本文主要是介绍Seurat -- ScaleData学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
brief
seurat提供了一个教学,其中global scale normalization之后又对数据进行了scale。
默认是对上一步 selected highly variable features进行scale。
- 概要图以及系列博文可以参见链接。

如果是 SCTransform则不需要手动运行这一步。
- 下面是就是教程提供的流程:
library(dplyr)
library(Seurat)
library(patchwork)
library(sctransform)
library(ggplot2)rm(list=ls())
# 使用read10X读取output of the cellranger pipeline from 10X,包括barcodes,genes,matrix.mtx三个文件
pbmc.data <- Read10X(data.dir = "D:/djs/pbmc3k_filtered_gene_bc_matrices/filtered_gene_bc_matrices/hg19")
# 使用 CreateSeuratObject函数构造seurat对象
pbmc <- CreateSeuratObject(counts = pbmc.data, project = "pbmc3k",min.cells = 3, min.features = 200,names.delim = "-",names.field = 1)# 计算 a percentage of cell reads originating from the mitochondrial genes
pbmc[["percent.mt"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(pbmc, pattern = "^MT-")
# 计算 complexity of the RNA species
pbmc@meta.data$log10GenesPerUMI <- log10(pbmc$nFeature_RNA) / log10(pbmc$nCount_RNA)pbmc <- subset(pbmc, subset = nFeature_RNA > 200 & nFeature_RNA < 2500 & percent.mt < 5)pbmc <- subset(pbmc, subset = nFeature_RNA > 200 & nFeature_RNA < 2500 & percent.mt < 5)
pbmc <- NormalizeData(pbmc, normalization.method = "LogNormalize", scale.factor = 10000)
pbmc <- FindVariableFeatures(pbmc,assay = "RNA" ,selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000)all.genes <- rownames(pbmc)
pbmc <- ScaleData(pbmc, features = all.genes,assay = "RNA")pbmc <- RunPCA(pbmc)
- 这里是该函数具体的参数以及意义:

-
features
Vector of features names to scale/center. Default is variable features. -
vars.to.regress
Variables to regress out (previously latent.vars in RegressOut). For example, nUMI, or percent.mito. -
split.by
Name of variable in object metadata or a vector or factor defining grouping of cells. See argument f in split for more details -
model.use
Use a linear model or generalized linear model (poisson, negative binomial) for the regression. Options are ‘linear’ (default), ‘poisson’, and ‘negbinom’ -
use.umi
Regress on UMI count data. Default is FALSE for linear modeling, but automatically set to TRUE if model.use is ‘negbinom’ or ‘poisson’ -
do.scale
Whether to scale the data. -
do.center
Whether to center the data. -
scale.max
Max value to return for scaled data. The default is 10. Setting this can help reduce the effects of features that are only expressed in a very small number of cells. If regressing out latent variables and using a non-linear model, the default is 50. -
block.size
Default size for number of features to scale at in a single computation. Increasing block.size may speed up calculations but at an additional memory cost. -
min.cells.to.block
If object contains fewer than this number of cells, don’t block for scaling calculations. -
verbose
Displays a progress bar for scaling procedure -
assay
Name of Assay to scale
-
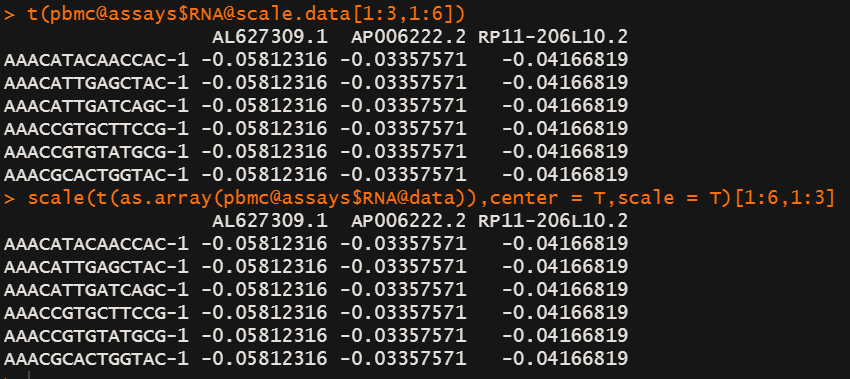
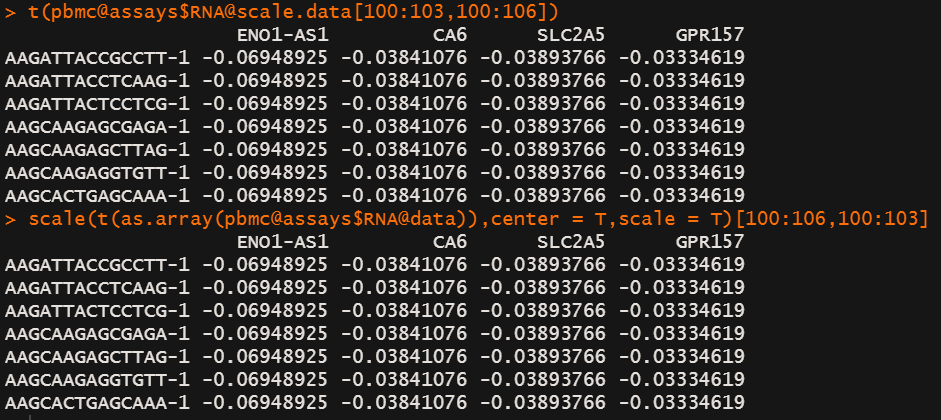
这个函数和 基础函数scale()的结果一样吗?
没区别
可能是调用代码不一样~~
t(pbmc@assays$RNA@scale.data[1:3,1:6])scale(t(as.array(pbmc@assays$RNA@data)),center = T,scale = T)[1:6,1:3]
为什么要scale?
一个gene 的表达量在不同细胞中的分布可以认为是正态分布,当你将这个gene的表达量中心化以及标准化成为标准正态分布后(z-score),不同gene的表达量分布就在同一个尺度上了,方便比较。
高表达的gene在下游的分析中和低表达gene在下游分析中权重也就一致了,不然高表达的gene在下游的分析中比如PCA就会占据主导地位,而细胞间的变异需要同时考虑gene的表达量以及gene的特异性表达,特异性表达的基因表达量通常不高。
ScaleData()后的数据存放和后续应用
-
scale标准化的数据储存在"RNA" assay的 seurat_obj[[‘RNA’]]@scale.data中
-
我们也注意到seurat_obj[[‘RNA’]]@data全是非负数,而且是针对基因矩阵的所有基因;而seurat_obj[[‘RNA’]]@scale.data则有正负数,默认情况,只针对高可变基因进行scale标准化;
-
那么,我们在seurat下游分析中,什么情况使用data,什么时候使用scale.data:
-
下游分析中的PCA线性降维聚类,umap、tsne聚类均是应用高可变基因的scale.data进行后续分析的;
-
在基因可视化分析中,FeaturePlot、FeatureScatter、VlnPlot、DotPlot等函数默认slot =“data”,只有DoHeatmap()默认使用slot = “scale.data”,多个基因跨细胞比较;
-
FindAllMarkers()找差异基因是默认slot =“data”,它是针对所有基因找差异基因,而不是高可变基因集
-
多个数据集整合应该怎样调用ScaleData()
-
这里的多个数据集只包括scRNA-seq数据集。
-
如果仅仅是数据集之间的merge(需要做简单的QC验证没有批次效应),那应该使用 RNA assays下面的data进行 scale。当然你也可以在运行ScaleData时加入split.by区分数据集以分别进行scale(没验证过会出现什么问题)。
-
如果数据集之间进行了integrated运算,那应该使用integrated assays下面的data进行 scale
这篇关于Seurat -- ScaleData学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!