本文主要是介绍还在用 SimpleDateFormat 做时间格式化?小心项目崩掉!,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Hollis的新书限时折扣中,一本深入讲解Java基础的干货笔记!
来源:blog.csdn.net/QiuHaoqian/article/details/116594422
今天聊聊 SimpleDateFormat 在多线程环境下存在线程安全问题。
1 SimpleDateFormat.parse() 方法的线程安全问题
1.1 错误示例
错误使用SimpleDateFormat.parse()的代码如下:
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;public class SimpleDateFormatTest {private static final SimpleDateFormat SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");public static void main(String[] args) {/*** SimpleDateFormat线程不安全,没有保证线程安全(没有加锁)的情况下,禁止使用全局SimpleDateFormat,否则报错 NumberFormatException** private static final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");*/for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {try {// 错误写法会导致线程安全问题System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT.parse("2020-06-01 11:35:00"));} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "Thread-" + i);thread.start();}}
}报错:
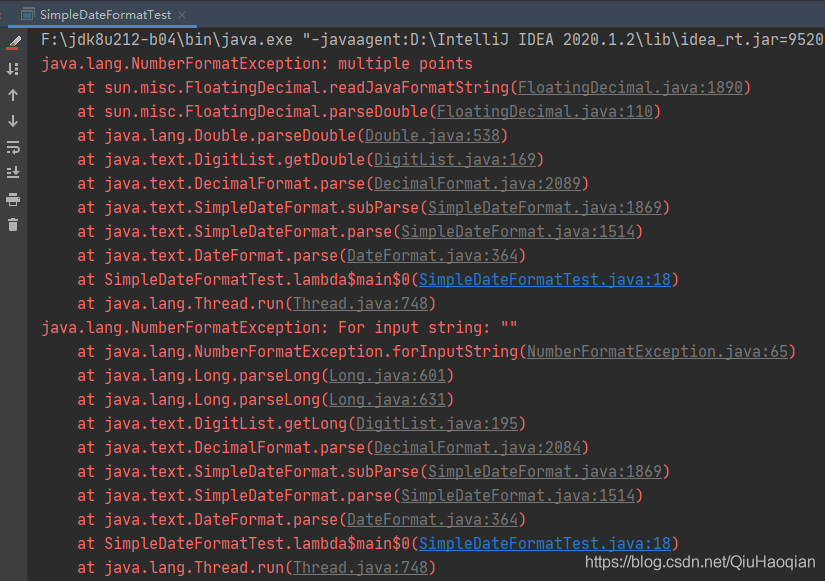
1.2 非线程安全原因分析
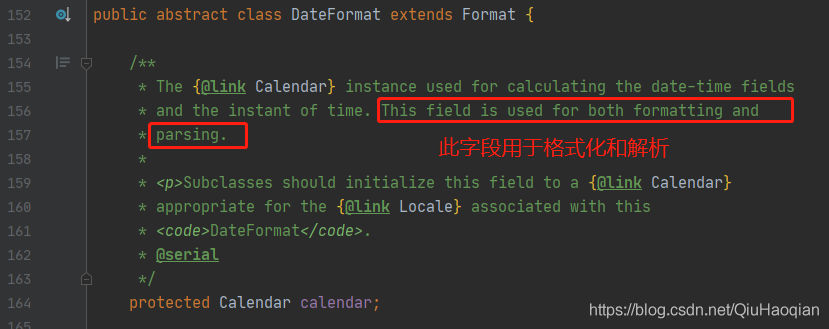
查看源码中可以看到:SimpleDateFormat继承DateFormat类,SimpleDateFormat转换日期是通过继承自DateFormat类的Calendar对象来操作的,Calendar对象会被用来进行日期-时间计算,既被用于format方法也被用于parse方法。
SimpleDateFormat 的 parse(String source) 方法 会调用继承自父类的 DateFormat 的 parse(String source) 方法
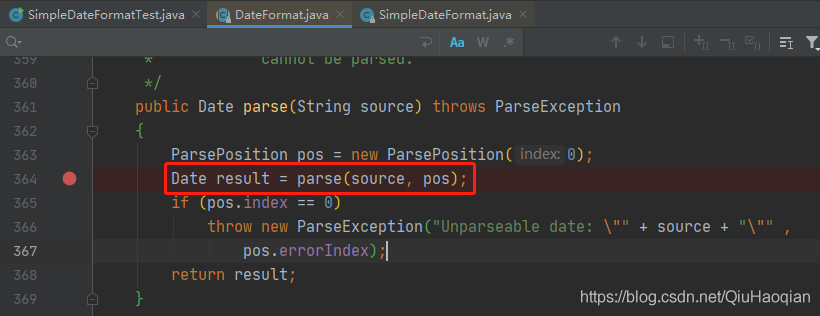
DateFormat 的 parse(String source) 方法会调用SimpleDateFormat中重写的 parse(String text, ParsePosition pos) 方法,该方法中有个地方需要关注
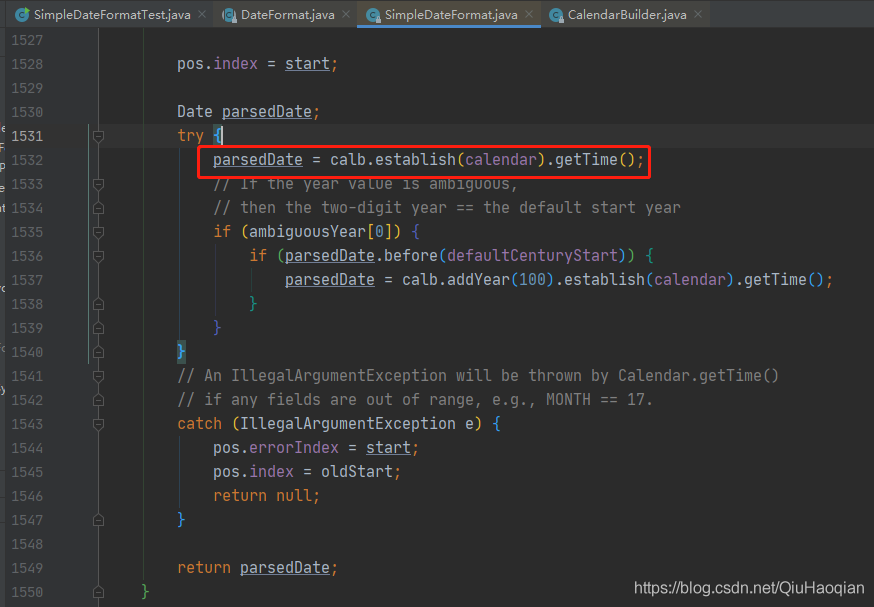
SimpleDateFormat 中重写的 parse(String text, ParsePosition pos) 方法中调用了 establish(calendar) 这个方法:
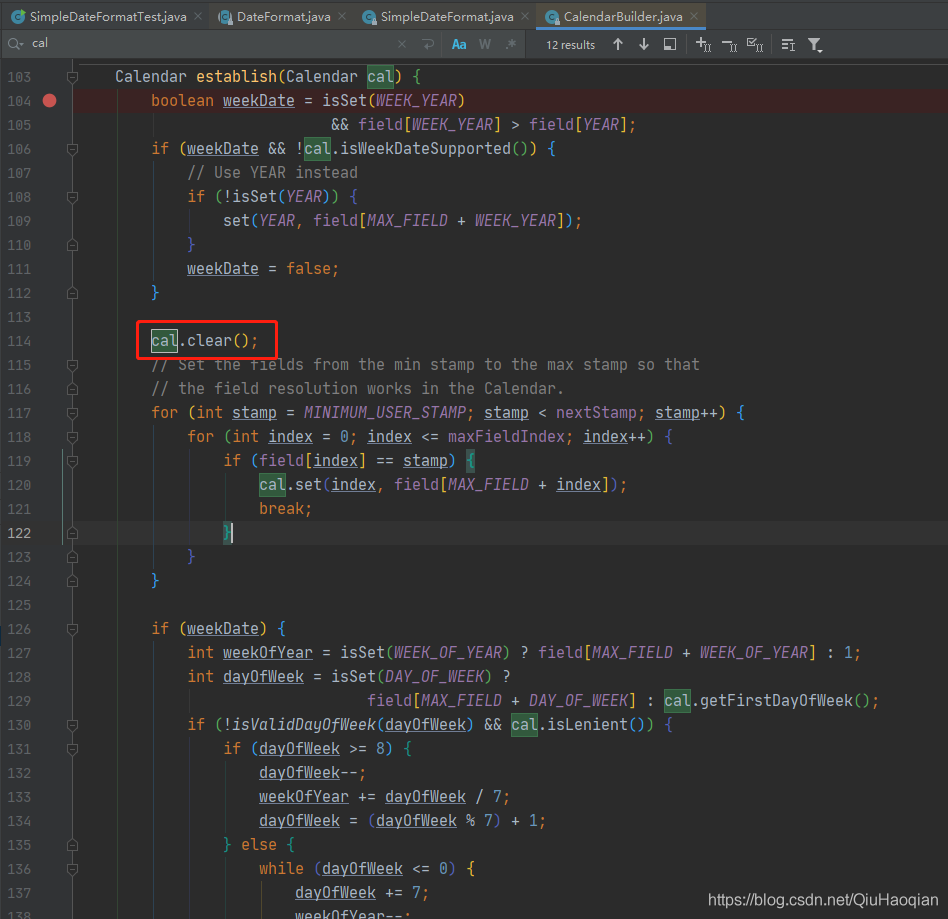
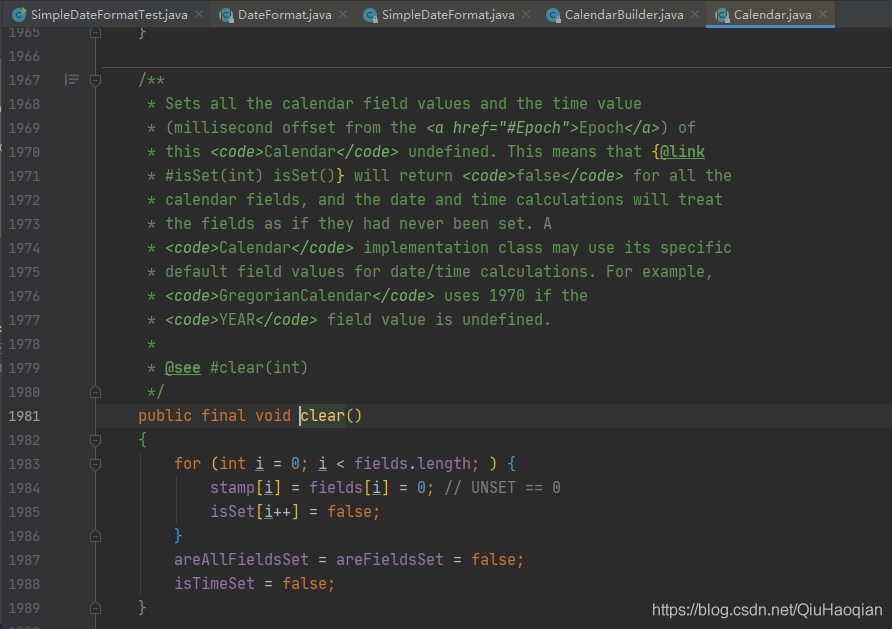
该方法中调用了 Calendar 的 clear() 方法
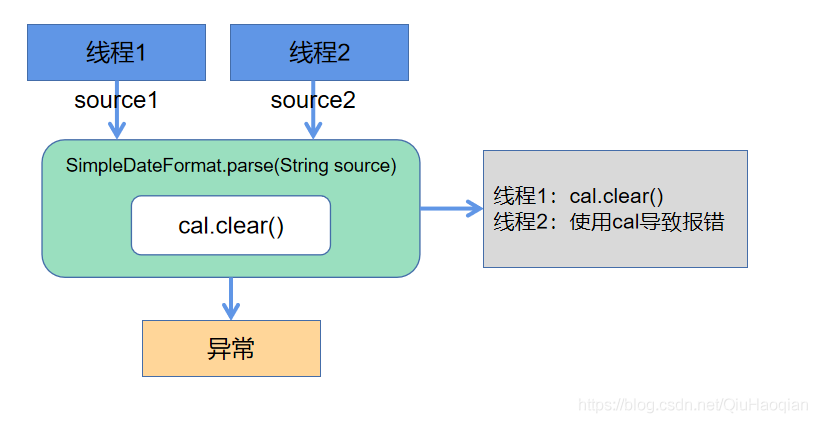
可以发现整个过程中Calendar对象它并不是线程安全的,如果,a线程将calendar清空了,calendar 就没有新值了,恰好此时b线程刚好进入到parse方法用到了calendar对象,那就会产生线程安全问题了!
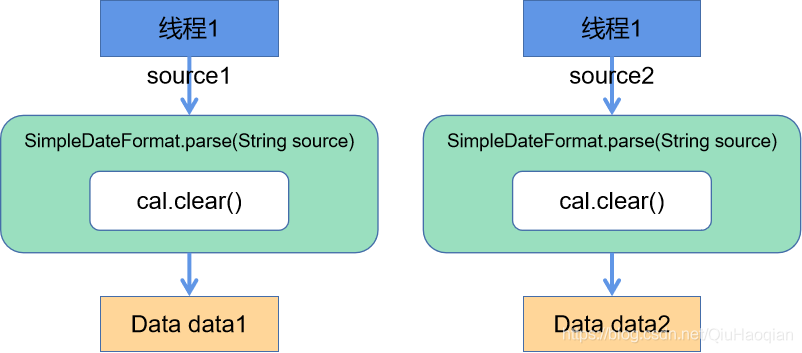
正常情况下:
非线程安全的流程:
1.3 解决方法
方法1:每个线程都new一个SimpleDateFormat
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;public class SimpleDateFormatTest {public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {try {// 每个线程都new一个SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + simpleDateFormat.parse("2020-06-01 11:35:00"));} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "Thread-" + i);thread.start();}}
}方式2:synchronized等方式加锁
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {private static final SimpleDateFormat SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {try {synchronized (SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT.parse("2020-06-01 11:35:00"));}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "Thread-" + i);thread.start();}}
}方式3:使用ThreadLocal 为每个线程创建一个独立变量
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;public class SimpleDateFormatTest {private static final ThreadLocal<DateFormat> SAFE_SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT = ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));public static void main(String[] args) {for (int i = 0; i < 20; ++i) {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {try {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--" + SAFE_SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT.get().parse("2020-06-01 11:35:00"));} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}, "Thread-" + i);thread.start();}}
}2 SimpleDateFormat.format() 方法的线程安全问题
2.1 错误示例
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;public class SimpleDateFormatTest {// 时间格式化对象private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss");public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 创建线程池执行任务ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {int finalI = i;// 执行任务threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000); // 得到时间对象formatAndPrint(date); // 执行时间格式化}});}threadPool.shutdown(); // 线程池执行完任务之后关闭}/*** 格式化并打印时间*/private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {String result = simpleDateFormat.format(date); // 执行格式化System.out.println("时间:" + result); // 打印最终结果}
}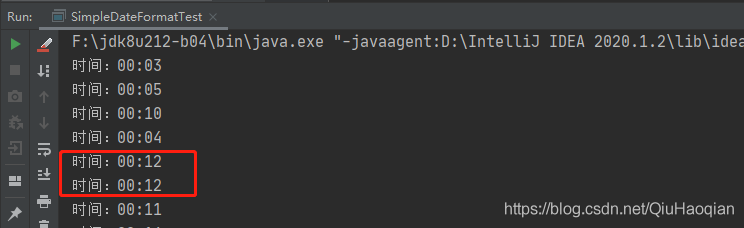
从上述结果可以看出,程序的打印结果竟然有重复内容的,正确的情况应该是没有重复的时间才对。
2.2 非线程安全原因分析
为了找到问题所在,查看 SimpleDateFormat 中 format 方法的源码来排查一下问题,format 源码如下:
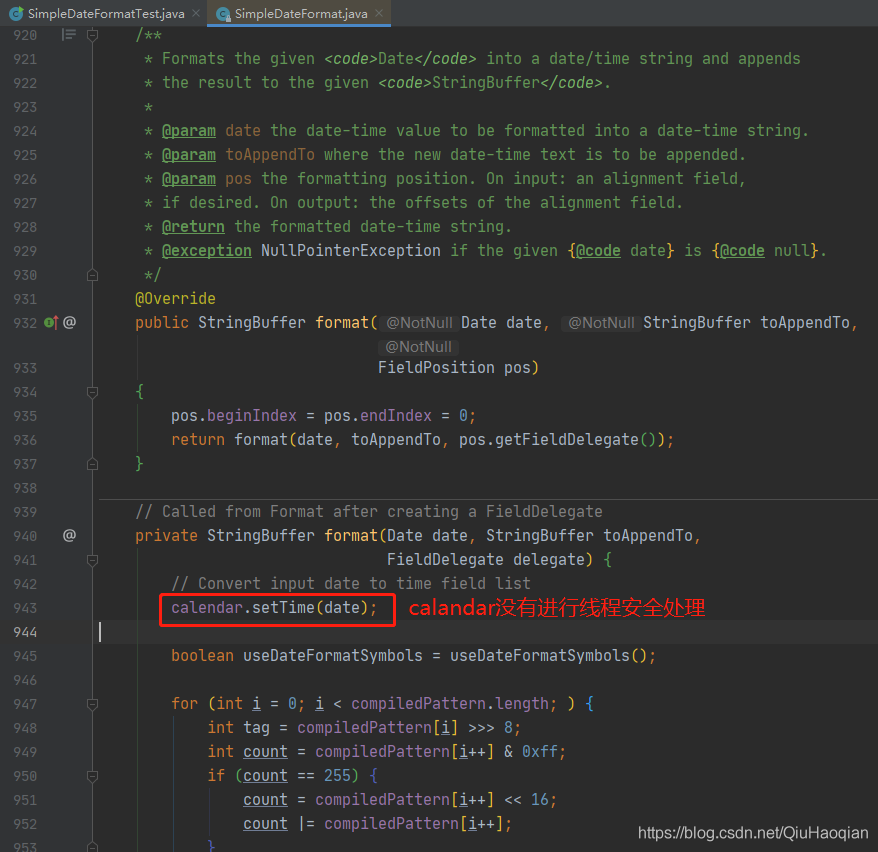
从上述源码可以看出,在执行 SimpleDateFormat.format() 方法时,会使用 calendar.setTime() 方法将输入的时间进行转换,那么我们想想一下这样的场景:
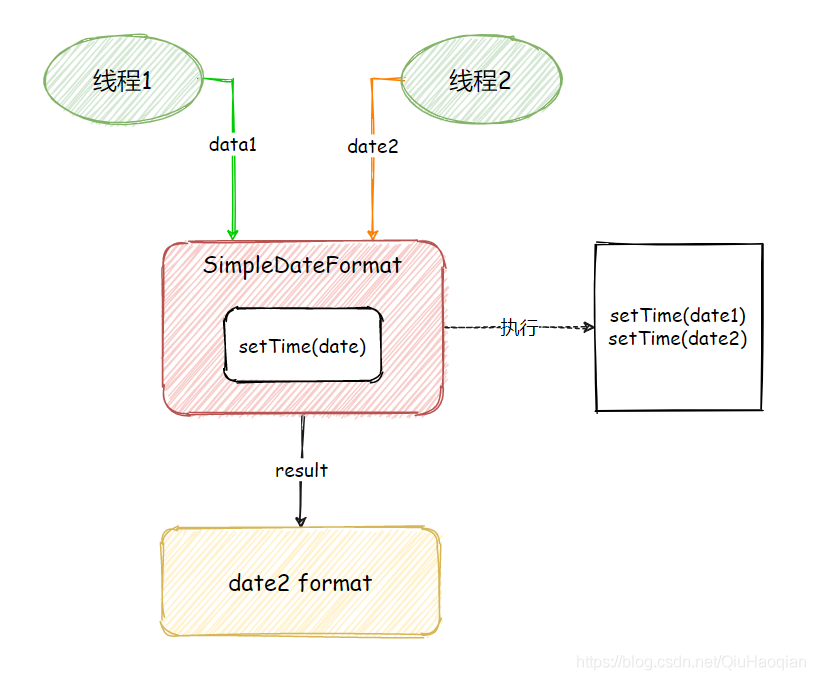
线程 1 执行了 calendar.setTime(date) 方法,将用户输入的时间转换成了后面格式化时所需要的时间;
线程 1 暂停执行,线程 2 得到 CPU 时间片开始执行;
线程 2 执行了 calendar.setTime(date) 方法,对时间进行了修改;
线程 2 暂停执行,线程 1 得出 CPU 时间片继续执行,因为线程 1 和线程 2 使用的是同一对象,而时间已经被线程 2 修改了,所以此时当线程 1 继续执行的时候就会出现线程安全的问题了。
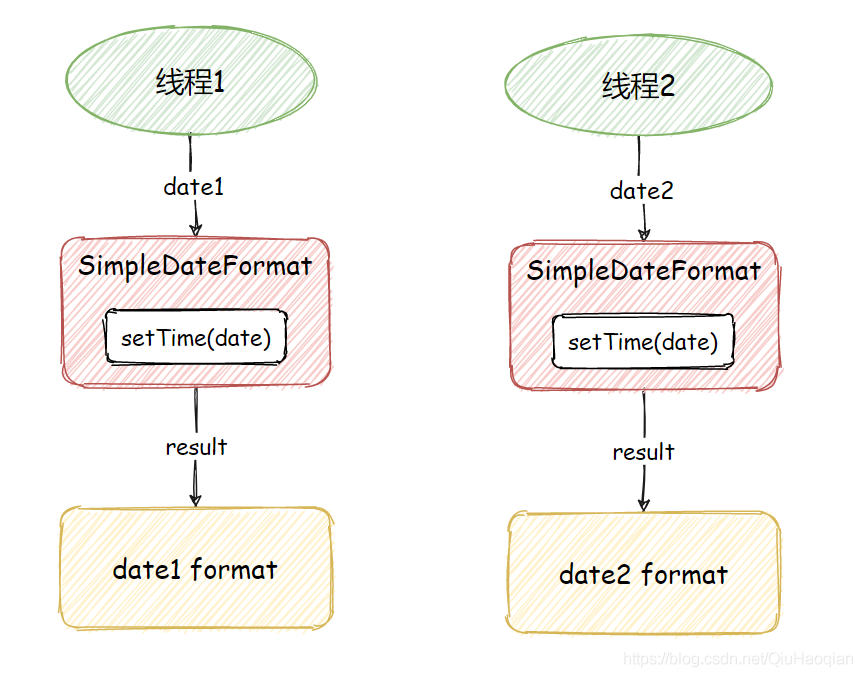
正常的情况下,程序的执行是这样的:
非线程安全的执行流程是这样的:
2.3 解决方法
同样有三种解决方法
方法1:每个线程都new一个SimpleDateFormat
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 创建线程池执行任务ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {int finalI = i;// 执行任务threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 得到时间对象Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000);// 执行时间格式化formatAndPrint(date);}});}// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭threadPool.shutdown();}/*** 格式化并打印时间*/private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {String result = new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss").format(date); // 执行格式化System.out.println("时间:" + result); // 打印最终结果}
}方式2:synchronized等方式加锁
所有的线程必须排队执行某些业务才行,这样无形中就降低了程序的运行效率了
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {// 时间格式化对象private static SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss");public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 创建线程池执行任务ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {int finalI = i;// 执行任务threadPool.execute(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000); // 得到时间对象formatAndPrint(date); // 执行时间格式化}});}// 线程池执行完任务之后关闭threadPool.shutdown();}/*** 格式化并打印时间*/private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {// 执行格式化String result = null;// 加锁synchronized (SimpleDateFormatTest.class) {result = simpleDateFormat.format(date);}// 打印最终结果System.out.println("时间:" + result);}
}方式3:使用ThreadLocal 为每个线程创建一个独立变量
public class SimpleDateFormatTest {// 创建 ThreadLocal 并设置默认值private static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> dateFormatThreadLocal =ThreadLocal.withInitial(() -> new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss"));public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建线程池执行任务ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 60,TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(1000));// 执行任务for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {int finalI = i;// 执行任务threadPool.execute(() -> {Date date = new Date(finalI * 1000); // 得到时间对象formatAndPrint(date); // 执行时间格式化});}threadPool.shutdown(); // 线程池执行完任务之后关闭}/*** 格式化并打印时间*/private static void formatAndPrint(Date date) {String result = dateFormatThreadLocal.get().format(date); // 执行格式化System.out.println("时间:" + result); // 打印最终结果}
}完
我的新书《深入理解Java核心技术》已经上市了,上市后一直蝉联京东畅销榜中,目前正在6折优惠中,想要入手的朋友千万不要错过哦~长按二维码即可购买~

长按扫码享受6折优惠
往期推荐
入职一家新公司,如何快速熟悉代码?

揭秘:春晚微信红包,是如何抗住 100 亿次请求的?
你还不明白如何解决分布式Session?看这篇就够了!
如果你喜欢本文,
请长按二维码,关注 Hollis.

转发至朋友圈,是对我最大的支持。
点个 在看
喜欢是一种感觉
在看是一种支持
↘↘↘
这篇关于还在用 SimpleDateFormat 做时间格式化?小心项目崩掉!的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




