本文主要是介绍Android源码解析(二十八)--电源开关机按键事件流程,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
转载请标明出处:一片枫叶的专栏
前面我们讲解了系统截屏按键处理流程,HOME按键处理流程,今天再来讲解一下电源开关机按键事件流程,当然这也是系统按键处理流程方面的最后一篇博客了。
和截屏按键、HOME按键的处理流程类似,电源按键由于也是系统级别的按键,所以对其的事件处理逻辑是和截屏按键、HOME按键类似,不在某一个App中,而是在PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandledKey方法中。所以和前面两篇类似,这里我们也是从PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandledKey方法开始我们今天电源开关机按键的事件流程分析。
下面首先看一下dispatchUnhandledKey方法的实现逻辑:
public KeyEvent dispatchUnhandledKey(WindowState win, KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {...KeyEvent fallbackEvent = null;if ((event.getFlags() & KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK) == 0) {final KeyCharacterMap kcm = event.getKeyCharacterMap();final int keyCode = event.getKeyCode();final int metaState = event.getMetaState();final boolean initialDown = event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN&& event.getRepeatCount() == 0;// Check for fallback actions specified by the key character map.final FallbackAction fallbackAction;if (initialDown) {fallbackAction = kcm.getFallbackAction(keyCode, metaState);} else {fallbackAction = mFallbackActions.get(keyCode);}if (fallbackAction != null) {if (DEBUG_INPUT) {Slog.d(TAG, "Fallback: keyCode=" + fallbackAction.keyCode+ " metaState=" + Integer.toHexString(fallbackAction.metaState));}final int flags = event.getFlags() | KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK;fallbackEvent = KeyEvent.obtain(event.getDownTime(), event.getEventTime(),event.getAction(), fallbackAction.keyCode,event.getRepeatCount(), fallbackAction.metaState,event.getDeviceId(), event.getScanCode(),flags, event.getSource(), null);if (!interceptFallback(win, fallbackEvent, policyFlags)) {fallbackEvent.recycle();fallbackEvent = null;}if (initialDown) {mFallbackActions.put(keyCode, fallbackAction);} else if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_UP) {mFallbackActions.remove(keyCode);fallbackAction.recycle();}}}...return fallbackEvent;}通过前面两篇文章的分析
( android源码解析(二十六)–>截屏事件流程
android源码解析(二十七)–>HOME事件流程)
我们知道关于系统按键的处理逻辑被下放到了interceptFallback方法中,所以我们继续看一下interceptFallback方法的实现逻辑。
private boolean interceptFallback(WindowState win, KeyEvent fallbackEvent, int policyFlags) {int actions = interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(fallbackEvent, policyFlags);if ((actions & ACTION_PASS_TO_USER) != 0) {long delayMillis = interceptKeyBeforeDispatching(win, fallbackEvent, policyFlags);if (delayMillis == 0) {return true;}}return false;}通过分析interceptFallback方法的源码,我们知道关于电源按键的处理逻辑在interceptKeyBeforeQueueing方法中,所以我们需要继续看一下interceptKeyBeforeQueueing方法中关于电源按键的处理逻辑。
public int interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {...case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_POWER: {result &= ~ACTION_PASS_TO_USER;isWakeKey = false; // wake-up will be handled separatelyif (down) {interceptPowerKeyDown(event, interactive);} else {interceptPowerKeyUp(event, interactive, canceled);}break;}...return result;}这里我们重点看一下电源按键的处理事件,可以发现当电源按键按下的时候我们调用了interceptPowerKeyDown方法,可以看出,这个方法就是处理电源事件的了,既然如此,我们继续看一下interceptPowerKeyDown方法的执行逻辑。
private void interceptPowerKeyDown(KeyEvent event, boolean interactive) {...// Latch power key state to detect screenshot chord.if (interactive && !mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTriggered&& (event.getFlags() & KeyEvent.FLAG_FALLBACK) == 0) {mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTriggered = true;mScreenshotChordPowerKeyTime = event.getDownTime();interceptScreenshotChord();}// Stop ringing or end call if configured to do so when power is pressed.TelecomManager telecomManager = getTelecommService();boolean hungUp = false;if (telecomManager != null) {if (telecomManager.isRinging()) {// Pressing Power while there's a ringing incoming// call should silence the ringer.telecomManager.silenceRinger();} else if ((mIncallPowerBehavior& Settings.Secure.INCALL_POWER_BUTTON_BEHAVIOR_HANGUP) != 0&& telecomManager.isInCall() && interactive) {// Otherwise, if "Power button ends call" is enabled,// the Power button will hang up any current active call.hungUp = telecomManager.endCall();}}// If the power key has still not yet been handled, then detect short// press, long press, or multi press and decide what to do.mPowerKeyHandled = hungUp || mScreenshotChordVolumeDownKeyTriggered|| mScreenshotChordVolumeUpKeyTriggered;if (!mPowerKeyHandled) {if (interactive) {// When interactive, we're already awake.// Wait for a long press or for the button to be released to decide what to do.if (hasLongPressOnPowerBehavior()) {Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS);msg.setAsynchronous(true);mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,ViewConfiguration.get(mContext).getDeviceGlobalActionKeyTimeout());}} else {wakeUpFromPowerKey(event.getDownTime());if (mSupportLongPressPowerWhenNonInteractive && hasLongPressOnPowerBehavior()) {Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS);msg.setAsynchronous(true);mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg,ViewConfiguration.get(mContext).getDeviceGlobalActionKeyTimeout());mBeganFromNonInteractive = true;} else {final int maxCount = getMaxMultiPressPowerCount();if (maxCount <= 1) {mPowerKeyHandled = true;} else {mBeganFromNonInteractive = true;}}}}}这里我们重点看一下if(interactive)分支,在这里我们发送一个一个异步消息,并且msg的what为MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS,即长按电源事件的异步消息,所以我们看一下mHandler的handleMessage方法对该what消息的处理逻辑。
case MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS:powerLongPress();break;我们可以发现在mHandler的handleMessage方法中当msg的what为MSG_POWER_LONG_PRESS时我们调用了powerLongPress方法,这个方法应该就是处理电源按键长按的逻辑,下面我们来看一下powerLongPress方法的实现。
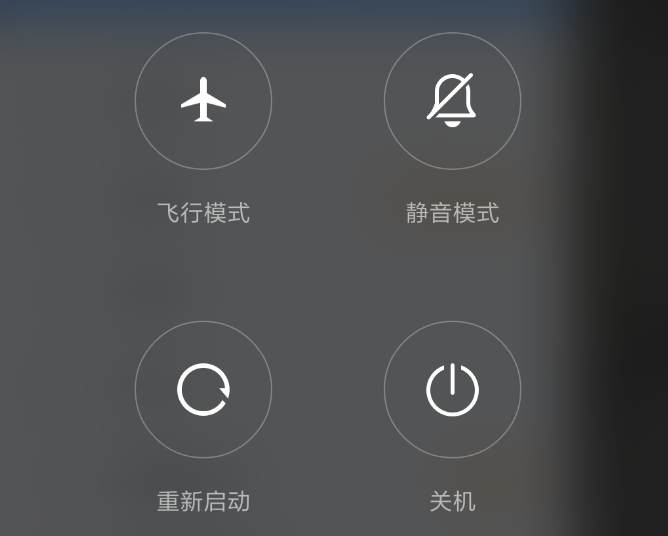
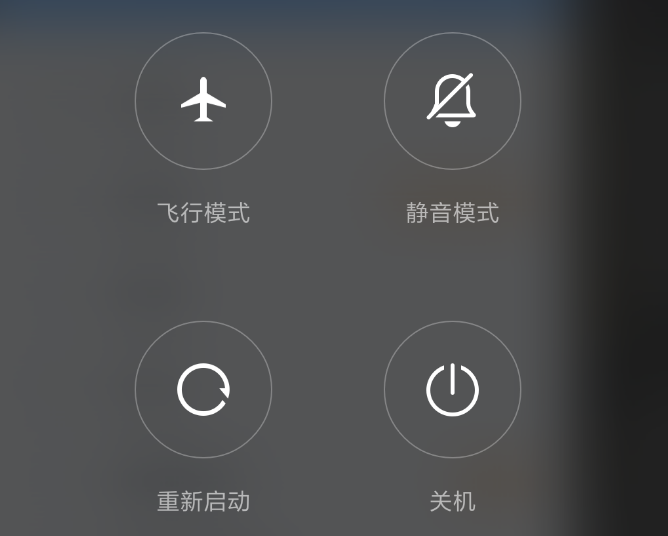
private void powerLongPress() {final int behavior = getResolvedLongPressOnPowerBehavior();switch (behavior) {case LONG_PRESS_POWER_NOTHING:break;case LONG_PRESS_POWER_GLOBAL_ACTIONS:mPowerKeyHandled = true;if (!performHapticFeedbackLw(null, HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS, false)) {performAuditoryFeedbackForAccessibilityIfNeed();}showGlobalActionsInternal();break;case LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF:case LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF_NO_CONFIRM:mPowerKeyHandled = true;performHapticFeedbackLw(null, HapticFeedbackConstants.LONG_PRESS, false);sendCloseSystemWindows(SYSTEM_DIALOG_REASON_GLOBAL_ACTIONS);mWindowManagerFuncs.shutdown(behavior == LONG_PRESS_POWER_SHUT_OFF);break;}}可以发现这里有四个switch分之,其中第一个什么都不做直接break掉,第二个case则需要弹出选择操作界面,比如:飞行模式,开关机,静音模式,重新启动等,这里可以参看一下小米手机的关机界面:
然后第三第四个case分之则是直接调用关机方法,这里我们先看第二个case,看看系统是如何显示出关机操作界面的。那我们看一下showGlobalActionsInternal方法的实现逻辑。
void showGlobalActionsInternal() {sendCloseSystemWindows(SYSTEM_DIALOG_REASON_GLOBAL_ACTIONS);if (mGlobalActions == null) {mGlobalActions = new GlobalActions(mContext, mWindowManagerFuncs);}final boolean keyguardShowing = isKeyguardShowingAndNotOccluded();mGlobalActions.showDialog(keyguardShowing, isDeviceProvisioned());if (keyguardShowing) {// since it took two seconds of long press to bring this up,// poke the wake lock so they have some time to see the dialog.mPowerManager.userActivity(SystemClock.uptimeMillis(), false);}}可以发现我们首先调用了sendCloseSystemWindows方法,前面我们分析HOME按键流程的时候(android源码解析(二十七)–>HOME事件流程)知道该方法用于关机系统弹窗,比如输入法,壁纸等。然后我们创建了一个GlobalActions对象,并调用了其showDialog方法,通过分析源码,我们发现该方法就是用于显示长按电源按键弹出操作界面的,我们首先看一下GlobalActions的构造方法:
public GlobalActions(Context context, WindowManagerFuncs windowManagerFuncs) {mContext = context;mWindowManagerFuncs = windowManagerFuncs;mAudioManager = (AudioManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.AUDIO_SERVICE);mDreamManager = IDreamManager.Stub.asInterface(ServiceManager.getService(DreamService.DREAM_SERVICE));// receive broadcastsIntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_CLOSE_SYSTEM_DIALOGS);filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SCREEN_OFF);filter.addAction(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_EMERGENCY_CALLBACK_MODE_CHANGED);context.registerReceiver(mBroadcastReceiver, filter);ConnectivityManager cm = (ConnectivityManager)context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);mHasTelephony = cm.isNetworkSupported(ConnectivityManager.TYPE_MOBILE);// get notified of phone state changesTelephonyManager telephonyManager =(TelephonyManager) context.getSystemService(Context.TELEPHONY_SERVICE);telephonyManager.listen(mPhoneStateListener, PhoneStateListener.LISTEN_SERVICE_STATE);mContext.getContentResolver().registerContentObserver(Settings.Global.getUriFor(Settings.Global.AIRPLANE_MODE_ON), true,mAirplaneModeObserver);Vibrator vibrator = (Vibrator) mContext.getSystemService(Context.VIBRATOR_SERVICE);mHasVibrator = vibrator != null && vibrator.hasVibrator();mShowSilentToggle = SHOW_SILENT_TOGGLE && !mContext.getResources().getBoolean(com.android.internal.R.bool.config_useFixedVolume);}可以看到在GlobalActions对象的构造方法中我们主要用于初始化其成员变量,由于我们的电源长按操作界面是一个全局页面,所以这里自定义了一个Window对象,下面我们看一下GlobalActions的showDialog方法。
public void showDialog(boolean keyguardShowing, boolean isDeviceProvisioned) {mKeyguardShowing = keyguardShowing;mDeviceProvisioned = isDeviceProvisioned;if (mDialog != null) {mDialog.dismiss();mDialog = null;// Show delayed, so that the dismiss of the previous dialog completesmHandler.sendEmptyMessage(MESSAGE_SHOW);} else {handleShow();}}可以看到在showDialog方法中我们首先判断mDialog是否为空,若为空则发送msg的what为MESSAGE_SHOW的异步消息,否则调用handleShow方法,而这里的mDialog是一个类型为GlobalActionsDialog的变量,由于我们的mDialog为空,所以下面我们看一下handleShow方法。
private void handleShow() {awakenIfNecessary();mDialog = createDialog();prepareDialog();// If we only have 1 item and it's a simple press action, just do this action.if (mAdapter.getCount() == 1&& mAdapter.getItem(0) instanceof SinglePressAction&& !(mAdapter.getItem(0) instanceof LongPressAction)) {((SinglePressAction) mAdapter.getItem(0)).onPress();} else {WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs = mDialog.getWindow().getAttributes();attrs.setTitle("GlobalActions");mDialog.getWindow().setAttributes(attrs);mDialog.show();mDialog.getWindow().getDecorView().setSystemUiVisibility(View.STATUS_BAR_DISABLE_EXPAND);}在方法体中我们调用了createDialog方法,创建了GlobalActionsDialog类型的mDialog,这里我们看一下createDialog的实现方法。
private GlobalActionsDialog createDialog() {...mAirplaneModeOn = new ToggleAction(R.drawable.ic_lock_airplane_mode,R.drawable.ic_lock_airplane_mode_off,R.string.global_actions_toggle_airplane_mode,R.string.global_actions_airplane_mode_on_status,R.string.global_actions_airplane_mode_off_status) {void onToggle(boolean on) {if (mHasTelephony && Boolean.parseBoolean(SystemProperties.get(TelephonyProperties.PROPERTY_INECM_MODE))) {mIsWaitingForEcmExit = true;// Launch ECM exit dialogIntent ecmDialogIntent =new Intent(TelephonyIntents.ACTION_SHOW_NOTICE_ECM_BLOCK_OTHERS, null);ecmDialogIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);mContext.startActivity(ecmDialogIntent);} else {changeAirplaneModeSystemSetting(on);}}@Overrideprotected void changeStateFromPress(boolean buttonOn) {if (!mHasTelephony) return;// In ECM mode airplane state cannot be changedif (!(Boolean.parseBoolean(SystemProperties.get(TelephonyProperties.PROPERTY_INECM_MODE)))) {mState = buttonOn ? State.TurningOn : State.TurningOff;mAirplaneState = mState;}}public boolean showDuringKeyguard() {return true;}public boolean showBeforeProvisioning() {return false;}};onAirplaneModeChanged();mItems = new ArrayList<Action>();String[] defaultActions = mContext.getResources().getStringArray(com.android.internal.R.array.config_globalActionsList);ArraySet<String> addedKeys = new ArraySet<String>();for (int i = 0; i < defaultActions.length; i++) {String actionKey = defaultActions[i];if (addedKeys.contains(actionKey)) {// If we already have added this, don't add it again.continue;}if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_POWER.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(new PowerAction());} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_AIRPLANE.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(mAirplaneModeOn);} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_BUGREPORT.equals(actionKey)) {if (Settings.Global.getInt(mContext.getContentResolver(),Settings.Global.BUGREPORT_IN_POWER_MENU, 0) != 0 && isCurrentUserOwner()) {mItems.add(getBugReportAction());}} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_SILENT.equals(actionKey)) {if (mShowSilentToggle) {mItems.add(mSilentModeAction);}} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_USERS.equals(actionKey)) {if (SystemProperties.getBoolean("fw.power_user_switcher", false)) {addUsersToMenu(mItems);}} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_SETTINGS.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(getSettingsAction());} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_LOCKDOWN.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(getLockdownAction());} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_VOICEASSIST.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(getVoiceAssistAction());} else if (GLOBAL_ACTION_KEY_ASSIST.equals(actionKey)) {mItems.add(getAssistAction());} else {Log.e(TAG, "Invalid global action key " + actionKey);}// Add here so we don't add more than one.addedKeys.add(actionKey);}mAdapter = new MyAdapter();AlertParams params = new AlertParams(mContext);params.mAdapter = mAdapter;params.mOnClickListener = this;params.mForceInverseBackground = true;GlobalActionsDialog dialog = new GlobalActionsDialog(mContext, params);dialog.setCanceledOnTouchOutside(false); // Handled by the custom class.dialog.getListView().setItemsCanFocus(true);dialog.getListView().setLongClickable(true);dialog.getListView().setOnItemLongClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemLongClickListener() {@Overridepublic boolean onItemLongClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position,long id) {final Action action = mAdapter.getItem(position);if (action instanceof LongPressAction) {return ((LongPressAction) action).onLongPress();}return false;}});dialog.getWindow().setType(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG);dialog.setOnDismissListener(this);return dialog;}方法体的内容比较长,我们看重点的内容,首先我们通过调用mContext.getResources().getStringArray(com.android.internal.R.array.config_globalActionsList)获得操作列表,这里可能包含:飞行模式、开关机、静音模式、重启等等,然后我们轮训操作列表,并添加相应的Action最后我们将这个操作列表保存到Dialog的adapter中并返回该dialog,然后我们回到我们刚刚的handleShow方法,在得到返回的dialog之后我们调用了dialog的show方法,这样我们就显示出了电源长按操作界面,比如小米的界面:
好吧,继续我们的分析,当我们长按电源按键弹出操作弹窗之后,这时候点击关机是怎么样的流程呢?我们发现在createDialog方法中关机操作adapter的item,我们添加了:
mItems.add(new PowerAction());这样不难发现我们对关机按钮的操作封装在了PowerAction中,所以我们继续看一下PowerAction的实现。
private final class PowerAction extends SinglePressAction implements LongPressAction {private PowerAction() {super(com.android.internal.R.drawable.ic_lock_power_off,R.string.global_action_power_off);}@Overridepublic boolean onLongPress() {UserManager um = (UserManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.USER_SERVICE);if (!um.hasUserRestriction(UserManager.DISALLOW_SAFE_BOOT)) {mWindowManagerFuncs.rebootSafeMode(true);return true;}return false;}@Overridepublic boolean showDuringKeyguard() {return true;}@Overridepublic boolean showBeforeProvisioning() {return true;}@Overridepublic void onPress() {// shutdown by making sure radio and power are handled accordingly.mWindowManagerFuncs.shutdown(false /* confirm */);}}可以发现在PowerAction类的成员函数onPress方法中我们调用了mWindowManagerFuncs.showdown方法,而这个方法也就是开始执行我们的关机操作了,那么这里的mWindowManagerFuncs又是什么呢?它是在什么时候赋值的呢?通过分析我们发现这里的mWindowManagerFuncs成员变量是在GlobalActions的构造方法中赋值的。
public GlobalActions(Context context, WindowManagerFuncs windowManagerFuncs) {...mWindowManagerFuncs = windowManagerFuncs;...
}好吧,回到我们的PhoneWindowManager,早构造GlobalActions时,直接传递的是PhoneWindowManager的成员变量mWindowManagerFuncs,那么PhoneWindowManager的mWindowManagerFuncs成员变量又是何时被赋值的呢?通过分析源码我们能够看到PhoneWindowManager的mWindowManagerFuncs变量是在PhoneWindowManager的init方法中初始化的,好吧,再次查找PhoneWindowManager的init方法是何时被调用的。
经过查找终于在WindowManagerService中我们找到了PhoneWindowManager的init方法的调用。
private void initPolicy() {UiThread.getHandler().runWithScissors(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {WindowManagerPolicyThread.set(Thread.currentThread(), Looper.myLooper());mPolicy.init(mContext, WindowManagerService.this, WindowManagerService.this);}}, 0);}这里的mPolicy就是一个PhoneWindowManager的实力,可以发现这里的init方法中mWindowManagerFuncs传递的就是一个WindowManagerService的实例,O(∩_∩)O哈哈~,让我们好找。
然么在PowerAction的onPress方法中调用的mWindowManagerFuncs.shutdown(false /* confirm */);方法,实际上调用的就是WindowManagerService的shutdown方法,这样我们继续看一下WindowManagerService的shutdown方法的实现。
@Overridepublic void shutdown(boolean confirm) {ShutdownThread.shutdown(mContext, confirm);}好吧,这里很简单就是直接调用了ShutdownThread的shutdown方法,看样子这里就是执行关机操作的封装了,继续看一下ShutdownThread的shutdown方法。
public static void shutdown(final Context context, boolean confirm) {mReboot = false;mRebootSafeMode = false;shutdownInner(context, confirm);}可以看到在ShutdownThread的shutdown方法中代码很简单,具体的操作下发到了shutdownInner方法中,那么我们继续看一下shutdownInner方法的实现。
static void shutdownInner(final Context context, boolean confirm) {// ensure that only one thread is trying to power down.// any additional calls are just returnedsynchronized (sIsStartedGuard) {if (sIsStarted) {Log.d(TAG, "Request to shutdown already running, returning.");return;}}final int longPressBehavior = context.getResources().getInteger(com.android.internal.R.integer.config_longPressOnPowerBehavior);final int resourceId = mRebootSafeMode? com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_safemode_confirm: (longPressBehavior == 2? com.android.internal.R.string.shutdown_confirm_question: com.android.internal.R.string.shutdown_confirm);Log.d(TAG, "Notifying thread to start shutdown longPressBehavior=" + longPressBehavior);if (confirm) {final CloseDialogReceiver closer = new CloseDialogReceiver(context);if (sConfirmDialog != null) {sConfirmDialog.dismiss();}sConfirmDialog = new AlertDialog.Builder(context).setTitle(mRebootSafeMode? com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_safemode_title: com.android.internal.R.string.power_off).setMessage(resourceId).setPositiveButton(com.android.internal.R.string.yes, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {beginShutdownSequence(context);}}).setNegativeButton(com.android.internal.R.string.no, null).create();closer.dialog = sConfirmDialog;sConfirmDialog.setOnDismissListener(closer);sConfirmDialog.getWindow().setType(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG);sConfirmDialog.show();} else {beginShutdownSequence(context);}}可以看到方法体中,首先判断若用户点击了关机按键是否弹出确认框,若弹出则弹出关机确认框,若不需要确认,则直接调用beginShutdownSequence方法,执行关机操作。而在关机确认框中我们的确认按钮也是执行了beginShutdownSequence方法,所以我们继续看一下关机方法beginShutdownSequence。
private static void beginShutdownSequence(Context context) {synchronized (sIsStartedGuard) {if (sIsStarted) {Log.d(TAG, "Shutdown sequence already running, returning.");return;}sIsStarted = true;}...if (PowerManager.REBOOT_RECOVERY.equals(mRebootReason)) {mRebootUpdate = new File(UNCRYPT_PACKAGE_FILE).exists();if (mRebootUpdate) {pd.setTitle(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_to_update_title));pd.setMessage(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_to_update_prepare));pd.setMax(100);pd.setProgressNumberFormat(null);pd.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);pd.setProgress(0);pd.setIndeterminate(false);} else {// Factory reset path. Set the dialog message accordingly.pd.setTitle(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_to_reset_title));pd.setMessage(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.reboot_to_reset_message));pd.setIndeterminate(true);}} else {pd.setTitle(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.power_off));pd.setMessage(context.getText(com.android.internal.R.string.shutdown_progress));pd.setIndeterminate(true);}pd.setCancelable(false);pd.getWindow().setType(WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_KEYGUARD_DIALOG);pd.show();sInstance.mProgressDialog = pd;sInstance.mContext = context;sInstance.mPowerManager = (PowerManager)context.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);// make sure we never fall asleep againsInstance.mCpuWakeLock = null;try {sInstance.mCpuWakeLock = sInstance.mPowerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, TAG + "-cpu");sInstance.mCpuWakeLock.setReferenceCounted(false);sInstance.mCpuWakeLock.acquire();} catch (SecurityException e) {Log.w(TAG, "No permission to acquire wake lock", e);sInstance.mCpuWakeLock = null;}// also make sure the screen stays on for better user experiencesInstance.mScreenWakeLock = null;if (sInstance.mPowerManager.isScreenOn()) {try {sInstance.mScreenWakeLock = sInstance.mPowerManager.newWakeLock(PowerManager.FULL_WAKE_LOCK, TAG + "-screen");sInstance.mScreenWakeLock.setReferenceCounted(false);sInstance.mScreenWakeLock.acquire();} catch (SecurityException e) {Log.w(TAG, "No permission to acquire wake lock", e);sInstance.mScreenWakeLock = null;}}// start the thread that initiates shutdownsInstance.mHandler = new Handler() {};sInstance.start();}在方法beginShutdownSequence中我们首先初始化了一个Process的dialog,该dialog用于显示关机界面,然后我们调用了sInstance.start方法,再往下的方法中就是真正的shutdown方法的实现,同时也是native方法,我们这里就不做过得解读了。。。
总结:
电源按键是系统按键,所以对电源按键的处理逻辑也是在PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandledKey方法中;
在PhoneWindowManager的dispatchUnhandleKey方法处理Power按键之后会首先显示系统操作弹窗,一般包括但不限于:飞行模式,静音模式,重新启动,关机等;
当用户点击关机按钮是调用的是WindowManagerService.shutdown方法,而内部调用的是ShutdownThread.shutdown方法;
另外对android源码解析方法感兴趣的可参考我的:
android源码解析之(一)–>android项目构建过程
android源码解析之(二)–>异步消息机制
android源码解析之(三)–>异步任务AsyncTask
android源码解析之(四)–>HandlerThread
android源码解析之(五)–>IntentService
android源码解析之(六)–>Log
android源码解析之(七)–>LruCache
android源码解析之(八)–>Zygote进程启动流程
android源码解析之(九)–>SystemServer进程启动流程
android源码解析之(十)–>Launcher启动流程
android源码解析之(十一)–>应用进程启动流程
android源码解析之(十二)–>系统启动并解析Manifest的流程
android源码解析之(十三)–>apk安装流程
android源码解析之(十四)–>Activity启动流程
android源码解析之(十五)–>Activity销毁流程
android源码解析(十六)–>应用进程Context创建流程
android源码解析(十七)–>Activity布局加载流程
android源码解析(十八)–>Activity布局绘制流程
android源码解析(十九)–>Dialog加载绘制流程
android源码解析(二十)–>Dialog取消绘制流程
android源码解析(二十一)–>PopupWindow加载绘制流程
android源码解析(二十二)–>Toast加载绘制流程
android源码解析(二十三)–>Android异常处理流程
android源码解析(二十四)–>onSaveInstanceState执行时机
android源码解析(二十五)–>onLowMemory执行流程
android源码解析(二十六)–>截屏事件流程
android源码解析(二十七)–>HOME事件流程
本文以同步至github中:https://github.com/yipianfengye/androidSource,欢迎star和follow
这篇关于Android源码解析(二十八)--电源开关机按键事件流程的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!