本文主要是介绍BD第7课:分析罩杯销售,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文会利用 SQL 语句和 Pandas 对前面抓取和整理的的胸罩数据进行分析,本文主要分析了胸罩销售的比例,以及 A、B、C、D 罩杯的销售比例。
用 SQL 语句分析胸罩(按罩杯尺寸)的销售比例
既然销售数据都保存在 SQLite 数据库中,那么我们不妨先用 SQL 语句做一下统计分析,本节将对胸罩按罩杯的销售量做一个销售比例统计分析。由于抓取的数据没有超过 D 罩杯的,所以做数据分析时就不考虑 D 以上罩杯的胸罩销售数据了,这里只考虑 A、B、C 和 D 罩杯胸罩的销售数据。
本节要统计的是某一个尺寸的胸罩销售数量占整个销售数量的百分比,这里需要统计和计算如下3类数据。
某一个尺寸的胸罩销售数量 胸罩销售总数量 第1类数据和第2类数据的差值(百分比) 这3类数据完全可以用一条 SQL 语句搞定,为了同时搞定 A、B、C 和 D 罩杯的销售比例,可以用4条类似的 SQL 语句,中间用 union all 连接。
select 'A' as 罩杯,printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例 from t_sales where size1='A'
union all
select 'B',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) from t_sales where size1='B'
union all
select 'C',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) from t_sales where size1='C'
union all
select 'D',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) from t_sales where size1='D' 执行上面的 SQL 语句,会看到如图1所示的查询结果。
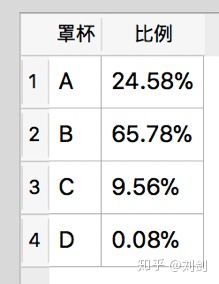
图1 查询结果
不过图1所示的分析结果有些问题,就是没有按销量排序,而且没有显示具体的销量。如果要按销量排序,而且加上具体的销量,需要使用下面的 SQL 语句。
select 'A' as 罩杯,printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例, count(*) as 销量 from t_sales where size1='A'
union all
select 'B',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) , count(*) as c from t_sales where size1='B'
union all
select 'C',printf("%0.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) , count(*) as c from t_sales where size1='C'
union all
select 'D',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) , count(*) as c from t_sales where size1='D'
order by 销量 desc 上面的 SQL 语句不仅加入了销售比例,还加入了销售数量,并且按销量降序排列。这些 SQL 语句需要考虑 size1 字段空值的情况,因为抓取的少部分销售记录并没有罩杯尺寸数据。执行上面的 SQL 语句后,会输出如图2所示的查询结果。
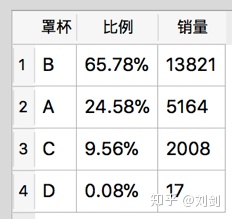
从图2的统计结果可以看出,B 罩杯占总体的销售比例最大,其次是 A 罩杯,也就是说中国女性胸部尺寸主要集中在 A 和 B 罩杯。
用 Pandas 和 Matplotlib 分析对胸罩销售比例进行可视化分析
既然 Python 提供了这么好的 Pandas 和 Matplotlib,那么就可以完全不使用 SQL 语句进行数据分析了,可以 100% 使用 Python 代码搞定一切。
本节将使用 Pandas 完成与前面相同的数据分析,并使用 Matplotlib 将分析结果以图形化方式展现出来。
Pandas 在前面的文章已经讲过了,这里不再深入介绍。本次分析主要使用了 groupby 方法按罩杯(size1)分组,然后使用 count 方法统计组内数量,最后使用 insert 方法添加了一个“比例”字段。
from pandas import *
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
import sqlite3
import sqlalchemy
# 打开bra.sqlite数据库
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('sqlite:///bra.sqlite')
rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# 查询t_sales表中所有的数据
sales = read_sql('select source,size1 from t_sales',engine)
# 对size1进行分组,并统计每一组的记录数
size1Count = sales.groupby('size1')['size1'].count()
print(size1Count)
# 计算总销售数量
size1Total = size1Count.sum()
print(size1Total)
print(type(size1Count))
# 将Series转换为DataFrame
size1 = size1Count.to_frame(name='销量')
print(size1)
# 格式化浮点数
options.display.float_format = '{:,.2f}%'.format
# 插入新的“比例”列
size1.insert(0,'比例', 100 * size1Count / size1Total)
print(size1)
# 将索引名改为“罩杯”
size1.index.names=['罩杯']
print(size1)# 数据可视化
print(size1['销量'])
# 饼图要显示的文本
labels = ['A罩杯','B罩杯','C罩杯','D罩杯']
# 用饼图绘制销售比例
size1['销量'].plot(kind='pie',labels = labels, autopct='%.2f%%')
# 设置长宽相同
axis('equal')
legend()
show() 运行程序,会看到在窗口上绘制了如图3所示的胸罩销售比例,用 Pandas 分析得到的数据与使用 SQL 分析得到的数据完全相同。
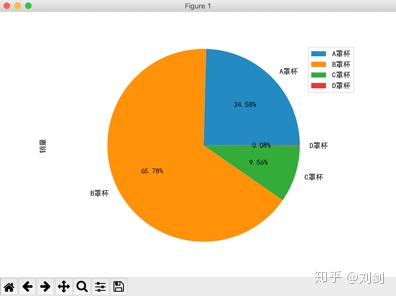
直接在 Python 脚本中使用复杂的 SQL 语句
如果读者不想过多使用 Pandas 的 API 进行数据分析,也可以直接在 Pandas 中使用复杂的 SQL 语句,一步到位地获取分析结果。下面的代码直接通过 SQL 语句分析出了结果,最后只是利用 Matplotlib 将数据可视化。
# 直接使用复杂的SQL语句和视图
from pandas import *
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
import sqlite3
import sqlalchemy
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('sqlite:///bra.sqlite')
rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
# 执行复杂的SQL语句
sales = read_sql('''
select 'A' as 罩杯, printf('%.2f%%',(100.0 * count(*) / (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例,count(*) as 销量 from t_sales where size1='A'
union all
select 'B' , printf('%.2f%%',(100.0 * count(*) / (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例,count(*) from t_sales where size1='B'
union all
select 'C' , printf('%.2f%%',(100.0 * count(*) / (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例,count(*)from t_sales where size1='C'
union all
select 'D' , printf('%.2f%%',(100.0 * count(*) / (select count(*) from t_sales where size1 is not null))) as 比例,count(*) from t_sales where size1='D'
order by 销量 desc
''',engine)
print(sales)
# 将前面的SQL语句建成一个视图,然后执行,效果相同
sales1 = read_sql('select * from v_sales', engine)labels = ['A罩杯','B罩杯','C罩杯','D罩杯']
sales1['销量'].plot(kind='pie',labels = labels, autopct='%.2f%%')
axis('equal')
legend()
show() 执行上面的程序,会看到如图4所示的效果。
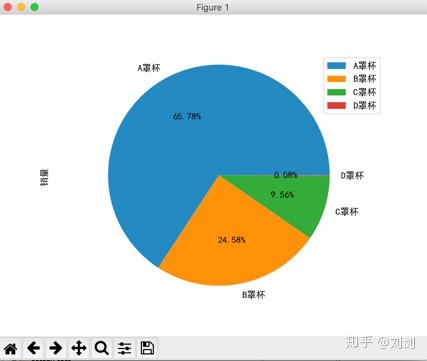
用 SQL 语句对天猫商城胸罩销售数据进行分析
我们可以利用 SQL 语句分别统计天猫和京东关于胸罩销售的比例,下面现以天猫为例进行统计。
select 'A' as 罩杯,printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1 is not null))) as 比例 from t_sales where size1='A' and source='天猫'
union all
select 'B',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1 is not null))) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1='B'
union all
select 'C',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1 is not null))) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1='C'
union all
select 'D',printf("%.2f%%",(100.0 * count(*)/ (select count(*) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1 is not null))) from t_sales where source='天猫' and size1='D' 上面 SQL 语句的执行结果如图5所示。
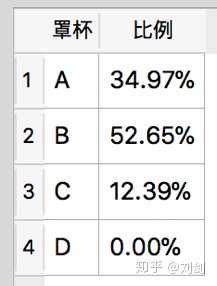
我们可以看到,天猫商城胸罩销售比例与总体销售比例的趋势类似,只是具体的数值有差异,但仍然是 B 罩杯销售的最好。
使用 Pandas 分别对天猫和京东胸罩销售数据进行分析
# 分析与可视化天猫和京东胸罩ABCD罩杯的销售比例
from pandas import *
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
import sqlite3
import sqlalchemy
# 打开数据库
engine = sqlalchemy.create_engine('sqlite:///bra.sqlite')
rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
options.display.float_format = '{:,.2f}%'.format# 只选取source和size1,source表示数据来源(天猫或京东)
sales = read_sql('select source,size1 from t_sales',engine)
# 过滤天猫胸罩销售数据,并按罩杯分组(size1字段),统计出每个罩杯的具体销量
tmallSize1GroupCount = sales[sales['source'] == '天猫'].groupby('size1')['size1'].count()
# 计算出总销量
tmallSize1Total = tmallSize1GroupCount.sum()
print(tmallSize1Total)
# 将Series转换为DataFrame
tmallSize1 = tmallSize1GroupCount.to_frame(name='销量')
# 插入一个“比例”字段,用于显示销售比例
tmallSize1.insert(0,'比例',100 * tmallSize1GroupCount / tmallSize1Total)
# 将索引名改成“罩杯”
tmallSize1.index.names=['罩杯']
print(tmallSize1)# 京东的分析方式与天猫类似
jdSize1GroupCount = sales[sales['source'] == '京东'].groupby('size1')['size1'].count()
jdSize1Total = jdSize1GroupCount.sum()
print(jdSize1GroupCount)
# 将Series转换为DataFrame
jdSize1 = jdSize1GroupCount.to_frame(name='销量')jdSize1.insert(0,'比例',100 * jdSize1GroupCount / jdSize1Total)
jdSize1.index.names=['罩杯']
print(jdSize1)labels1 = []
labels2 = []
labels1 = tmallSize1.index.tolist()
labels2= jdSize1.index.tolist()
for i in range(len(labels1)):labels1[i] = labels1[i] + '罩杯'
for i in range(len(labels2)):labels2[i] = labels2[i] + '罩杯'
# 下面的代码会将天猫和京东的胸罩销售数据饼图放到同一个窗口显示
fig,(ax1,ax2) = subplots(1,2,figsize=(12,6))
ax1.pie(tmallSize1['销量'],labels = labels1, autopct='%.2f%%')
ax2.pie(jdSize1['销量'],labels = labels2, autopct='%.2f%%')
ax1.legend()
ax2.legend()
ax1.axis('equal')
ax2.axis('equal')
show() 执行上面的代码,会显示如图6所示的胸罩销售比例统计图。
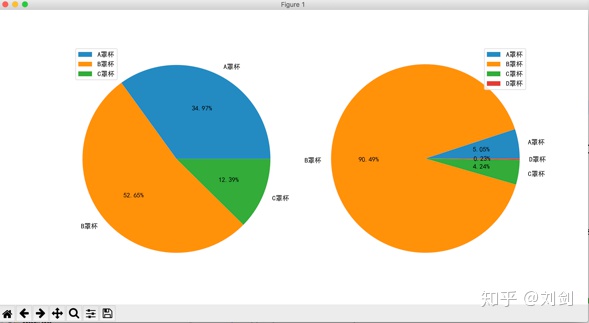
从图6的分析结果可以看出,天猫和京东的 B 罩杯销售比例都很大,不过京东 B 罩杯销售比例特别大,不知道是什么原因导致的,姑且认为到京东买胸罩的大多都是 B 罩杯吧!
如果你有疑问欢迎加微信咨询:

也可以关注我的公众号想我提问:

这篇关于BD第7课:分析罩杯销售的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






