本文主要是介绍Android事件分发机制源码畅游解析(View篇),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
趁着上篇文章的热乎劲儿没过,赶紧再来一发。
本文是参考一些大神习作的基础上,自己琢磨、研究、加工而成。欢迎大家批评、讨论。
1、为什么首先是View
本篇是事件分发机制的开篇,平时操作最直观的感受就是,在当前界面中,点击一个Button,就会响应onClick事件,好像跟contain它的Linearlayout和Activity无关。还有就是你会发现所有的展示出来的东西归根到底其实还是一个个的View,ViewGroup也是extends View。
那么就从事件”发生地“开始,一步步的找出其最初的根源。
2、在View中找出事件始发点
我们想要得到一个一个onClick事件的回调,一般会设置button.setOnClickListener(xxx),那我们就ctrl+鼠标左键,找啊找,最终你会发现一个这样的寻找历程:
(Button).button.setOnClickListener监听 -> 进入View中的setOnClickListener方法
->getListenerInfo().mOnClickListener -> performClick() ->onTouchEvent
->mOnTouchListener.onTouch -> dispatchTouchEvent()
所以,上面的倒过来就是View中MotionEvent(触摸事件)的真实传播过程。
3、分析View的dispatchTouchEvent()
APILevel 25 源码
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {// If the event should be handled by accessibility focus first.if (event.isTargetAccessibilityFocus()) {// We don't have focus or no virtual descendant has it, do not handle the event.if (!isAccessibilityFocusedViewOrHost()) {return false;}// We have focus and got the event, then use normal event dispatch.event.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);}boolean result = false;if (mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onTouchEvent(event, 0);}final int actionMasked = event.getActionMasked();if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {// Defensive cleanup for new gesturestopNestedScroll();}if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {if ((mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED && handleScrollBarDragging(event)) {result = true;}//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatementListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {result = true;}if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {result = true;}}if (!result && mInputEventConsistencyVerifier != null) {mInputEventConsistencyVerifier.onUnhandledEvent(event, 0);}// Clean up after nested scrolls if this is the end of a gesture;// also cancel it if we tried an ACTION_DOWN but we didn't want the rest// of the gesture.if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP ||actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL ||(actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN && !result)) {stopNestedScroll();}return result;}
好吧,有点儿长,我们只是要分析MotionEvent最简单直观的流程,精简一下:
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {boolean result = false;if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatementListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {result = true;}if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {result = true;}}return result;}
简要分析:
1、 上面第***3*** 行onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)是表示过滤掉Window被遮盖的情况。如下代码中的第***5*** 行注释
public boolean onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(MotionEvent event) {//noinspection RedundantIfStatementif ((mViewFlags & FILTER_TOUCHES_WHEN_OBSCURED) != 0&& (event.getFlags() & MotionEvent.FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED) != 0) {// Window is obscured, drop this touch.return false;}return true;}
2、 第***6-10*** 行if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null && (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) 就是说当我们setTouchListener后,一定会回调onTouch方法(就不说Disabled的情况了),但是如果我们手动把返回值改为return true;那么9行result = true,就会直接跳过第***12*** 行的if判断,本view的dispatchTouchEvent就已经结束。
3、但是我们要分析事件啊,onTouch中返回false时,就会走到第***12*** 行的onTouchEvent(event)
4、分析onTouchEvent
大部分时候,控件textview等的onTouchEvent还是调用了View中的方法。好纠结,源码好长,但是内涵很多。
如果只是为了看一个流程,那么在case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP 条件下,
if (mPerformClick == null) {mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {performClick();
}
最终会走到performClick(),然后调用mOnClickListener的方法。一个View的事件过程就结束了。
既然来都来了,我们就仔细看一下源码,暂时只是为了知道机制流程的可以先不用看此段落。完整代码如下:
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {final float x = event.getX();final float y = event.getY();final int viewFlags = mViewFlags;final int action = event.getAction();if ((viewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == DISABLED) {if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_UP && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {setPressed(false);}// A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch// events, it just doesn't respond to them.return (((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE|| (viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE)|| (viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE);}if (mTouchDelegate != null) {if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {return true;}}if (((viewFlags & CLICKABLE) == CLICKABLE ||(viewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) ||(viewFlags & CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) == CONTEXT_CLICKABLE) {switch (action) {case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {// take focus if we don't have it already and we should in// touch mode.boolean focusTaken = false;if (isFocusable() && isFocusableInTouchMode() && !isFocused()) {focusTaken = requestFocus();}if (prepressed) {// The button is being released before we actually// showed it as pressed. Make it show the pressed// state now (before scheduling the click) to ensure// the user sees it.setPressed(true, x, y);}if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {// This is a tap, so remove the longpress checkremoveLongPressCallback();// Only perform take click actions if we were in the pressed stateif (!focusTaken) {// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling// performClick directly. This lets other visual state// of the view update before click actions start.if (mPerformClick == null) {mPerformClick = new PerformClick();}if (!post(mPerformClick)) {performClick();}}}if (mUnsetPressedState == null) {mUnsetPressedState = new UnsetPressedState();}if (prepressed) {postDelayed(mUnsetPressedState,ViewConfiguration.getPressedStateDuration());} else if (!post(mUnsetPressedState)) {// If the post failed, unpress right nowmUnsetPressedState.run();}removeTapCallback();}mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:mHasPerformedLongPress = false;if (performButtonActionOnTouchDown(event)) {break;}// Walk up the hierarchy to determine if we're inside a scrolling container.boolean isInScrollingContainer = isInScrollingContainer();// For views inside a scrolling container, delay the pressed feedback for// a short period in case this is a scroll.if (isInScrollingContainer) {mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();}mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());} else {// Not inside a scrolling container, so show the feedback right awaysetPressed(true, x, y);checkForLongClick(0, x, y);}break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:setPressed(false);removeTapCallback();removeLongPressCallback();mInContextButtonPress = false;mHasPerformedLongPress = false;mIgnoreNextUpEvent = false;break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:drawableHotspotChanged(x, y);// Be lenient about moving outside of buttonsif (!pointInView(x, y, mTouchSlop)) {// Outside buttonremoveTapCallback();if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0) {// Remove any future long press/tap checksremoveLongPressCallback();setPressed(false);}}break;}return true;}return false;
}
1、 第***7-16*** 行,A disabled view that is clickable still consumes the touch events, it just doesn’t respond to them.就是说即使这个view是diabled的,可是只要“有”clickable功能,仍旧会消费这个MotionEvent事件。要小心了啊,哈哈,明白就好。
2、 第***17-21*** 行,值得是被一个mTouchDelegate代理了事件。暂不讨论。
3、 第***23-134*** 行,就是一个view(比如button)consume事件的经典场景;先看***133*** 行,如果此view可点击(CLICKABLE、LONG_CLICKABLE、CONTEXT_CLICKABLE),无论过程怎样,都会return true;消费掉事件。
4、 先看***80*** 行,case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN,这是一个事件的开始。
5、 第***81*** 行 ,mHasPerformedLongPress = false;初始化是否触发长按动作的标识。
6、 第***92*** 行是判断是否可scroll,比如ScrollView返回的是true,LinearyLayout为false。可以点金***88*** 行的方法观察一下。
7、 第***93*** 行,mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED,mPrivateFlags设置成PFLAG_PREPRESSED状态。
8、 第***95***行,进入CheckForTap
private final class CheckForTap implements Runnable {public float x;public float y;@Overridepublic void run() {mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_PREPRESSED;setPressed(true, x, y);checkForLongClick(ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout(), x, y);}}
首先mPrivateFlags取消PFLAG_PREPRESSED状态,归位。调用setPressed(true, x, y)
private void setPressed(boolean pressed, float x, float y) {if (pressed) {drawableHotspotChanged(x, y);}setPressed(pressed);}
进入setPressed(pressed)方法
public void setPressed(boolean pressed) {final boolean needsRefresh = pressed != ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) == PFLAG_PRESSED);if (pressed) {mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PRESSED;} else {mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_PRESSED;}if (needsRefresh) {refreshDrawableState();}dispatchSetPressed(pressed);}
pressed=true时,mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PRESSED;置为PFLAG_PRESSED状态,refreshDrawableState()是跟view绘制有关,比如button的按压效果等。
9、第***99*** 行,postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap,ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout()),ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout()判断超过的话是scroll,小于是tap。apilevel 25种的300,300毫秒后执行CheckForTap的run方法,其中checkForLongClick(ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout(), x, y);
private void checkForLongClick(int delayOffset, float x, float y) {if ((mViewFlags & LONG_CLICKABLE) == LONG_CLICKABLE) {mHasPerformedLongPress = false;if (mPendingCheckForLongPress == null) {mPendingCheckForLongPress = new CheckForLongPress();}mPendingCheckForLongPress.setAnchor(x, y);mPendingCheckForLongPress.rememberWindowAttachCount();postDelayed(mPendingCheckForLongPress,ViewConfiguration.getLongPressTimeout() - delayOffset);}}
判断超过进入CheckForLongPress的run()方法,表示触发longclick状态
private final class CheckForLongPress implements Runnable {private int mOriginalWindowAttachCount;private float mX;private float mY;@Overridepublic void run() {if (isPressed() && (mParent != null)&& mOriginalWindowAttachCount == mWindowAttachCount) {if (performLongClick(mX, mY)) {mHasPerformedLongPress = true;}}}
mHasPerformedLongPress = true;并且执行performLongClick(mX, mY)方法,触发事件状态等。
10、第***100-104*** 行,代码原理参考上面。
11、来看107行的case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE,第***120*** 行,pointInView(x, y, mTouchSlop)判断是否事件是否已move出本view,如果已经过界,则执行removeLongPressCallback()且 mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_PRESSED归原始位。
12、来看***27*** 行case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP。28 行boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;如果是在一个scrollview中,CheckForTap没有还没开始执行时为true;29 行if中的mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED,是setPressed方法执行后,如102行。正常情况下至少有一个true。
13、第***45*** 行,if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent),其中mHasPerformedLongPress表示CheckForLongPress是否已经执行,判断条件看第9条解释的最后部分。mIgnoreNextUpEvent=true一般是鼠标的事件的hover时,此处为false。假如CheckForLongPress并没有执行,那么就会进入45行的if判断中去。47 行移除将要执行的CheckForLongPress,
14、第***54-59*** 行,最终都会走到performClick(),其中的li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);不用说了吧哈呀呀…
public boolean performClick() {final boolean result;final ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;if (li != null && li.mOnClickListener != null) {playSoundEffect(SoundEffectConstants.CLICK);li.mOnClickListener.onClick(this);result = true;} else {result = false;}sendAccessibilityEvent(AccessibilityEvent.TYPE_VIEW_CLICKED);return result;}
5、简单例子,纵观历程
1、通过extends Button自定义一个MyButton
public class MyButton extends Button {private static final String TAG = MyButton.class.getSimpleName();public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);}@Overridepublic boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {int action = event.getAction();switch (action) {case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:Log.e(TAG,"onTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:Log.e(TAG,"onTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE");break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:Log.e(TAG,"onTouchEvent ACTION_UP");break;}return super.onTouchEvent(event);}@Overridepublic boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {int action = event.getAction();switch (action) {case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:Log.e(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent ACTION_DOWN");break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:Log.e(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent ACTION_MOVE");break;case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:Log.e(TAG,"dispatchTouchEvent ACTION_UP");break;}return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);}
}
2、一个layout布局,引用自定义的MyButton
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"tools:context="com.hds.viewevent.MainActivity"><com.hds.viewevent.MyButtonandroid:id="@+id/button"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="Button"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.5"tools:layout_constraintRight_creator="1"tools:layout_constraintLeft_creator="1" /></android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
3、运行的Activity文件
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();private ImageView imageView;@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {Log.d(TAG, "onclick");}});button.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {@Overridepublic boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {Log.d(TAG, "onTouch");return false;}});}}
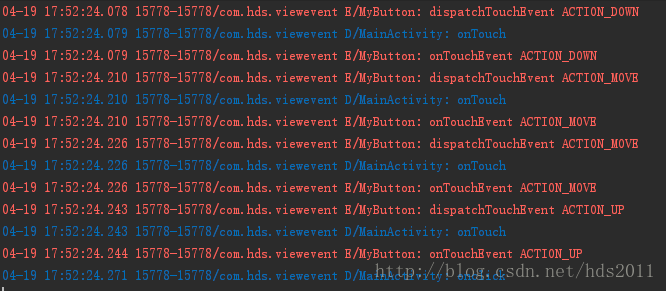
4、日至打印结果
看这手抖的,大家同时可以试验,在各个阶段return的false改为true试试,会理解的更深如。
6、View事件触发次序
dispatchTouchEvent -> onTouch -> onTouchEvent -> (onLongClick)onClick
当然是否能走到onclick看前面家伙们return的脸色了,人家要是return true,就不用等了,回家洗洗睡了。
歇一歇,捋一捋,理解好了可以接着下一锅Android事件分发机制源码畅游解析(ViewGroup篇) ,新鲜出炉!
这篇关于Android事件分发机制源码畅游解析(View篇)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!