积和长度都是在投影坐标系下进行的。还有那个大神可以告诉我geopandas里面我的线图层和面图层怎么叠加,就是在这个底图的基础上加入路网图层。
这篇关于利用ArcGIS和Python计算路网密度的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





