本文主要是介绍js继承的几种方式(原型链继承、构造函数继承、组合式继承、寄生组合式继承、ES6的Class类继承),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1.原型链继承
实现原理:子类的原型指向父类实例。子类在自身实例上找不到属性和方法时去它父类实例(父类实例和实例的原型对象)上查找,从而实现对父类属性和方法的继承
缺点:
- 子类创建时不能传参(即没有实现super()的功能);
- 父类实例的修改会影响子类所有实例
function Parent(name){this.name = "父级的name";}Parent.prototype.getName = function(){console.log("getName:"+this.name);}function Child(){}// 子类原型指向父类的实例Child.prototype = new Parent();Child.prototype.constructor = Child;//这句话和原型链继承没有关系,只是根据原型链规则绑定constructor// 测试var child = new Child();console.log(child.name);//父级的namechild.getName();//getName:父级的name// 缺点:不能传参;父类实例改变子类所有实例也改变2.构造函数继承
实现原理:子类构造函数中执行父类的构造函数,并且为父类构造函数绑定子类的this,父类的构造函数把成员属性和方法都挂到子类的this上去,这样既能避免实例之间共享一个原型实例,又能向父类构造方法传参
缺点:无法继承父类原型上的属性和方法
// 构造函数继承function Parent(name) {this.name = name;console.log("父类构造函数");}Parent.prototype.getName = function () {console.log("getName:" + this.name);}function Child(name){Parent.call(this, name);}var child = new Child("张三");console.log(child);//Child {name: '张三'}// 不能继承父类原型上的方法和属性child.getName();//报错,child.getName is not a function3.组合式继承
实现原理:原型链继承+构造函数继承
缺点:父类构造函数会执行两次(Parent.call()和new Parent()),这不影响子类对父类的继承,但是每次创建子类实例时原型中都会有两份相同的属性和方法
// 组合式继承:原型链继承+构造函数继承function Parent(name) {this.name = name;console.log("父类构造函数");}Parent.prototype.getName = function () {console.log("getName:" + name);}function Child(name) {Parent.call(this, this.name);}Child.prototype = new Parent();Child.prototype.constructor = Child;var child = new Child("张三");console.log(child);//Child {name: '张三'}child.getName();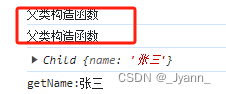
4.寄生式组合继承
实现原理:父类构造函数会执行两次(Parent.call()和new Parent()),那么在原型链继承时就只继承父类的原型,就不会执行两次父类构造函数 Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;
缺点:操作子类原型对象,会影响到父类原型对象,例如给Child.prototype增加一个getName()方法,那么会导致Parent.prototype也增加或被覆盖一个getName()方法
// 寄生式组合继承:原型链继承(只继承父类原型)+构造函数继承function Parent(name) {this.name = name;}Parent.prototype.getName = function () {console.log("getName:" + this.name);}function Child(name) {Parent.call(this, name);}Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;Child.prototype.constructor = Child;var child = new Child("张三");console.log(child);//Child {name: '张三'}child.getName();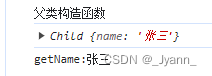
4.1解决寄生式组合继承的缺点(使用Object.create()进行继承)
如下,对Child.prototype.getName子类中原型上属性或方法进行修改时,父类也被修改
function Parent(name) {this.name = name;console.log("父类构造函数");}Parent.prototype.getName = function () {console.log("父类getName");}function Child(name) {Parent.call(this, name);}Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;Child.prototype.constructor = Child;Child.prototype.getName = function(){console.log("子类getName");}var child = new Child("张三");console.log(child);//Child {name: '张三'}child.getName();var parent = new Parent("李四");parent.getName();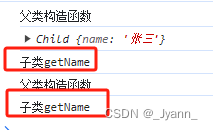
解决:加上Object.create()方法即可
// Child.prototype = Parent.prototype;Child.prototype = Object.create(Parent.prototype); 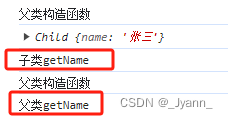
5.ES6的Class继承
实现原理:ES6新增,是ES5中构造函数+原型链继承组合继承,寄生组合式继承的结合
缺点:兼容性不好
6.扩展——对象的几种创建方式
- 字面量创建
- var obj = new Object()创建
- 构造函数创建
- Object.create()创建
// 字面量创建let obj1 = {name: 'lmf1',say() {console.log("lmf1 say");}}// new Object()创建let obj2 = new Object({name: 'lmf2',say() {console.log("lmf2 say");}});// 构造函数创建function Person(name) {this.name = name;}let obj3 = new Person("lmf3");Person.say = function () {console.log("静态方法");}Person.prototype.say = function () {console.log("lmf3 say");}// Object.create()创建let obj4 = Object.create(obj3);console.log(obj1, obj2, obj3, obj4);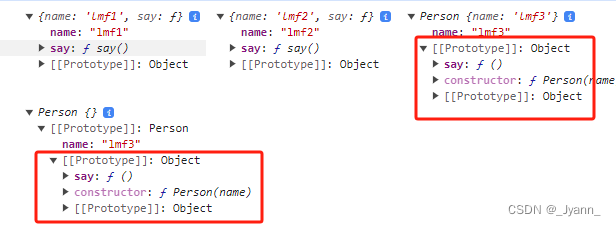
这篇关于js继承的几种方式(原型链继承、构造函数继承、组合式继承、寄生组合式继承、ES6的Class类继承)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




