本文主要是介绍一棵树的成长史——JAVA如何把数据库的数据处理成树形结构(核心代码直接使用即可),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
JAVA如何把数据库的数据处理成树形结构
- 💨前言
- 😎实现思路😎
- 🧡完整代码🧡
- 😜总结-核心代码😜
💨前言

不知道大家在做项目的时候有没有接触到将平平无奇数据结合处理成有层次的数据呢,类似下面这样
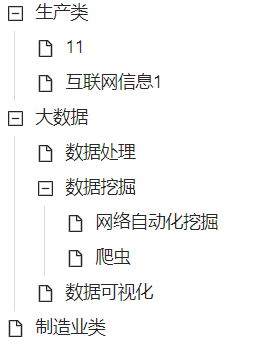
或者 生活处处都有,我想大家都应该接触过的,下面直接看怎么实现,我会大概讲一下思路,当然也可以直接跳到最后去看代码实现的哈
follow me!go go go!
❗此篇文章也只是一个简单的学习记录,不详细的对代码进行讲解
😎实现思路😎
首先一般数据库的模型设计如下

sql脚本
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for product
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `product`;
CREATE TABLE `product` (`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`uuid` varchar(64) NOT NULL,`name` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '名称',`sort` int(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '排序',`parent_uuid` varchar(64) NOT NULL DEFAULT '-1' COMMENT '父亲 无父级为-1',`level` varchar(10) NOT NULL COMMENT '产品层级',`create_time` datetime NOT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='产品表';-- ----------------------------
-- Records of product
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('1', '4dbf40d2-2af7-425c-a103-0349caaa26cf', '生产类', '1', '-1', '1', '2021-09-23 15:34:36');
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('2', '3062deff-8ec7-44c4-bd4e-88fe3c7b835c', '22', '1', '4dbf40d2-2af7-425c-a103-0349caaa26cf', '2', '2021-09-23 15:37:20');
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('3', '32afe426-9337-41c1-83e8-caf3248ba57e', '互联网信息', '2', '4dbf40d2-2af7-425c-a103-0349caaa26cf', '2', '2021-09-23 15:38:19');
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('4', '34c5239f-db2d-4394-b367-a57f8ae6f8ff', '33', '1', '3062deff-8ec7-44c4-bd4e-88fe3c7b835c', '3', '2021-09-23 15:53:29');
INSERT INTO `product` VALUES ('5', '19eedcd3-aa7f-4a2d-8182-d3f795e99b9d', '44', '1', '34c5239f-db2d-4394-b367-a57f8ae6f8ff', '4', '2021-09-23 15:53:56');我们观察一下,可以发现我们的关注重点在name、uuid、parent_uuid上面:
name:分类名称
uuid:UUID 是 通用唯一识别码(Universally Unique Identifier)的缩写,是一种软件建构的标准,其目的,是让分布式系统中的所有元素,都能有唯一的辨识信息,而不需要通过中央控制端来做辨识信息的指定。这里可以简单看作一个唯一标识码(类似于ID但不等于ID)
parent_uuid:子类的父类UUID,最高级规定为-1(这个可以自己定义,不会有相同的就好)
下面就是我创建的模拟数据
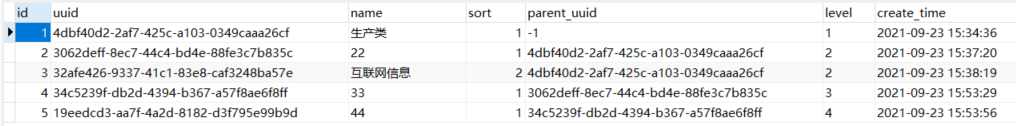
想要实现数形状结构,肯定要以某一属性来作为突破口,它就是parent_uuid,那么到底是如何实现的 来看具体代码
🧡完整代码🧡
只贴重点代码
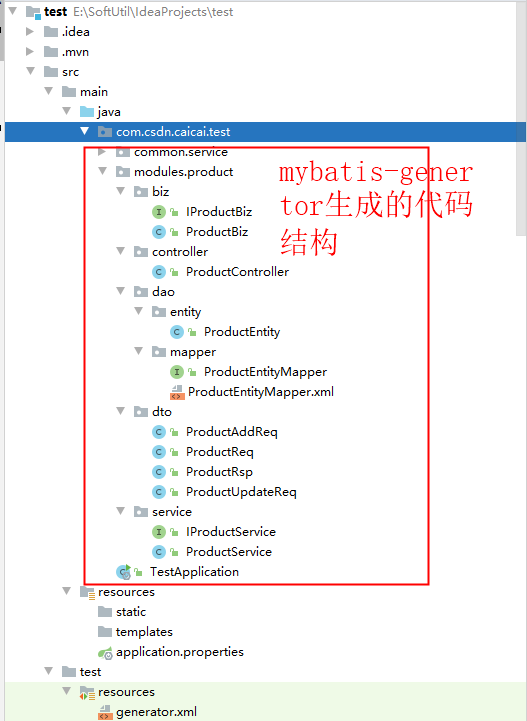
首先使用了Mabatis-generator生成了通用后端代码,结构如下:
ProductController.class
package com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.controller;import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto.ProductRsp;
import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.biz.IProductBiz;import java.util.List;/*** 产品表** @author* @date*/@RestController
@Api(tags = {"产品表"})
@RequestMapping("/caicai/product")
@Validated
public class ProductController {private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ProductController.class);@Autowiredprivate IProductBiz productBiz;/*** 产品树*/@ApiOperation(value = "产品树")@RequestMapping(path = "/tree", method = RequestMethod.GET)public List<ProductRsp> tree() {return productBiz.tree();}}IProductBiz.class
package com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.biz;import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto.ProductRsp;import java.util.List;/*** @author* @date*/
public interface IProductBiz {List<ProductRsp> tree();
}ProductBiz.class
package com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.biz;import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.assertj.core.util.Lists;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;import tk.mybatis.mapper.entity.Example;import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.service.IProductService;
import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dao.entity.ProductEntity;
import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto.ProductReq;
import com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto.ProductRsp;import static java.util.stream.Collectors.toList;/*** @author* @date*/
@Service("productBiz")
public class ProductBiz implements IProductBiz {@Autowiredprivate IProductService productService;/*** 根据条件查询** @param productReq* @return*/public List<ProductEntity> selectByCondition(ProductReq productReq) {Example example = new Example(ProductEntity.class);//下面添加自定义收索条件return productService.selectByExample(example);}@Overridepublic List<ProductRsp> tree() {ProductReq req = new ProductReq();List<ProductRsp> list = selectByCondition(req).stream().map(this::productConvert).collect(Collectors.toList());return buildTree(list, req.getParentUuid());}private ProductRsp productConvert(ProductEntity e) {ProductRsp orgNode = new ProductRsp();orgNode.setId(e.getId());orgNode.setUuid(e.getUuid());orgNode.setName(e.getName());orgNode.setLevel(e.getLevel());orgNode.setSort(e.getSort());orgNode.setParentUuid(e.getParentUuid());return orgNode;}public static List<ProductRsp> buildTree(List<ProductRsp> all, String parentUuid) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(all))return Lists.newArrayList();List<ProductRsp> parentList = all.stream().filter(e -> StringUtils.isBlank(e.getParentUuid())|| "-1".equals(e.getParentUuid())|| e.getParentUuid().equals(parentUuid)).collect(toList());getSubList(parentList, all);return parentList;}private static void getSubList(List<ProductRsp> parentList, List<ProductRsp> all) {parentList.forEach(e -> {List<ProductRsp> subList = all.stream().filter(o -> o.getParentUuid().equals(e.getUuid())).collect(toList());e.setSubList(subList);if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(subList))getSubList(subList, all);});}
}ProductReq.class
package com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.Data;import java.io.Serializable;/**
* @author
* @date
*/
@ApiModel(value = "ProductReq", description = "产品表")
@Data
public class ProductReq implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/****/@ApiModelProperty(value = "", name = "id")private Long id;/****/@ApiModelProperty(value = "", name = "uuid")private String uuid;/*** 名称*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "名称", name = "name")private String name;/*** 排序*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "排序", name = "sort")private Integer sort;/*** 父亲 无父级为-1*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "父亲 无父级为-1", name = "parentUuid")private String parentUuid;/*** 产品层级*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "产品层级", name = "level")private String level;
}ProductRsp.class
package com.csdn.caicai.test.modules.product.dto;import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModel;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiModelProperty;
import lombok.Data;import java.io.Serializable;import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;/**
* @author
* @date
*/
@ApiModel(value = "ProductRsp", description = "产品表")
@Data
public class ProductRsp implements Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;/****/@ApiModelProperty(value = "", name = "id")private Long id;/****/@ApiModelProperty(value = "", name = "uuid")private String uuid;/*** 名称*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "名称", name = "name")private String name;/*** 排序*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "排序", name = "sort")private Integer sort;/*** 父亲 无父级为-1*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "父亲 无父级为-1", name = "parentUuid")private String parentUuid;/*** 产品层级*/@ApiModelProperty(value = "产品层级", name = "level")private String level;/****/@ApiModelProperty(value = "", name = "createTime")private Date createTime;@ApiModelProperty(value = "下属产品", name = "subList")private List<ProductRsp> subList;
}测试一下
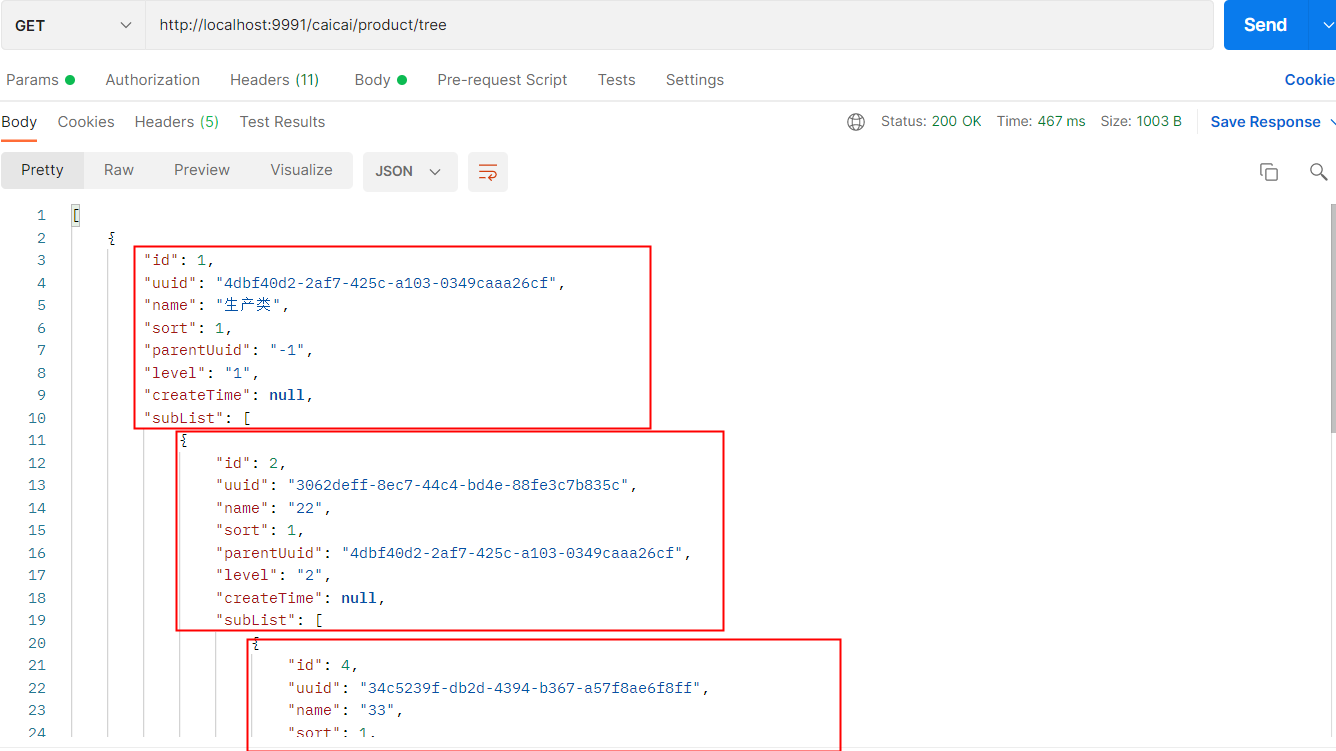
可以看到,实现了我们的效果
😜总结-核心代码😜
上面罗里吧嗦,其实核心代码就是以下代码,亲们来试着理解一下,然后就可以在此基础上美化一下就好了:
ProductRsp、ProductReq 是实体类,可以自行替换里面的内容
private ProductRsp productConvert(ProductEntity e) {ProductRsp orgNode = new ProductRsp();orgNode.setId(e.getId());orgNode.setUuid(e.getUuid());orgNode.setName(e.getName());orgNode.setLevel(e.getLevel());orgNode.setSort(e.getSort());orgNode.setParentUuid(e.getParentUuid());return orgNode;}public static List<ProductRsp> buildTree(List<ProductRsp> all, String parentUuid) {if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(all))return Lists.newArrayList();List<ProductRsp> parentList = all.stream().filter(e -> StringUtils.isBlank(e.getParentUuid())|| "-1".equals(e.getParentUuid())|| e.getParentUuid().equals(parentUuid)).collect(toList());getSubList(parentList, all);return parentList;}private static void getSubList(List<ProductRsp> parentList, List<ProductRsp> all) {parentList.forEach(e -> {List<ProductRsp> subList = all.stream().filter(o -> o.getParentUuid().equals(e.getUuid())).collect(toList());e.setSubList(subList);if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(subList))getSubList(subList, all);});}

这篇关于一棵树的成长史——JAVA如何把数据库的数据处理成树形结构(核心代码直接使用即可)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





