本文主要是介绍【递归】(三) (Memorization) 记忆化技术,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
一、递归中的重复计算
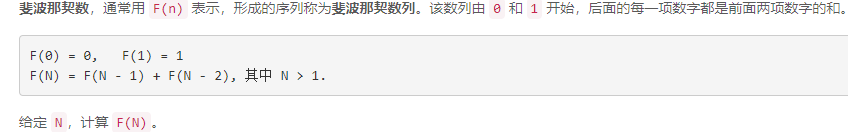
二、斐波那契数
2.1 题目要求
2.2 解决过程
三、爬楼梯
3.1 题目要求
3.2 解决过程
四、爬楼梯多解
一、递归中的重复计算

# Python implementation
def fibonacci(n):""":type n: int:rtype: int"""if n < 2:return nelse:return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)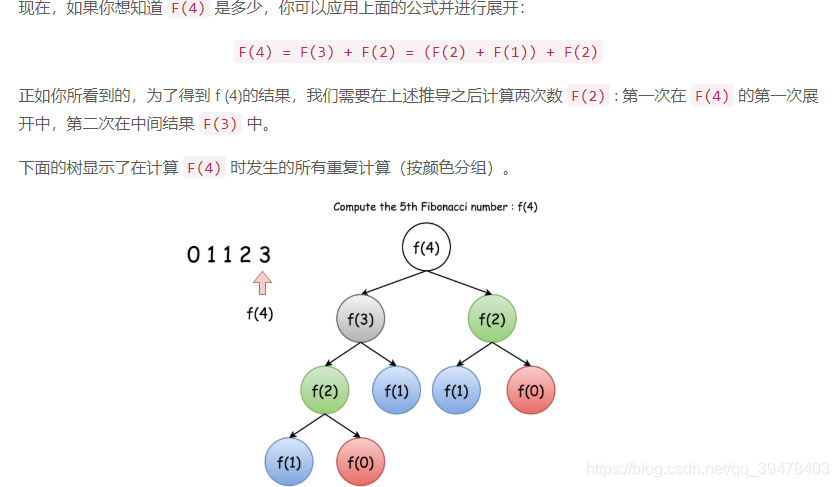

def fib(self, N):""":type N: int:rtype: int"""cache = {}def recur_fib(N):if N in cache:return cache[N]if N < 2:result = Nelse:result = recur_fib(N-1) + recur_fib(N-2)# put result in cache for later reference.cache[N] = resultreturn resultreturn recur_fib(N)
参考文献:https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/orignial/card/recursion-i/258/memorization/1211/
二、斐波那契数
2.1 题目要求

2.2 解决过程
个人实现
法一:无记忆递归。
2020/07/19 - 18.27% (800ms) - 最简单但低效的方法
class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N == 1:return 1if N == 0:return 0return self.fib(N-1) + self.fib(N-2)法二:有记忆递归。使用字典 memory 来记忆计算过的结果,避免重复冗余的计算。
2020/07/19 - 53.74% (44ms) - 性能显著提升,但由于实现存在问题,未能发挥最佳效果 (对比官方法三)
class Solution:def __init__(self):self.memory = {0: 0, 1: 1} # 计算记录, 但其实这种方式效率并不高, 详见官方法三def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N in self.memory:return self.memory[N]else:self.memory[N] = self.fib(N-1) + self.fib(N-2) # 记忆return self.memory[N]官方实现与说明


class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N <= 1:return Nreturn self.fib(N-1) + self.fib(N-2)2020/07/19 - 12.98% (800ms)


class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N <= 1:return Nreturn self.memoize(N)def memoize(self, N: int) -> {}:cache = {0: 0, 1: 1}# Since range is exclusive and we want to include N, we need to put N+1.for i in range(2, N+1):cache[i] = cache[i-1] + cache[i-2]return cache[N]
2020/07/19 - 73.37% (40ms)


## 这比个人实现二还要好, 注意对比 cache 的来源与差异
class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N <= 1:return Nself.cache = {0: 0, 1: 1} # 比放在数据成员的个人实现法二要好return self.memoize(N)def memoize(self, N: int) -> {}:if N in self.cache:return self.cache[N]self.cache[N] = self.memoize(N-1) + self.memoize(N-2)return self.memoize(N)2020/07/19 - 99.21% (28ms) - 接近最佳 (注意,实现时将递归体封装在另一个成员函数中了)
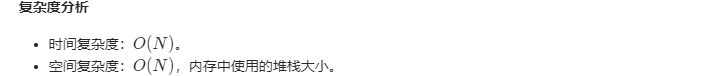

class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if (N <= 1):return Nif (N == 2):return 1current = 0prev1 = 1prev2 = 1# Since range is exclusive and we want to include N, we need to put N+1.for i in range(3, N+1):current = prev1 + prev2prev2 = prev1prev1 = currentreturn current2020/07/19 - 53.74% (44ms)
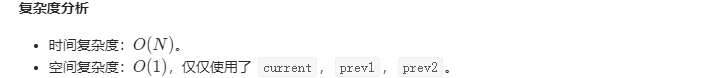

## 这就牛掰了, 开始使用数学思想了, 所以更有些费解, 但很值得学习!
class Solution:def fib(self, N: int) -> int:if (N <= 1):return NA = [[1, 1], [1, 0]] # 中间幂矩阵的基数矩阵self.matrix_power(A, N-1) # 使用递归函数 matrixPower 计算给定矩阵 A 的幂。幂为 N-1return A[0][0]def matrix_power(self, A: list, N: int):if (N <= 1):return Aself.matrix_power(A, N//2) # matrixPower 函数将对 N/2 个斐波那契数进行操作!self.multiply(A, A) # 矩阵乘法B = [[1, 1], [1, 0]]if (N%2 != 0): # 奇数次补乘 如 3, 因为对于偶数次幂 N=2x 而奇数次幂 N=2x+1self.multiply(A, B)def multiply(self, A: list, B: list):x = A[0][0] * B[0][0] + A[0][1] * B[1][0]y = A[0][0] * B[0][1] + A[0][1] * B[1][1]z = A[1][0] * B[0][0] + A[1][1] * B[1][0]w = A[1][0] * B[0][1] + A[1][1] * B[1][1]A[0][0] = xA[0][1] = yA[1][0] = zA[1][1] = w
2020/07/19 - 96.20% (32ms) - 接近最佳,强大的 O(logn) 复杂度

# 这是什么神仙操作 ...
class Solution:def fib(self, N):golden_ratio = (1 + 5 ** 0.5) / 2return int((golden_ratio ** N + 1) / 5 ** 0.5)
2020/07/19 - 96.20% (32ms) - 最佳,惊人的 O(1) 复杂度
其他实现
若此时要求 通过递归返回斐波那契数列的前 N 项,则出了有记忆递归,还可以:
LRU cache 缓存装饰器 (decorator):根据参数缓存每次函数调用结果,对于相同参数的,无需重新函数计算,直接返回之前缓存的返回值。缓存数据是并不一定快,要综合考量缓存的代价以及缓存的时效大小。经典例子是改造 fib 序列。
- 若 maxsize=None,则禁用 LRU 功能,且缓存可无限制增长;当 maxsize=2^x 时,LRU 功能执行得最好;
- 若 typed=True,则不同类型的函数参数将单独缓存。例如,f(2) 和 f(2.0) 将被视为具有不同结果的不同调用;
- 缓存是有内存存储空间限制的;
2020/07/20 - 73.37% (40ms) - 不错
from functools import lru_cache
class Solution:@lru_cachedef fib(self, N: int) -> int:if N <= 1:return Nreturn self.fib(N-1) + self.fib(N-2)参考文献
https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/orignial/card/recursion-i/258/memorization/1212/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/fibonacci-number/solution/fei-bo-na-qi-shu-by-leetcode/
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1e8318220bba
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU0MDczMDUzMQ==&mid=2247484006&idx=1&sn=04d79d1ac51eabec5dfe2f3f444abff6&chksm=fb35f7aacc427ebccfaeb9faf55a9240d5e0dd35a8d4c1b0eff37637ef0243b30ccbe4b5da7d&scene=158#rd
三、爬楼梯
3.1 题目要求


3.2 解决过程
个人实现
法一:数学法 - 组合。通过排列组合中的 组合公式,累计 1 和 2 元素的各组合数。对本题而言,不论是爬一大步还是爬一小步,只要是爬 1 阶,就都是 无差别的,2 阶同理。故此处使用组合而非排列,通过 m!消除重复的排列情况。空间复杂度 O(1),时间复杂度 O(n^2) ?
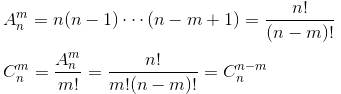
此外,该实现的高效性得益于 math.factorial() 函数的底层优化,否则手写阶乘函数效率将会极其低下。
2020/07/21 - 98.95% (28ms) - 数学法往往效果很好
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 4:return none = n # 初始化 n 个 1two = 0 # 初始化 0 个 2limit = n // 2 # 2 个数上限count = 0 # 种类计数while two <= limit:# 数据准备summ = one + two # nminn = min(one, two) # mdiff = summ - minn # n-m# 组合 C^m_n = A^m_n / m! = n! / (n-m)! / m!count += (math.factorial(summ) // math.factorial(diff)) // math.factorial(minn) # 更新组合元素 one -= 2 # 减少 2 个 1two += 1 # 增加 1 个 2return count法二:数学法 - 找规律。根据测试用例及其结果,可以发现如下数列规律:
- 输入:1、2、3、4、5、6、7 ...
- 输出:1、2、3、5、8、13、21 ...
即从第三个数字开始,每个数字都是前两个数字之和,这就是 斐波那契数列 的性质,因此可以直接使用斐波那契数的解法来处理本题。
2020/07/22 - 15.86% (48ms) - 实现相对低效
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 4:return nself.cache = {1: 1, 2: 2, 3: 3}return self.fib(n)def fib(self, m):if m in self.cache:return self.cache[m]self.cache[m] = self.fib(m-1) + self.fib(m-2)return self.cache[m]法三:数学法 - 黄金分割比。修改自上一题 —— 斐波那契数的官方实现六。空间复杂度 O(1),时间复杂度 O(1)。
2020/07/22 - 85.31% (36ms) - 强大
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 4:return ngolden_ratio = (1 + 5 ** 0.5) / 2return int((golden_ratio ** (n+1) + 1) / 5 ** 0.5) # n 改成 n+1官方实现与说明

个人理解:因为第 x-1 阶与第 x-2 阶有别,故各自的攀爬方案 f(x-1) 与 f(x-2) 一定完全不同。而要想一次爬到第 x 阶,只有两种初始情况:从第 x-1 阶爬 1 步 or 从第 x-2 阶爬 2 步。故第 x 阶的攀爬方案满足 f(x) = f(x-1) + f(x-2)。
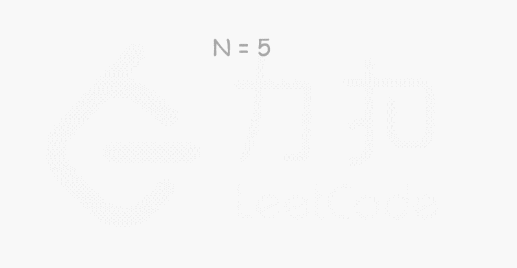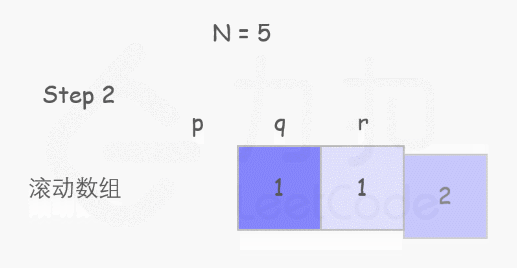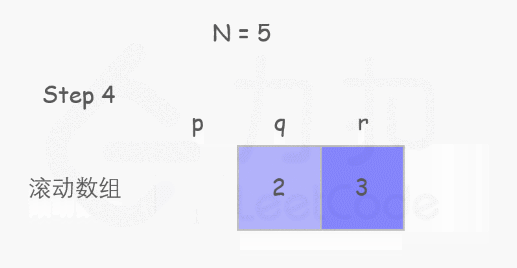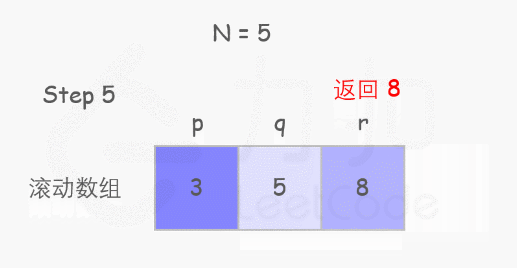
// C++ implementation
class Solution {
public:int climbStairs(int n) {int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {p = q; q = r; r = p + q;}return r;}
};
// JAVA implementation
class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {int p = 0, q = 0, r = 1;for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {p = q; q = r; r = p + q;}return r;}
}

![]()


// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {int[][] q = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};int[][] res = pow(q, n);return res[0][0];}public int[][] pow(int[][] a, int n) {int[][] ret = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};while (n > 0) {if ((n & 1) == 1) {ret = multiply(ret, a);}n >>= 1;a = multiply(a, a);}return ret;}public int[][] multiply(int[][] a, int[][] b) {int[][] c = new int[2][2];for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {c[i][j] = a[i][0] * b[0][j] + a[i][1] * b[1][j];}}return c;}
}

// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {double sqrt5 = Math.sqrt(5);double fibn = Math.pow((1 + sqrt5) / 2, n + 1) - Math.pow((1 - sqrt5) / 2, n + 1);return (int)(fibn / sqrt5);}
}# Python implementation
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:if n < 4:return nsqrt5 = math.sqrt(5)fibn = math.pow((1+sqrt5) / 2, n+1) - math.pow((1-sqrt5) / 2, n+1)return int(fibn / sqrt5)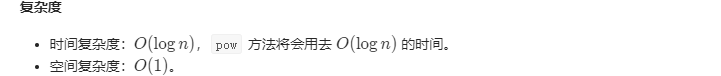

参考文献
https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/orignial/card/recursion-i/258/memorization/1213/
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/solution/pa-lou-ti-by-leetcode-solution/
四、爬楼梯

// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {climb_Stairs(0, n);}public int climb_Stairs(int i, int n) {if (i > n) {return 0;}if (i == n) {return 1;}return climb_Stairs(i + 1, n) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n);}
}# Python implementation
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:return self.climb_Stairs(0, n)def climb_Stairs(self, i, n):if i > n:return 0if i == n:return 1return self.climb_Stairs(i+1, n) + self.climb_Stairs(i+2, n)

![]()

// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {int memo[] = new int[n + 1];return climb_Stairs(0, n, memo);}public int climb_Stairs(int i, int n, int memo[]) {if (i > n) {return 0;}if (i == n) {return 1;}if (memo[i] > 0) {return memo[i];}memo[i] = climb_Stairs(i + 1, n, memo) + climb_Stairs(i + 2, n, memo);return memo[i];}
}# Python implementation
class Solution:def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:memo = [0 for _ in range(n+1)] # memo = [0] * (n+1)return self.climb_Stairs(0, n, memo)def climb_Stairs(self, i, n, memo):if i > n:return 0if i == n:return 1if memo[i] > 0:return memo[i]memo[i] = self.climb_Stairs(i+1, n, memo) + self.climb_Stairs(i+2, n, memo)return memo[i]


// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {if (n == 1) {return 1;}int[] dp = new int[n + 1];dp[1] = 1;dp[2] = 2;for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2];}return dp[n];}
}

// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {if (n == 1) {return 1;}int first = 1;int second = 2;for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {int third = first + second;first = second;second = third;}return second;}
}


// JAVA implementationpublic class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {int[][] q = {{1, 1}, {1, 0}};int[][] res = pow(q, n);return res[0][0];}public int[][] pow(int[][] a, int n) {int[][] ret = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}};while (n > 0) {if ((n & 1) == 1) {ret = multiply(ret, a);}n >>= 1;a = multiply(a, a);}return ret;}public int[][] multiply(int[][] a, int[][] b) {int[][] c = new int[2][2];for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {c[i][j] = a[i][0] * b[0][j] + a[i][1] * b[1][j];}}return c;}
}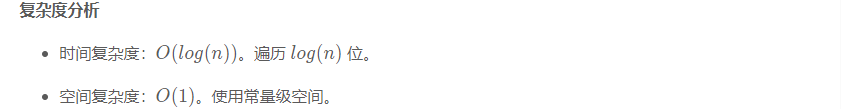





// JAVA implementation
public class Solution {public int climbStairs(int n) {double sqrt5=Math.sqrt(5);double fibn=Math.pow((1+sqrt5)/2,n+1)-Math.pow((1-sqrt5)/2,n+1);return (int)(fibn/sqrt5);}
}
参考文献:https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/orignial/card/recursion-i/258/memorization/1214/#3
这篇关于【递归】(三) (Memorization) 记忆化技术的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







