在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中已经介绍了关于Tomcat7.0处理请求前作的初始化和准备工作,请读者在阅读本文前确保掌握《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中的相关知识以及HTTP协议和TCP协议的一些内容。本文重点讲解Tomcat7.0在准备好接受请求后,请求过程的原理分析。
请求处理架构
在正式开始之前,我们先来看看图1中的Tomcat请求处理架构。
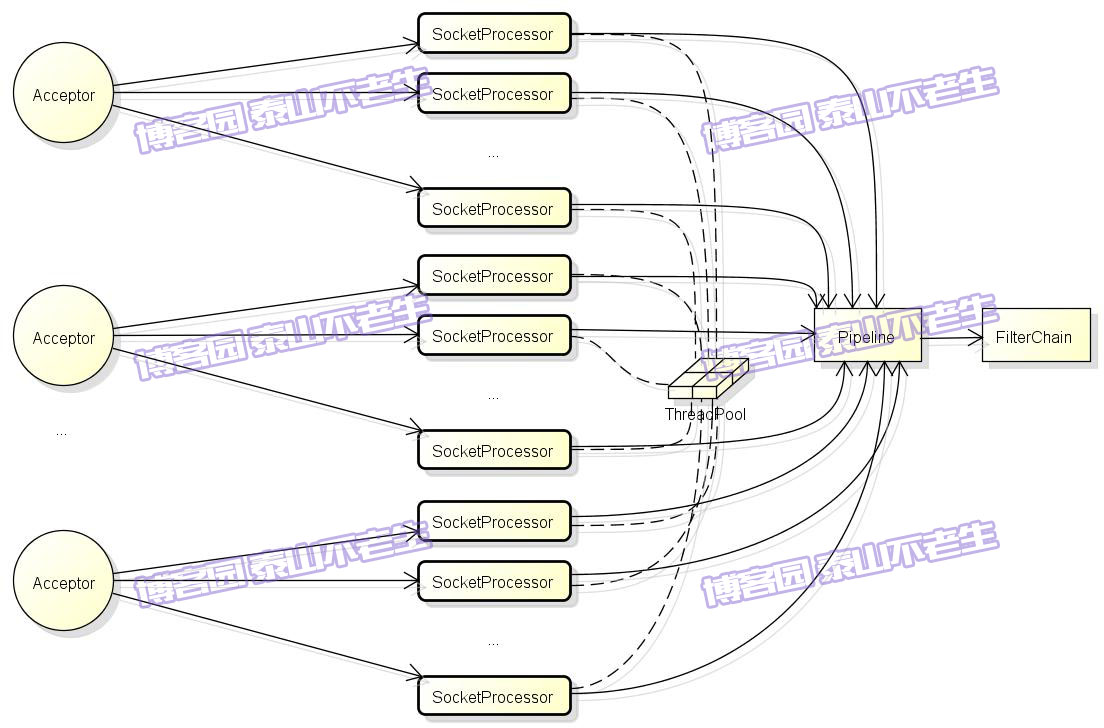
图1 Tomcat请求处理架构
图1列出了Tomcat请求处理架构中的主要组件,这里对它们做个简单介绍:
- Acceptor:负责从ServerSocket中接收新的连接,并将Socket转交给SocketProcessor处理。Acceptor是AbstractEndpoint的内部类,其实现已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍。Acceptor线程的默认大小为1,我们可以在server.xml的Connector配置中增加acceptorThreadCount的大小。
- SocketProcessor:负责对Acceptor转交的Socket进行处理,包括给Socket设置属性、读取请求行和请求头等,最终将处理交给Engine的Pipeline处理。
- ThreadPool:执行SocketProcessor的线程来自《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍的线程池,此线程池默认的最小线程数minSpareThreads等于10,最大线程数maxThreads等于200,我们可以在server.xml的Connector配置中调整它们的大小。
- Pipeline:SocketProcessor线程最后会将请求进一步交给Engine容器的Pipeline,管道Pipeline包括一系列的valve,如:StandardEngineValve、AccessLogValve、ErrorReportValve、StandardHostValve、 StandardContextValve、 StandardWrapperValve,它们就像地下水管中的一个个阀门,每一个都会对请求数据做不同的处理。
- FilterChain:管道Pipeline的最后一个valve是StandardWrapperValve,它会负责生成Servlet和Filter实例,并将它们组织成对请求处理的链条,这里正是Tomcat与J2EE规范相结合的部分。
默认情况下,Tomcat只有一个Acceptor线程,Acceptor不断循环从ServerSocket中获取Socket,当并发数大的情况下,这里会不会有性能问题?我想说的是,Acceptor的实现非常轻量级,它只负责两个动作:获取Socket和将Socket转交给SocketProcessor线程处理。另外,我们可以通过在server.xml的Connector配置中增加acceptorThreadCount的值,让我们同时可以拥有多个Acceptor线程。虽然我们可以修改maxThreads配置把SocketProcessor的线程数设置的很大,但是我们需要区别对待:
- 如果你部署在Tomcat上的Web服务主要用于计算,那么CPU的开销势必会很大,那么线程数不宜设置的过大,一般以CPU核数*2——CPU核数*3最佳。当然如果计算量非常大,就已经超出了Tomcat的使用范畴,我想此时,选择离线计算框架Hadoop或者实时计算框架Storm、Spark才是更好的选择。
- 如果部署在Tomcat上的Web服务主要是为了提供数据库访问,此时I/O的开销会很大,而CPU利用率反而低,此时应该将线程数设置的大一些,但是如果设置的过大,CPU为了给成百上千个线程分配时间片,造成CPU的精力都分散在线程切换上,反而造成性能下降。具体多大,需要对系统性能调优得出。
原理就讲这么多,下面具体分析下Tomcat处理请求的具体实现。
接收请求
在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中我们曾经介绍过AbstractEndpoint的内部类Acceptor,Acceptor实现了Runnable接口。Acceptor作为后台线程不断循环,每次循环都会sleep大约1秒钟(由于是线程级别的,所以并不保证准确),然后接收来自浏览器的Socket连接(用户在浏览器输入HTTP请求地址后,浏览器底层实际使用Socket通信的),最后将Socket交给外部类AbstractEndpoint的processSocket方法(见代码清单1)处理。
代码清单1
// ---------------------------------------------- Request processing methods/*** Process the given SocketWrapper with the given status. Used to trigger* processing as if the Poller (for those endpoints that have one)* selected the socket.** @param socketWrapper The socket wrapper to process* @param event The socket event to be processed* @param dispatch Should the processing be performed on a new* container thread** @return if processing was triggered successfully*/public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper,SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {try {if (socketWrapper == null) {return false;}SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop();if (sc == null) {sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);} else {sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);}Executor executor = getExecutor();if (dispatch && executor != null) {executor.execute(sc);} else {sc.run();}} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);return false;} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that// the pool and its queue are fullgetLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);return false;}return true;}
根据代码清单1,AbstractEndpoint的processSocket方法的处理步骤如下:
- 通过无界的LIFO同步队列获取SocketProcessorBase,如果没有则创建;
- 获取线程池对象并使用线程池(此线程池已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中启动PROTOCOLHANDLER一节介绍)执行。
代码清单2
@Overrideprotected SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> createSocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) {return new SocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);}
代码清单3
// ---------------------------------------------- SocketProcessor Inner Class/*** This class is the equivalent of the Worker, but will simply use in an* external Executor thread pool.*/protected class SocketProcessor extends SocketProcessorBase<NioChannel> {public SocketProcessor(SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event) {super(socketWrapper, event);}@Overrideprotected void doRun() {NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket();SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());try {int handshake = -1;try {if (key != null) {if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) {// No TLS handshaking required. Let the handler// process this socket / event combination.handshake = 0;} else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT ||event == SocketEvent.ERROR) {// Unable to complete the TLS handshake. Treat it as// if the handshake failed.handshake = -1;} else {handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable());// The handshake process reads/writes from/to the// socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once// the handshake completes. However, the handshake// happens when the socket is opened so the status// must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It// is OK to always set this as it is only used if// the handshake completes.event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ;}}} catch (IOException x) {handshake = -1;if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake",x);} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {handshake = -1;}if (handshake == 0) {SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN;// Process the request from this socketif (event == null) {state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);} else {state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event);}if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) {close(socket, key);}} else if (handshake == -1 ) {close(socket, key);} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ){socketWrapper.registerReadInterest();} else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE){socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest();}} catch (CancelledKeyException cx) {socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);} catch (VirtualMachineError vme) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(vme);} catch (Throwable t) {log.error("", t);socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);} finally {socketWrapper = null;event = null;//return to cacheif (running && !paused) {processorCache.push(this);}}}}
SocketProcessor线程专门用于处理Acceptor转交的Socket,其执行步骤如下:
- 调用handler的process方法处理请求。在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中我们讲过当处理AbstractProtocol协议时,handler默认为AbstractProtocol的内部类ConnectionHandler;
- 请求处理完毕后,如果state等于SocketState.CLOSED,则关闭Socket;如果state等于SocketState.OPEN,则保持连接;如果state等于SocketState.LONG,则会作为长连接对待。
- 最后把process归还到processorCache(LIFO的同步栈SynchronizedStack)栈中
以ConnectionHandler为例,我们重点分析它是如何进一步处理Socket的。ConnectionHandler的process方法,见代码清单6。
代码清单6
@Overridepublic SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) {if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.process",wrapper.getSocket(), status));}if (wrapper == null) {// Nothing to do. Socket has been closed.return SocketState.CLOSED;}S socket = wrapper.getSocket();Processor processor = connections.get(socket);if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.connectionsGet",processor, socket));}if (processor != null) {// Make sure an async timeout doesn't fire getProtocol().removeWaitingProcessor(processor);} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no// longer a processor associated with this socket.return SocketState.CLOSED;}ContainerThreadMarker.set();try {if (processor == null) {String negotiatedProtocol = wrapper.getNegotiatedProtocol();if (negotiatedProtocol != null) {UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol =getProtocol().getNegotiatedProtocol(negotiatedProtocol);if (upgradeProtocol != null) {processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());} else if (negotiatedProtocol.equals("http/1.1")) {// Explicitly negotiated the default protocol.// Obtain a processor below.} else {// TODO:// OpenSSL 1.0.2's ALPN callback doesn't support// failing the handshake with an error if no// protocol can be negotiated. Therefore, we need to// fail the connection here. Once this is fixed,// replace the code below with the commented out// block.if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",negotiatedProtocol));}return SocketState.CLOSED;/** To replace the code above once OpenSSL 1.1.0 is* used.// Failed to create processor. This is a bug.throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",negotiatedProtocol));*/}}}if (processor == null) {processor = recycledProcessors.pop();if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorPop",processor));}}if (processor == null) {processor = getProtocol().createProcessor();register(processor);}processor.setSslSupport(wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider()));// Associate the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor);SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;do {
//AbstractProcessorLight类的process方法state = processor.process(wrapper, status);if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {// Get the HTTP upgrade handlerUpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();// Retrieve leftover inputByteBuffer leftOverInput = processor.getLeftoverInput();if (upgradeToken == null) {// Assume direct HTTP/2 connectionUpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getUpgradeProtocol("h2c");if (upgradeProtocol != null) {processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);// Associate with the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor);} else {if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail","h2c"));}return SocketState.CLOSED;}} else {HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();// Release the Http11 processor to be re-used release(processor);// Create the upgrade processorprocessor = getProtocol().createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, upgradeToken);if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.upgradeCreate",processor, wrapper));}wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);// Mark the connection as upgradedwrapper.setUpgraded(true);// Associate with the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor);// Initialise the upgrade handler (which may trigger// some IO using the new protocol which is why the lines// above are necessary)// This cast should be safe. If it fails the error// handling for the surrounding try/catch will deal with// it.if (upgradeToken.getInstanceManager() == null) {httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);} else {ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null);try {httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);} finally {upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL);}}}}} while ( state == SocketState.UPGRADING);if (state == SocketState.LONG) {// In the middle of processing a request/response. Keep the// socket associated with the processor. Exact requirements// depend on type of long poll longPoll(wrapper, processor);if (processor.isAsync()) {getProtocol().addWaitingProcessor(processor);}} else if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {// In keep-alive but between requests. OK to recycle// processor. Continue to poll for the next request. connections.remove(socket);release(processor);wrapper.registerReadInterest();} else if (state == SocketState.SENDFILE) {// Sendfile in progress. If it fails, the socket will be// closed. If it works, the socket either be added to the// poller (or equivalent) to await more data or processed// if there are any pipe-lined requests remaining.} else if (state == SocketState.UPGRADED) {// Don't add sockets back to the poller if this was a// non-blocking write otherwise the poller may trigger// multiple read events which may lead to thread starvation// in the connector. The write() method will add this socket// to the poller if necessary.if (status != SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {longPoll(wrapper, processor);}} else if (state == SocketState.SUSPENDED) {// Don't add sockets back to the poller.// The resumeProcessing() method will add this socket// to the poller.} else {// Connection closed. OK to recycle the processor. Upgrade// processors are not recycled. connections.remove(socket);if (processor.isUpgrade()) {UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler();InstanceManager instanceManager = upgradeToken.getInstanceManager();if (instanceManager == null) {httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();} else {ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null);try {httpUpgradeHandler.destroy();} finally {try {instanceManager.destroyInstance(httpUpgradeHandler);} catch (Throwable e) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);}upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL);}}} else {release(processor);}}return state;} catch(java.net.SocketException e) {// SocketExceptions are normal getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.socketexception.debug"), e);} catch (java.io.IOException e) {// IOExceptions are normal getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.ioexception.debug"), e);} catch (ProtocolException e) {// Protocol exceptions normally mean the client sent invalid or// incomplete data. getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.protocolexception.debug"), e);}// Future developers: if you discover any other// rare-but-nonfatal exceptions, catch them here, and log as// above.catch (Throwable e) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(e);// any other exception or error is odd. Here we log it// with "ERROR" level, so it will show up even on// less-than-verbose logs.getLog().error(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.error"), e);} finally {ContainerThreadMarker.clear();}// Make sure socket/processor is removed from the list of current// connections connections.remove(socket);release(processor);return SocketState.CLOSED;}
根据代码清单6,可见ConnectionHandler的process方法的处理步骤如下:
- 先从connections(同步的map)中获取processor,假如有,则删除等待的processor。
- 然后再通过getNegotiatedProtocol获取processor。
- 从可以循环使用的recycledProcessors(类型为ConcurrentLinkedQueue)中获取;如果recycledProcessors中也没有可以使用的processor,则调用createProcessor方法(见代码清单7)创建AbstractHttp11Protocol;
- 如果当前Connector配置了指定了SSLEnabled="true",那么还需要给AbstractHttp11Protocol设置SSL相关的属性;
- 如果Socket是异步的,则调用AbstractProcessorLight的asyncPostProcess方法,否则调用AbstractProcessorLight的service(socketWrapper)方法;
- 请求处理完毕,如果Socket是UPGRADING的,则将Socket和AbstractHttp11Protocol一起放入connections缓存,否则从connections缓存中移除Socket和AbstractHttp11Protocol。
AbstractProcessorLight类的process方法:
@Overridepublic SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper, SocketEvent status)throws IOException {SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;Iterator<DispatchType> dispatches = null;do {if (dispatches != null) {DispatchType nextDispatch = dispatches.next();state = dispatch(nextDispatch.getSocketStatus());} else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT) {// Do nothing here, just wait for it to get recycled} else if (isAsync() || isUpgrade() || state == SocketState.ASYNC_END) {state = dispatch(status);if (state == SocketState.OPEN) {// There may be pipe-lined data to read. If the data isn't// processed now, execution will exit this loop and call// release() which will recycle the processor (and input// buffer) deleting any pipe-lined data. To avoid this,// process it now.
//Http11Processor.service()state = service(socketWrapper);}} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE) {// Extra write event likely after async, ignorestate = SocketState.LONG;} else if (status == SocketEvent.OPEN_READ){
//Http11Processor.service()state = service(socketWrapper);} else {// Default to closing the socket if the SocketEvent passed in// is not consistent with the current state of the Processorstate = SocketState.CLOSED;}if (state != SocketState.CLOSED && isAsync()) {state = asyncPostProcess();}if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug("Socket: [" + socketWrapper +"], Status in: [" + status +"], State out: [" + state + "]");}if (dispatches == null || !dispatches.hasNext()) {// Only returns non-null iterator if there are// dispatches to process.dispatches = getIteratorAndClearDispatches();}} while (state == SocketState.ASYNC_END ||dispatches != null && state != SocketState.CLOSED);return state;}
代码清单7
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Common code @SuppressWarnings("deprecation")@Overrideprotected Processor createProcessor() {Http11Processor processor = new Http11Processor(getMaxHttpHeaderSize(),getAllowHostHeaderMismatch(), getRejectIllegalHeaderName(), getEndpoint(),getMaxTrailerSize(), allowedTrailerHeaders, getMaxExtensionSize(),getMaxSwallowSize(), httpUpgradeProtocols, getSendReasonPhrase());processor.setAdapter(getAdapter());processor.setMaxKeepAliveRequests(getMaxKeepAliveRequests());processor.setConnectionUploadTimeout(getConnectionUploadTimeout());processor.setDisableUploadTimeout(getDisableUploadTimeout());processor.setCompressionMinSize(getCompressionMinSize());processor.setCompression(getCompression());processor.setNoCompressionUserAgents(getNoCompressionUserAgents());processor.setCompressibleMimeTypes(getCompressibleMimeTypes());processor.setRestrictedUserAgents(getRestrictedUserAgents());processor.setMaxSavePostSize(getMaxSavePostSize());processor.setServer(getServer());processor.setServerRemoveAppProvidedValues(getServerRemoveAppProvidedValues());return processor;}
根据之前的分析,我们知道Socket的处理方式有异步和同步两种,调用Http11Processor的asyncPostProcess和service方法,我们以同步处理为例,来看看接下来的处理逻辑。
同步处理
Http11Processor的service方法(见代码清单8)用于同步处理,由于其代码很多,所以此处在代码后面追加一些注释,便于读者理解。这里面有一些关键方法重点拿出来解释下:
- InternalInputBuffer的parseRequestLine方法用于读取请求行;
- InternalInputBuffer的parseHeaders方法用于读取请求头;
- prepareRequest用于在正式处理请求之前,做一些准备工作,如根据请求头获取请求的版本号是HTTP/1.1还是HTTP/0.9、keepAlive是否为true等,还会设置一些输入过滤器用于标记请求、压缩等;
- 调用CoyoteAdapter的service方法处理请求。
代码清单8
@Overridepublic SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper)throws IOException {RequestInfo rp = request.getRequestProcessor();rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PARSE);// Setting up the I/O setSocketWrapper(socketWrapper);inputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);outputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);// FlagskeepAlive = true;openSocket = false;readComplete = true;boolean keptAlive = false;SendfileState sendfileState = SendfileState.DONE;while (!getErrorState().isError() && keepAlive && !isAsync() && upgradeToken == null &&sendfileState == SendfileState.DONE && !endpoint.isPaused()) {// Parsing the request headertry {if (!inputBuffer.parseRequestLine(keptAlive)) {if (inputBuffer.getParsingRequestLinePhase() == -1) {return SocketState.UPGRADING;} else if (handleIncompleteRequestLineRead()) {break;}}if (endpoint.isPaused()) {// 503 - Service unavailableresponse.setStatus(503);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);} else {keptAlive = true;// Set this every time in case limit has been changed via JMX request.getMimeHeaders().setLimit(endpoint.getMaxHeaderCount());if (!inputBuffer.parseHeaders()) {// We've read part of the request, don't recycle it// instead associate it with the socketopenSocket = true;readComplete = false;break;}if (!disableUploadTimeout) {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(connectionUploadTimeout);}}} catch (IOException e) {if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse"), e);}setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);break;} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);UserDataHelper.Mode logMode = userDataHelper.getNextMode();if (logMode != null) {String message = sm.getString("http11processor.header.parse");switch (logMode) {case INFO_THEN_DEBUG:message += sm.getString("http11processor.fallToDebug");//$FALL-THROUGH$case INFO:log.info(message, t);break;case DEBUG:log.debug(message, t);}}// 400 - Bad Requestresponse.setStatus(400);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}// Has an upgrade been requested?Enumeration<String> connectionValues = request.getMimeHeaders().values("Connection");boolean foundUpgrade = false;while (connectionValues.hasMoreElements() && !foundUpgrade) {foundUpgrade = connectionValues.nextElement().toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH).contains("upgrade");}if (foundUpgrade) {// Check the protocolString requestedProtocol = request.getHeader("Upgrade");UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = httpUpgradeProtocols.get(requestedProtocol);if (upgradeProtocol != null) {if (upgradeProtocol.accept(request)) {// TODO Figure out how to handle request bodies at this// point. response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_SWITCHING_PROTOCOLS);response.setHeader("Connection", "Upgrade");response.setHeader("Upgrade", requestedProtocol);action(ActionCode.CLOSE, null);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);InternalHttpUpgradeHandler upgradeHandler =upgradeProtocol.getInternalUpgradeHandler(getAdapter(), cloneRequest(request));UpgradeToken upgradeToken = new UpgradeToken(upgradeHandler, null, null);action(ActionCode.UPGRADE, upgradeToken);return SocketState.UPGRADING;}}}if (!getErrorState().isError()) {// Setting up filters, and parse some request headers rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_PREPARE);try {prepareRequest();} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {log.debug(sm.getString("http11processor.request.prepare"), t);}// 500 - Internal Server Errorresponse.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}}if (maxKeepAliveRequests == 1) {keepAlive = false;} else if (maxKeepAliveRequests > 0 &&socketWrapper.decrementKeepAlive() <= 0) {keepAlive = false;}// Process the request in the adapterif (!getErrorState().isError()) {try {rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_SERVICE);getAdapter().service(request, response);// Handle when the response was committed before a serious// error occurred. Throwing a ServletException should both// set the status to 500 and set the errorException.// If we fail here, then the response is likely already// committed, so we can't try and set headers.if(keepAlive && !getErrorState().isError() && !isAsync() &&statusDropsConnection(response.getStatus())) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, null);}} catch (InterruptedIOException e) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CONNECTION_NOW, e);} catch (HeadersTooLargeException e) {log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), e);// The response should not have been committed but check it// anyway to be safeif (response.isCommitted()) {setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_NOW, e);} else {response.reset();response.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, e);response.setHeader("Connection", "close"); // TODO: Remove }} catch (Throwable t) {ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);log.error(sm.getString("http11processor.request.process"), t);// 500 - Internal Server Errorresponse.setStatus(500);setErrorState(ErrorState.CLOSE_CLEAN, t);getAdapter().log(request, response, 0);}}// Finish the handling of the request rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDINPUT);if (!isAsync()) {// If this is an async request then the request ends when it has// been completed. The AsyncContext is responsible for calling// endRequest() in that case. endRequest();}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDOUTPUT);// If there was an error, make sure the request is counted as// and error, and update the statistics counterif (getErrorState().isError()) {response.setStatus(500);}if (!isAsync() || getErrorState().isError()) {request.updateCounters();if (getErrorState().isIoAllowed()) {inputBuffer.nextRequest();outputBuffer.nextRequest();}}if (!disableUploadTimeout) {int soTimeout = endpoint.getConnectionTimeout();if(soTimeout > 0) {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(soTimeout);} else {socketWrapper.setReadTimeout(0);}}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_KEEPALIVE);sendfileState = processSendfile(socketWrapper);}rp.setStage(org.apache.coyote.Constants.STAGE_ENDED);if (getErrorState().isError() || endpoint.isPaused()) {return SocketState.CLOSED;} else if (isAsync()) {return SocketState.LONG;} else if (isUpgrade()) {return SocketState.UPGRADING;} else {if (sendfileState == SendfileState.PENDING) {return SocketState.SENDFILE;} else {if (openSocket) {if (readComplete) {return SocketState.OPEN;} else {return SocketState.LONG;}} else {return SocketState.CLOSED;}}}}
从代码清单8可以看出,最后的请求处理交给了CoyoteAdapter,CoyoteAdapter的service方法(见代码清单9)用于真正处理请求。
代码清单9
@Overridepublic void service(org.apache.coyote.Request req, org.apache.coyote.Response res)throws Exception {Request request = (Request) req.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);Response response = (Response) res.getNote(ADAPTER_NOTES);if (request == null) {// Create objectsrequest = connector.createRequest();request.setCoyoteRequest(req);response = connector.createResponse();response.setCoyoteResponse(res);// Link objects request.setResponse(response);response.setRequest(request);// Set as notes req.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, request);res.setNote(ADAPTER_NOTES, response);// Set query string encoding req.getParameters().setQueryStringCharset(connector.getURICharset());}if (connector.getXpoweredBy()) {response.addHeader("X-Powered-By", POWERED_BY);}boolean async = false;boolean postParseSuccess = false;req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(THREAD_NAME.get());try {// Parse and set Catalina and configuration specific// request parameterspostParseSuccess = postParseRequest(req, request, res, response);if (postParseSuccess) {//check valves if we support async request.setAsyncSupported(connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().isAsyncSupported());// Calling the container connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);}if (request.isAsync()) {async = true;ReadListener readListener = req.getReadListener();if (readListener != null && request.isFinished()) {// Possible the all data may have been read during service()// method so this needs to be checked hereClassLoader oldCL = null;try {oldCL = request.getContext().bind(false, null);if (req.sendAllDataReadEvent()) {req.getReadListener().onAllDataRead();}} finally {request.getContext().unbind(false, oldCL);}}Throwable throwable =(Throwable) request.getAttribute(RequestDispatcher.ERROR_EXCEPTION);// If an async request was started, is not going to end once// this container thread finishes and an error occurred, trigger// the async error processif (!request.isAsyncCompleting() && throwable != null) {request.getAsyncContextInternal().setErrorState(throwable, true);}} else {request.finishRequest();response.finishResponse();}} catch (IOException e) {// Ignore} finally {AtomicBoolean error = new AtomicBoolean(false);res.action(ActionCode.IS_ERROR, error);if (request.isAsyncCompleting() && error.get()) {// Connection will be forcibly closed which will prevent// completion happening at the usual point. Need to trigger// call to onComplete() here.res.action(ActionCode.ASYNC_POST_PROCESS, null);async = false;}// Access logif (!async && postParseSuccess) {// Log only if processing was invoked.// If postParseRequest() failed, it has already logged it.Context context = request.getContext();// If the context is null, it is likely that the endpoint was// shutdown, this connection closed and the request recycled in// a different thread. That thread will have updated the access// log so it is OK not to update the access log here in that// case.if (context != null) {context.logAccess(request, response,System.currentTimeMillis() - req.getStartTime(), false);}}req.getRequestProcessor().setWorkerThreadName(null);// Recycle the wrapper request and responseif (!async) {request.recycle();response.recycle();}}}
从代码清单9可以看出,CoyoteAdapter的service方法的执行步骤如下:
- 创建Request与Response对象并且关联起来;
- 调用postParseRequest方法(见代码清单10)对请求进行解析;
-
将真正的请求处理交给Engine的Pipeline去处理,代码:connector.getService().getContainer().getPipeline().getFirst().invoke(request, response);
代码清单10
protected boolean postParseRequest(org.apache.coyote.Request req, Request request,org.apache.coyote.Response res, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {// If the processor has set the scheme (AJP does this, HTTP does this if// SSL is enabled) use this to set the secure flag as well. If the// processor hasn't set it, use the settings from the connectorif (req.scheme().isNull()) {// Use connector scheme and secure configuration, (defaults to// "http" and false respectively) req.scheme().setString(connector.getScheme());request.setSecure(connector.getSecure());} else {// Use processor specified scheme to determine secure staterequest.setSecure(req.scheme().equals("https"));}// At this point the Host header has been processed.// Override if the proxyPort/proxyHost are setString proxyName = connector.getProxyName();int proxyPort = connector.getProxyPort();if (proxyPort != 0) {req.setServerPort(proxyPort);} else if (req.getServerPort() == -1) {// Not explicitly set. Use default ports based on the schemeif (req.scheme().equals("https")) {req.setServerPort(443);} else {req.setServerPort(80);}}if (proxyName != null) {req.serverName().setString(proxyName);}MessageBytes undecodedURI = req.requestURI();// Check for ping OPTIONS * requestif (undecodedURI.equals("*")) {if (req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("OPTIONS")) {StringBuilder allow = new StringBuilder();allow.append("GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE");// Trace if allowedif (connector.getAllowTrace()) {allow.append(", TRACE");}// Always allow optionsallow.append(", OPTIONS");res.setHeader("Allow", allow.toString());} else {res.setStatus(404);res.setMessage("Not found");}connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}MessageBytes decodedURI = req.decodedURI();if (undecodedURI.getType() == MessageBytes.T_BYTES) {// Copy the raw URI to the decodedURI decodedURI.duplicate(undecodedURI);// Parse the path parameters. This will:// - strip out the path parameters// - convert the decodedURI to bytes parsePathParameters(req, request);// URI decoding// %xx decoding of the URLtry {req.getURLDecoder().convert(decodedURI, false);} catch (IOException ioe) {res.setStatus(400);res.setMessage("Invalid URI: " + ioe.getMessage());connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}// Normalizationif (!normalize(req.decodedURI())) {res.setStatus(400);res.setMessage("Invalid URI");connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}// Character decoding convertURI(decodedURI, request);// Check that the URI is still normalizedif (!checkNormalize(req.decodedURI())) {res.setStatus(400);res.setMessage("Invalid URI character encoding");connector.getService().getContainer().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}} else {/* The URI is chars or String, and has been sent using an in-memory* protocol handler. The following assumptions are made:* - req.requestURI() has been set to the 'original' non-decoded,* non-normalized URI* - req.decodedURI() has been set to the decoded, normalized form* of req.requestURI()*/decodedURI.toChars();// Remove all path parameters; any needed path parameter should be set// using the request object rather than passing it in the URLCharChunk uriCC = decodedURI.getCharChunk();int semicolon = uriCC.indexOf(';');if (semicolon > 0) {decodedURI.setChars(uriCC.getBuffer(), uriCC.getStart(), semicolon);}}// Request mapping. MessageBytes serverName;if (connector.getUseIPVHosts()) {serverName = req.localName();if (serverName.isNull()) {// well, they did ask for itres.action(ActionCode.REQ_LOCAL_NAME_ATTRIBUTE, null);}} else {serverName = req.serverName();}// Version for the second mapping loop and// Context that we expect to get for that versionString version = null;Context versionContext = null;boolean mapRequired = true;while (mapRequired) {// This will map the the latest version by default connector.getService().getMapper().map(serverName, decodedURI,version, request.getMappingData());// If there is no context at this point, it is likely no ROOT context// has been deployedif (request.getContext() == null) {res.setStatus(404);res.setMessage("Not found");// No context, so use hostHost host = request.getHost();// Make sure there is a host (might not be during shutdown)if (host != null) {host.logAccess(request, response, 0, true);}return false;}// Now we have the context, we can parse the session ID from the URL// (if any). Need to do this before we redirect in case we need to// include the session id in the redirect String sessionID;if (request.getServletContext().getEffectiveSessionTrackingModes().contains(SessionTrackingMode.URL)) {// Get the session ID if there was onesessionID = request.getPathParameter(SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(request.getContext()));if (sessionID != null) {request.setRequestedSessionId(sessionID);request.setRequestedSessionURL(true);}}// Look for session ID in cookies and SSL session parseSessionCookiesId(request);parseSessionSslId(request);sessionID = request.getRequestedSessionId();mapRequired = false;if (version != null && request.getContext() == versionContext) {// We got the version that we asked for. That is it.} else {version = null;versionContext = null;Context[] contexts = request.getMappingData().contexts;// Single contextVersion means no need to remap// No session ID means no possibility of remapif (contexts != null && sessionID != null) {// Find the context associated with the sessionfor (int i = (contexts.length); i > 0; i--) {Context ctxt = contexts[i - 1];if (ctxt.getManager().findSession(sessionID) != null) {// We found a context. Is it the one that has// already been mapped?if (!ctxt.equals(request.getMappingData().context)) {// Set version so second time through mapping// the correct context is foundversion = ctxt.getWebappVersion();versionContext = ctxt;// Reset mapping request.getMappingData().recycle();mapRequired = true;// Recycle cookies and session info in case the// correct context is configured with different// settings request.recycleSessionInfo();request.recycleCookieInfo(true);}break;}}}}if (!mapRequired && request.getContext().getPaused()) {// Found a matching context but it is paused. Mapping data will// be wrong since some Wrappers may not be registered at this// point.try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// Should never happen }// Reset mapping request.getMappingData().recycle();mapRequired = true;}}// Possible redirectMessageBytes redirectPathMB = request.getMappingData().redirectPath;if (!redirectPathMB.isNull()) {String redirectPath = URLEncoder.DEFAULT.encode(redirectPathMB.toString(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);String query = request.getQueryString();if (request.isRequestedSessionIdFromURL()) {// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it// shouldn't matterredirectPath = redirectPath + ";" +SessionConfig.getSessionUriParamName(request.getContext()) +"=" + request.getRequestedSessionId();}if (query != null) {// This is not optimal, but as this is not very common, it// shouldn't matterredirectPath = redirectPath + "?" + query;}response.sendRedirect(redirectPath);request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}// Filter trace methodif (!connector.getAllowTrace()&& req.method().equalsIgnoreCase("TRACE")) {Wrapper wrapper = request.getWrapper();String header = null;if (wrapper != null) {String[] methods = wrapper.getServletMethods();if (methods != null) {for (int i=0; i<methods.length; i++) {if ("TRACE".equals(methods[i])) {continue;}if (header == null) {header = methods[i];} else {header += ", " + methods[i];}}}}res.setStatus(405);res.addHeader("Allow", header);res.setMessage("TRACE method is not allowed");request.getContext().logAccess(request, response, 0, true);return false;}doConnectorAuthenticationAuthorization(req, request);return true;}
从代码清单10可以看出,postParseRequest方法的执行步骤如下:
- 解析请求url中的参数;
- URI decoding的转换;
- 调用normalize方法判断请求路径中是否存在"\", "//", "/./"和"/../",如果存在则处理结束;
- 调用convertURI方法将字节转换为字符;
- 调用checkNormalize方法判断uri是否存在"\", "//", "/./"和"/../",如果存在则处理结束;
- 调用Connector的getMapper方法获取Mapper(已在《TOMCAT源码分析——请求原理分析(上)》一文中介绍),然后调用Mapper的map方法(见代码清单11)对host和context进行匹配(比如http://localhost:8080/manager/status会匹配host:localhost,context:/manager),其实质是调用internalMap方法;
- 使用ApplicationSessionCookieConfig.getSessionUriParamName获取sessionid的key,然后获取sessionid;
- 调用parseSessionCookiesId和parseSessionSslId方法查找cookie或者SSL中的sessionid。
代码清单11
/*** Map the specified host name and URI, mutating the given mapping data.** @param host Virtual host name* @param uri URI* @param version The version, if any, included in the request to be mapped* @param mappingData This structure will contain the result of the mapping* operation* @throws IOException if the buffers are too small to hold the results of* the mapping.*/public void map(MessageBytes host, MessageBytes uri, String version,MappingData mappingData) throws IOException {if (host.isNull()) {host.getCharChunk().append(defaultHostName);}host.toChars();uri.toChars();internalMap(host.getCharChunk(), uri.getCharChunk(), version,mappingData);}
CoyoteAdapter的service方法最后会将请求交给Engine的Pipeline去处理,我将在《Tomcat源码分析——请求原理分析(下)》一文中具体讲解。
如需转载,请标明本文作者及出处——作者:jiaan.gja,本文原创首发:博客园,原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/jiaan-geng/p/4894832.html



