本文主要是介绍Tsinghua OJ:灯塔(LightHouse),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
灯塔(LightHouse)
Description
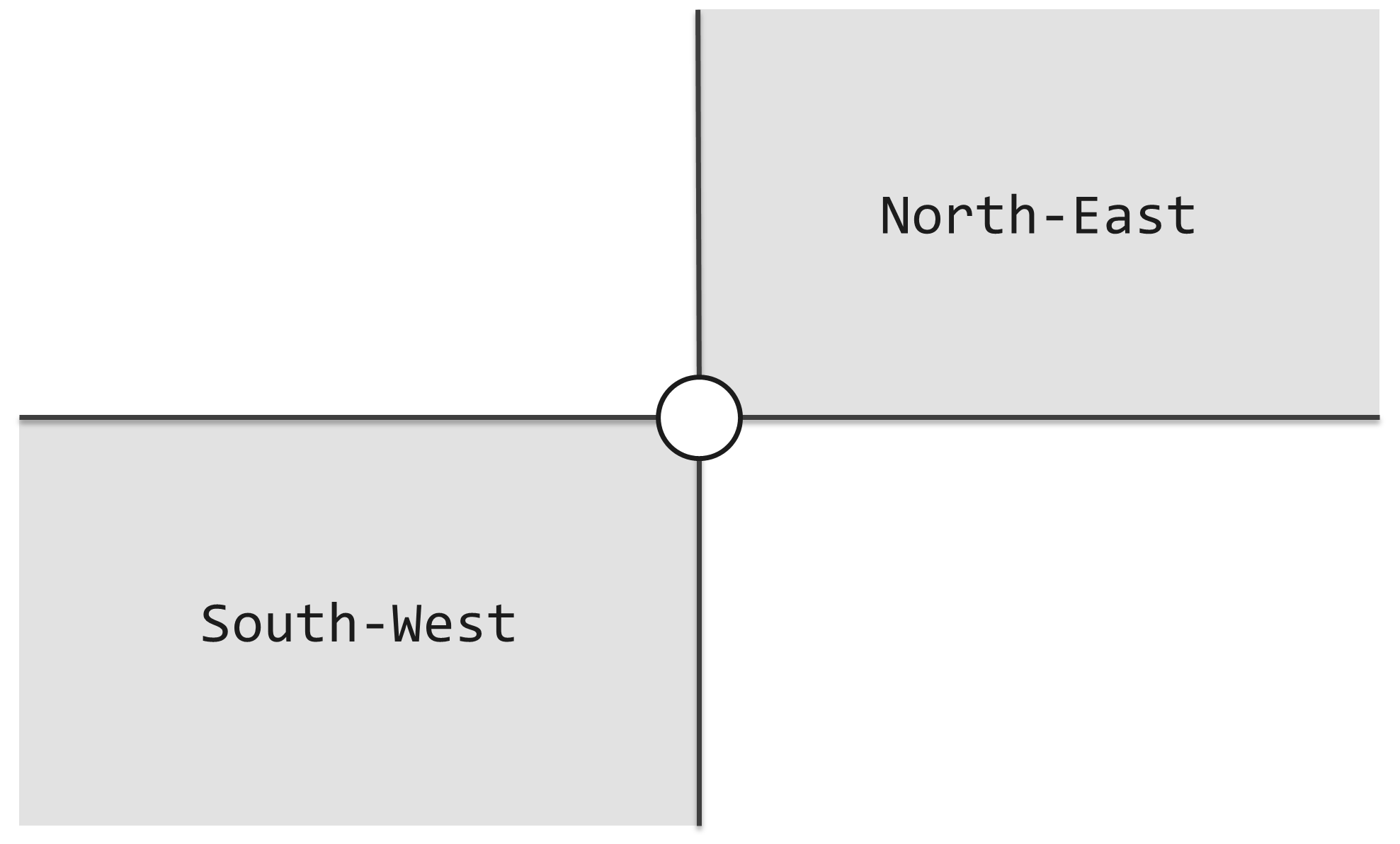
As shown in the following figure, If another lighthouse is in gray area, they can beacon each other.
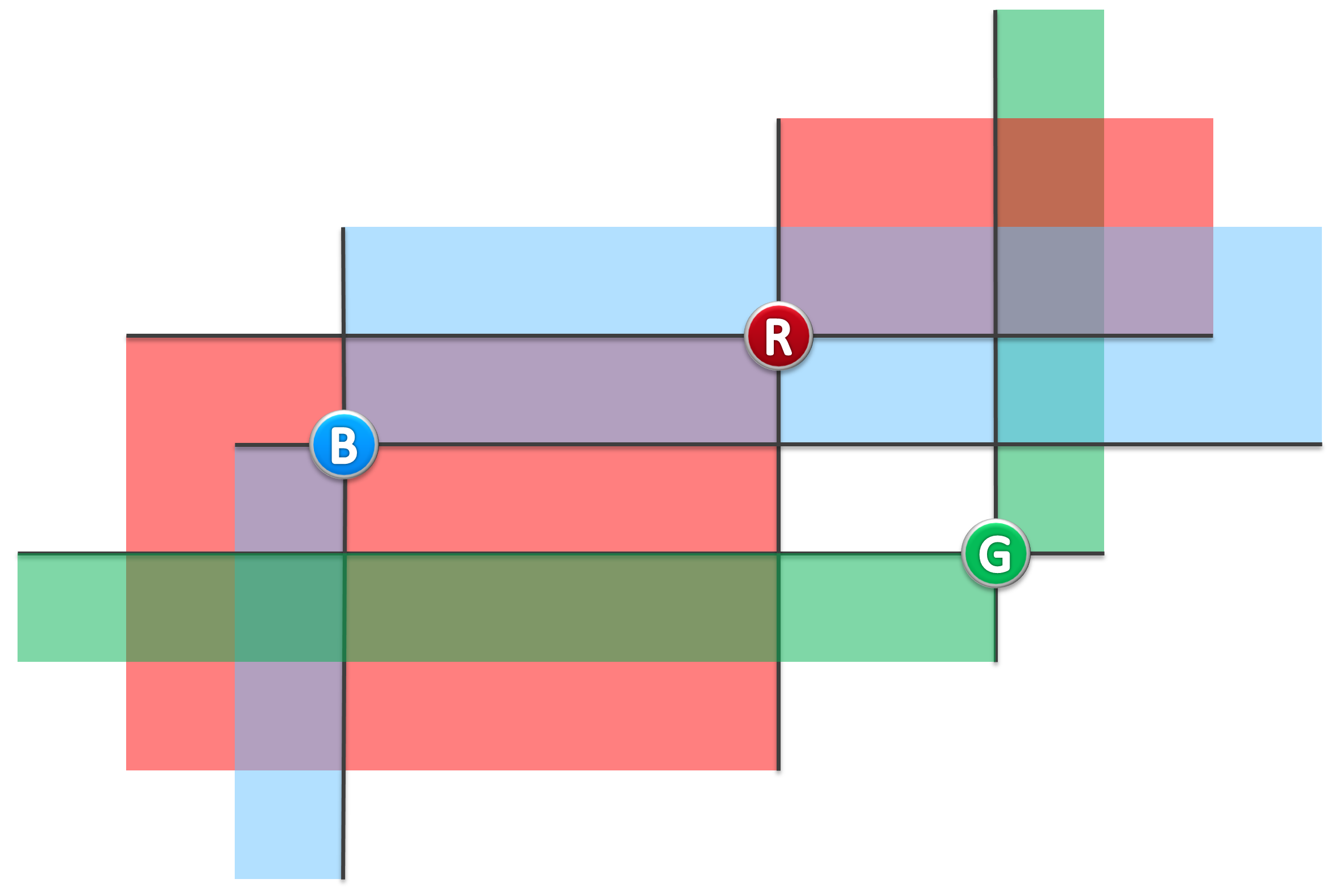
For example, in following figure, (B, R) is a pair of lighthouse which can beacon each other, while (B, G), (R, G) are NOT.
Input
1st line: N
2nd ~ (N + 1)th line: each line is X Y, means a lighthouse is on the point (X, Y).
Output
How many pairs of lighthourses can beacon each other
( For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same )
Example
Input
3
2 2
4 3
5 1
Output
1
Restrictions
For 90% test cases: 1 <= n <= 3 * 105
For 95% test cases: 1 <= n <= 106
For all test cases: 1 <= n <= 4 * 106
For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same.
1 <= x, y <= 10^8
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
The range of int is usually [-231, 231 - 1], it may be too small.
描述
海上有许多灯塔,为过路船只照明。

(图一)
如图一所示,每个灯塔都配有一盏探照灯,照亮其东北、西南两个对顶的直角区域。探照灯的功率之大,足以覆盖任何距离。灯塔本身是如此之小,可以假定它们不会彼此遮挡。

(图二)
若灯塔A、B均在对方的照亮范围内,则称它们能够照亮彼此。比如在图二的实例中,蓝、红灯塔可照亮彼此,蓝、绿灯塔则不是,红、绿灯塔也不是。
现在,对于任何一组给定的灯塔,请计算出其中有多少对灯塔能够照亮彼此。
输入
共n+1行。
第1行为1个整数n,表示灯塔的总数。
第2到n+1行每行包含2个整数x, y,分别表示各灯塔的横、纵坐标。
输出
1个整数,表示可照亮彼此的灯塔对的数量。
样例
见英文题面
限制
对于90%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 3×105
对于95%的测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 106
全部测例:1 ≤ n ≤ 4×106
灯塔的坐标x, y是整数,且不同灯塔的x, y坐标均互异
1 ≤ x, y ≤ 10^8
时间:2 sec
内存:256 MB
提示
注意机器中整型变量的范围,C/C++中的int类型通常被编译成32位整数,其范围为[-231, 231 - 1],不一定足够容纳本题的输出。
解题思路:
由照亮规则可以想到逆(顺)序规则(逆序)。
1、设B,R,G坐标分别为(x1,y1),(x2,y2),(x3,y3)。BR可以互相照亮,BG,RG互相不可照亮。
2 、BR构成顺序,BG,RG构成逆序。
3、归并排序是计算逆(顺)序的有效方法(可参考:逆序对),时间复杂度为O(nlogn)。
代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
// #include <stdlib.h>
/*
const int SZ = 1 << 20; //提升IO buff
struct fastio{
char inbuf[SZ];
char outbuf[SZ];
fastio(){
setvbuf(stdin, inbuf, _IOFBF, SZ);
setvbuf(stdout, outbuf, _IOFBF, SZ);
}
}io;
*/#define MAXN 4000010
struct Point // 坐标结构体
{long x;long y;
}points[MAXN];long count;
long src[MAXN];
long des[MAXN];// 快排,对x排序
void qsort(Point ps[], int l, int r)
{if (l < r){int i = l, j = r;Point tmp;tmp.x = ps[i].x;tmp.y = ps[i].y;int key = ps[i].x;while (i < j){while (i < j && key < ps[j].x) --j; ps[i].x = ps[j].x;ps[i].y = ps[j].y;while (i < j && ps[i].x < key) ++i;ps[j].x = ps[i].x;ps[j].y = ps[i].y;}ps[i].x = tmp.x;ps[i].y = tmp.y;qsort(ps, l, i - 1);qsort(ps, i + 1, r);}
}
// 归并,对y进行“顺序对”统计
void merge(long *src, long *des, int start, int mid, int end)
{int i = start, j = mid + 1;int k = start;while (i != mid + 1 && j != end + 1){if (src[i] < src[j]){des[k++] = src[i++];count += end - j + 1; // 统计“顺序”个数}else des[k++] = src[j++];}while (i != mid + 1) des[k++] = src[i++];while (j != end + 1) des[k++] = src[j++];for (i = start; i != end + 1; ++i)src[i] = des[i];
}void mergeSort(long *src, long *des, int start, int end)
{int mid;if (start < end){mid = (start + end) >> 1;mergeSort(src, des, start, mid);mergeSort(src, des, mid + 1, end);merge(src, des, start, mid, end);}
}
/*
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>// 定义排序规则,这里为从小到大return (*(Point *)a).x > (*(Point *)b).x ? 1 : -1;
}
*/
int main()
{int n;int i;scanf("%d", &n);for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)scanf("%ld %ld", &points[i].x, &points[i].y);// qsort(points, n, sizeof(points[0]), cmp); // 用系统的快排,最后一个实例不能通过qsort(points, 0, n - 1); // 用自己写的快排,最后一个实例可通过for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)src[i] = points[i].y;count = 0;mergeSort(src, des, 0, n - 1);printf("%ld\n", count);return 0;
}这篇关于Tsinghua OJ:灯塔(LightHouse)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!