本文主要是介绍使用ADT(抽象数据类型)对队列进行操作,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
这里写目录标题
- 一 、什么叫ADT
- 二 、创建新的数据类型和函数接口
- 三 、 实现函数接口
- 四 、编写主函数
- 五、运行结果
- 1. 添加数据
- 2. 删除数据
- 3. 查找和显示数据
一 、什么叫ADT
在这里用ADT(抽象数据类型)来对队列进行操作,那么什么叫抽象数据类型呢,简单的说就是设计一种新的数据类型,然后再对新类型构造一系列操控数据的方法,详细步骤如下(来自C primer PLUS)
-
提供类型属性和相关操作的抽象描述。这些描述既不能依赖特定的实 现,也不能依赖特定的编程语言。这种正式的抽象描述被称为抽象数据类型 (ADT)。
-
开发一个实现 ADT 的编程接口。也就是说,指明如何储存数据和执 行所需操作的函数。例如在 C中,可以提供结构定义和操控该结构的函数原 型。这些作用于用户定义类型的函数相当于作用于 C基本类型的内置运算 符。需要使用该新类型的程序员可以使用这个接口进行编程。
-
编写代码实现接口。这一步至关重要,但是使用该新类型的程序员无 需了解具体的实现细节。
二 、创建新的数据类型和函数接口
在了解了什么抽象数据类型之后,这里还是以最简单的整型队列为例,话不多说,让我们来coding吧,首先定义queue.h文件
#ifndef _QUEUE_H_
#define _QUEUE_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXITEMS 10// 定义队列
typedef int Item;typedef struct node
{Item item;struct node *next;
}Node;
typedef struct queue
{Node *head;Node *rear;int counts; // counts 为队列当中的项数
}Queue;// 定义操作队列的一系列方法
// 初始化队列
void InitialQueue(Queue *pq);//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueIsEmpty(const Queue *pq);//判断队列是否已满
bool QueueIsFull(const Queue *pq);//获取队列的项数
unsigned int CountInQueue(const Queue *pq);//在队列当中添加一个节点
bool AddNode(Item *pi,Queue *pq);//在队列当中删除节点
bool DeleteNode(Item *pi,Queue *pq);//查找队列当中的节点
bool FindNode(Item *pi,const Queue *pq);//清空队列节点
void EmptyQueue(Queue *pq);#endif
三 、 实现函数接口
在定义好数据类型和操作数据的接口函数之后,现在让我们来实现函数接口
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "queue.h" void InitialQueue(Queue *pq){pq->head=pq->rear=NULL; //将头指针和尾指针都赋为NULLpq->counts=0; // 把队列的项数初始化为0
}bool QueueIsEmpty(const Queue *pq){return pq->counts==0;
}bool QueueIsFull(const Queue *pq){return pq->counts==MAXITEMS ;
}unsigned int CountInQueue(const Queue *pq){return pq->counts;
}bool AddNode(Item *pi,Queue *pq){Node *pnew;if(QueueIsFull(pq))// 如果队列已满,返回falsereturn false;pnew=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));//给new分配内存空间if(pnew==NULL)//如果未分配到内存,提前返回falsereturn false;CopyToNode(pi,pnew);pnew->next=NULL; //将新添加的数据的next赋为NULLif(QueueIsEmpty(pq))// 如果队列为空,直接在队首插入新的元素pq->head=pnew;elsepq->rear->next=pnew; //把尾结点的next与新节点连接起来pq->rear=pnew;//把新节点赋值给尾结点pq->counts++;// 项数加1return true;
}static void CopyToNode(Item *pi,Node *pnew){pnew->item=*pi; // 添加结点的数据部分
}bool DeleteNode(Item *pi,Queue *pq){Node *temp;if(QueueIsEmpty(pq))return false;CopyToItem(pi,pq->head);temp=pq->head; // 用temp存储被删除的节点pq->head=pq->head-next; // 把头节点重置为头节点的next指针free(temp);pq->counts--;if(pq->couns==0) // 删除最后一项时,把尾指针赋为NULL,头指针已经重新赋值为头指针的next,已经为NULLpq->rear=NULL; return true;
}static void CopyToItem(Item *pi,Node *temp){*pi=temp->item; // 将被删除的节点数据部分保存到*pi
}
bool FindNode(Item *pi,const Queue *pq){Node *temp;if(QueueIsEmpty(pq))return false;temp=pq->head // 把头节点赋值给temp;while(temp!=NULL){if(temp->item==*pi)return true;temp=temp->next;// 节点后移}return false;
}
void EmptyQueue(Queue *pq){Item del;while(!QueueIsEmpty(pq)){DeleteNode(&del,pq);}
}
到这里对应的函数接口内容就全部完成了,接下来就是编写主函数了
四 、编写主函数
int main(void){Item temp;Queue line;char ch;InitialQueue(&pq);printf("Please input your select .a is add ,q is quit ,d is del,q is quit, f is findnode:\n");while((ch=getchar())!='q'){if(ch!='a'&&ch!='d'&&ch!='f')continue;if(ch=='a'){printf("Please input a number\n");scanf("%d",&temp);if(QueueIsFull(&line))printf("The Queue is FULL!!\n");else{AddNode(&temp,&line);printf("puttings %d into queue\n",temp);}}else if(ch=='d'){if(QueueIsEmpty(&line))printf("The Queue is Empty\n");else{DelNodeInQueue(&temp,&line);printf("Removing %d in the queue\n",temp);}}else{if(QueueIsEmpty(&line))printf("The Queue is Empty\n");else{printf("Please input you wish to find number\n");scanf("%d",&temp);if (FindNode(&temp,&line))printf("%d is in line\n",temp);elseprintf("%d is not in line\n",temp);}}printf("%d items in queue \n",CountInQueue(&line)); puts("Type a to add, d to delete, q to quit ,f is find:\n");}printf("Here is queue:\n");showqueue(&line);return 0;
}void showqueue(Queue *pq){if(QueueIsEmpty(pq))printf("The Queue is empty\n");while(pq->head!=NULL){printf("%d",pq->head->item);DeleteNode(&(pq->head->item),pq);}
}
五、运行结果
1. 添加数据
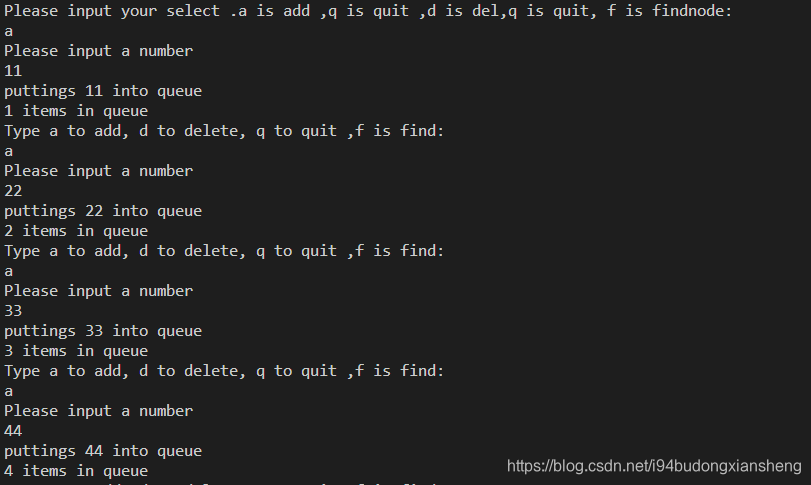
2. 删除数据
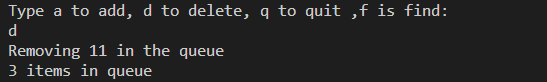
3. 查找和显示数据
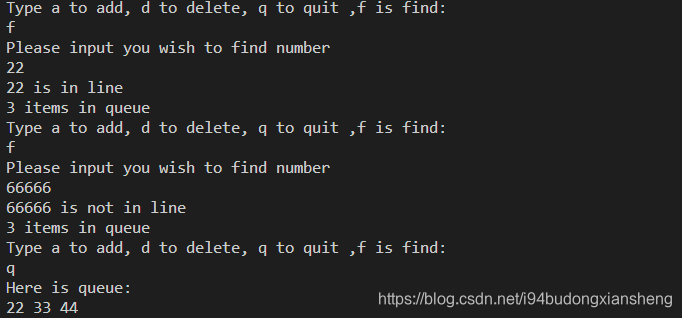
这篇关于使用ADT(抽象数据类型)对队列进行操作的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




