本文主要是介绍Linux Thermal 框架解析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Linux Thermal 是 Linux 系统下温度控制相关的模块,主要用来控制系统运行过程中芯片产生的热量,
使芯片温度和设备外壳温度维持在一个安全、舒适的范围。那下面我们就来一起看看对于温度控制这样一个需求,Linux 内核是怎么实现的。Thermal 的主要框架
要实现一个温度控制的需求,试想一下我们是不是最少要有获取温度的设备和控制温度的
设备这两个最基本的东西?当然附带的也会产生一些使用温度控制设备的策略。
那上面这些东西在 Linux Thermal 框架中怎么体现呢?通过阅读源码我们发现代码中对
上面的东西进行了一些抽象。
获取温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Zone Device;
控制温度的设备:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Cooling Device;
控制温度策略:在 Thermal 框架中被抽象为 Thermal Governor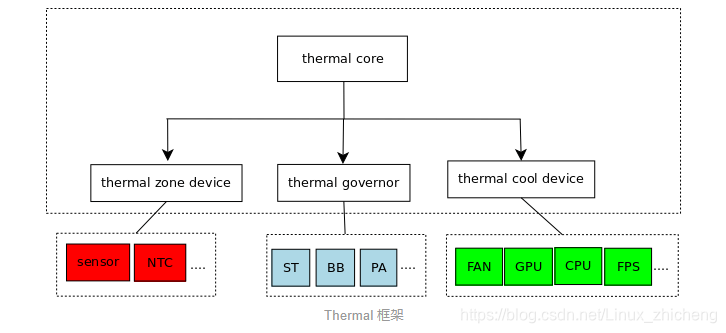
Thermal Zone Device
上面说到 Thermal Zone Device 是获取温度设备的抽象,怎么抽象的?终究我们还是要 RTFSC。
RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)即阅读源代码!!struct thermal_zone_device {int id;char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct device device;struct thermal_attr *trip_temp_attrs;struct thermal_attr *trip_type_attrs;struct thermal_attr *trip_hyst_attrs;void *devdata;int trips;/* 轮询时间 */int passive_delay;int polling_delay;int temperature;int last_temperature;int emul_temperature;int passive;unsigned int forced_passive;/* 设备的操作函数 */struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;struct thermal_governor *governor;struct list_head thermal_instances;struct idr idr;struct mutex lock;struct list_head node;/* 用来循环处理的 delayed_work */struct delayed_work poll_queue;
};struct thermal_zone_device_ops {/* 绑定函数 */int (*bind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,struct thermal_cooling_device *);int (*unbind) (struct thermal_zone_device *,struct thermal_cooling_device *);/* 获取温度函数 */int (*get_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long *);int (*get_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,enum thermal_device_mode *);int (*set_mode) (struct thermal_zone_device *,enum thermal_device_mode);int (*get_trip_type) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trip_type *);/* 获取触发点温度 */int (*get_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,unsigned long *);int (*set_trip_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,unsigned long);int (*get_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,unsigned long *);int (*set_trip_hyst) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,unsigned long);int (*get_crit_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long *);int (*set_emul_temp) (struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long);int (*get_trend) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trend *);int (*notify) (struct thermal_zone_device *, int,enum thermal_trip_type);
};通过代码我们可以看到,一个能提供温度的设备操作函数主要有 : 绑定函数、获取温度函数、获取触发点温度函数。绑定函数 : Thermal core 用来绑定用的 , 这个后面会讲 ;获取温度函数 : 获取设备温度用的,这个也好理解 , 一般 SOC 内部会有温度传感器提供温度,
有些热敏电阻通过 ADC 也算出温度,这个函数就是取这些温度值 ;获取触发点温度函数 : 这个是什么用来做什么呢 ? 这个其实是 thermal 框架里面一个关键点,因为要控制温度,
那么什么时候控制就需要有东西来描述,描述什么时候控制的东西就是触发点,每个 thermal zone device 会定义很多触发点,
那么每个触发点的温度就是通过该函数获得;Thermal Cooling Devices
Thermal Cooling Device 是可以降温设备的抽象,能降温的设备比如风扇,
这些好理解,但是想 CPU,GPU 这些 Cooling devices 怎么理解呢?其实降温可以从两方面来理解,一个是加快散热,另外一个就是降低产热量。
风扇,散热片这些是用来加快散热,CPU,GPU 这些 Cooling devices 是通过降低产热来降温。那代码是怎么将这两个方式统一起来呢?
struct thermal_cooling_device {int id;char type[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];struct device device;struct device_node *np;void *devdata;/* cooling device 操作函数 */const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;bool updated; /* true if the cooling device does not need update */struct mutex lock; /* protect thermal_instances list */struct list_head thermal_instances;struct list_head node;
};struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *);/* 设定等级 */int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long);
};Thermal Cooling device 抽象的方式是,认为所有的能降温的设备有很多可以单独控制的状态。
例如,风扇有不同的风速状态,CPU/GPU Cooling device 有不同最大运行频率状态,这样当温度高了之后通过调整这些状态来
降低温度;Thermal Governor
Thermal Governor 是降温策略的一个抽象 , 主要是根据温度来选择 thermal cooling devices
等级的方法,举个简单的例子,当前的温度升高速很快,选择风扇3档风,温度升高不快,选择1档风。
这就是一个 Governor。/*** struct thermal_governor - structure that holds thermal governor information* @name: name of the governor* @throttle: callback called for every trip point even if temperature is* below the trip point temperature* @governor_list: node in thermal_governor_list (in thermal_core.c)*/
struct thermal_governor {char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];/* 策略函数 */int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);struct list_head governor_list;
};很简单,所有的策略都通过 throttle 这个函数实现,内核已经实现了一些策略,
step_wise, user_space, power_allocator, bang_bang 等具体实现算法细节就不展开;Thermal Core
有了获取温度的设备,有了温控控制的设备,有了控制方法,Thermal Core 就负责把这些整合在一起。
下面看一下整合的简单流程。1.注册函数 ,thermal Core 通过对外提供注册的接口,让 thermal zone device、
thermal cooling device、thermal governor 注册进来。struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_zone_device_register(const char *, int, int,void *, struct thermal_zone_device_ops *,const struct thermal_zone_params *, int, int);struct thermal_cooling_device *thermal_cooling_device_register(char *, void *,const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *);int thermal_register_governor(struct thermal_governor *);2.Thermal zone/cooling device 注册的过程中 thermal core 会调用绑定函数,
绑定的过程最主要是一个 cooling device 绑定到一个 thremal_zone 的触发点上int thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{struct thermal_instance *dev;struct thermal_instance *pos;struct thermal_zone_device *pos1;struct thermal_cooling_device *pos2;unsigned long max_state;int result;.../* thermal_instace 就是绑定之后的实例 */dev =kzalloc(sizeof(struct thermal_instance), GFP_KERNEL);if (!dev)return -ENOMEM;dev->tz = tz;dev->cdev = cdev;dev->trip = trip;dev->upper = upper;...sysfs_create_link(&tz->device.kobj, &cdev->device.kobj, dev->name);if (result)goto release_idr;sprintf(dev->attr_name, "cdev%d_trip_point", dev->id);sysfs_attr_init(&dev->attr.attr);...list_for_each_entry(pos, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node)if (pos->tz == tz && pos->trip == trip && pos->cdev == cdev) {result = -EEXIST;break;}if (!result) {/* 绑定完了就添加到链表中 */list_add_tail(&dev->tz_node, &tz->thermal_instances);list_add_tail(&dev->cdev_node, &cdev->thermal_instances);}...return result;
}3.Thermal core 使能 delayed_work 循环处理 , 使整个 thermal 控制流程运转起来。static void thermal_zone_device_check(struct work_struct *wrok)
{struct thermal_zone_device *tz = container_of(work, structthermal_zone_device,poll_queue.work);/* 处理函数 */thermal_zone_device_update(tz);
}void thermal_zone_device_update(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{int count;if (!tz->ops->get_temp)return;/* 更新温度 */update_temperature(tz);-for (count = 0; count < tz->trips; count++)/* 处理触发点,这里面就会调到具体的 governor */handle_thermal_trip(tz, count);
}static void thermal_zone_device_set_polling(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int delay)
{if (delay > 1000)/* 更改 delayed_work 下次唤醒时间完成轮询 */mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_wq, &tz->poll_queue,round_jiffies(msecs_to_jiffies(delay)));else if (delay)mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_wq, &tz->poll_queue,msecs_to_jiffies(delay));elsecancel_delayed_work(&tz->poll_queue);
}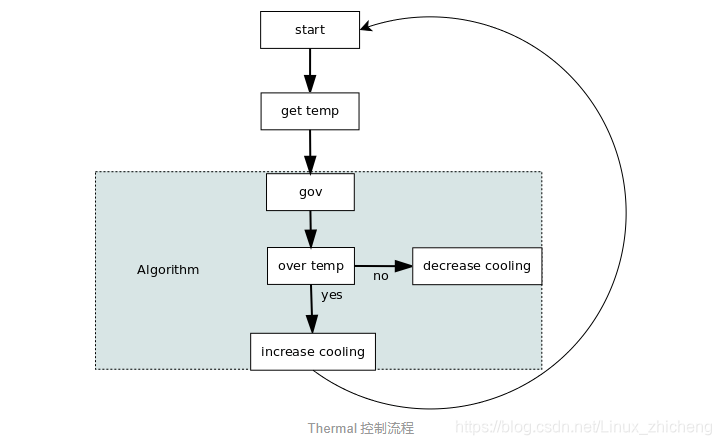
当温度升高超过温度触发点的话,就会使能对应的 cooling device 进行降温处理,
至此 Linux Thermal 相关的一些基本框架就介绍完了。
这篇关于Linux Thermal 框架解析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



