本文主要是介绍POJ1151 Atlantis(线段树,扫描线,离散化,矩形面积并),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目:
Atlantis
Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K
Total Submissions: 23220 Accepted: 8657
Description
There are several ancient Greek texts that contain descriptions of the fabled island Atlantis. Some of these texts even include maps of parts of the island. But unfortunately, these maps describe different regions of Atlantis. Your friend Bill has to know the total area for which maps exist. You (unwisely) volunteered to write a program that calculates this quantity.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case starts with a line containing a single integer n (1 <= n <= 100) of available maps. The n following lines describe one map each. Each of these lines contains four numbers x1;y1;x2;y2 (0 <= x1 < x2 <= 100000;0 <= y1 < y2 <= 100000), not necessarily integers. The values (x1; y1) and (x2;y2) are the coordinates of the top-left resp. bottom-right corner of the mapped area.
The input file is terminated by a line containing a single 0. Don’t process it.
Output
For each test case, your program should output one section. The first line of each section must be “Test case #k”, where k is the number of the test case (starting with 1). The second one must be “Total explored area: a”, where a is the total explored area (i.e. the area of the union of all rectangles in this test case), printed exact to two digits to the right of the decimal point.
Output a blank line after each test case.
Sample Input
2
10 10 20 20
15 15 25 25.5
0
Sample Output
Test case #1
Total explored area: 180.00
Source
Mid-Central European Regional Contest 2000
[Submit] [Go Back] [Status] [Discuss]
思路:
这题是我线段树扫描线的第一题,题目给了n个矩形,每个矩形给了左下角和右上角的坐标,矩形可能会重叠,求的是矩形最后的面积。因为变化范围比较大,我们要用到离散化,离散化就不说了,重点说一说扫描线的过程:
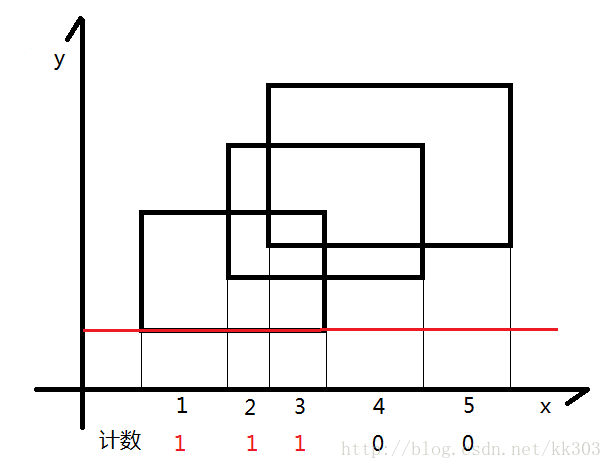
下面有个矩形
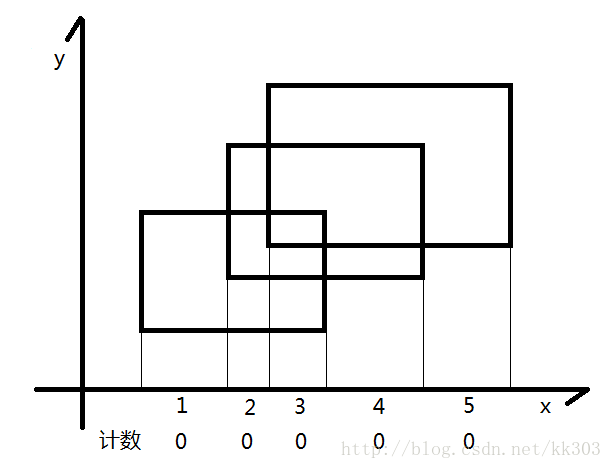
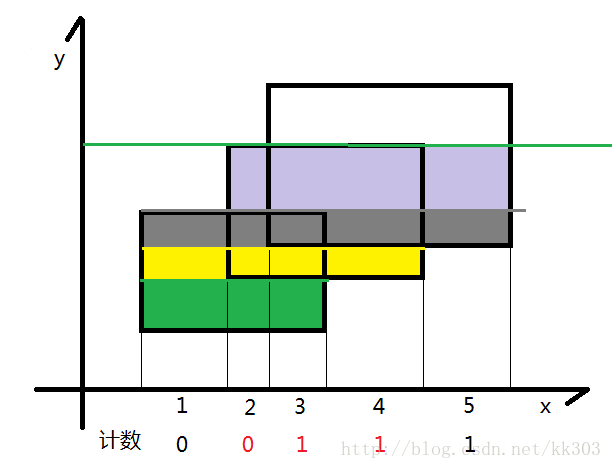
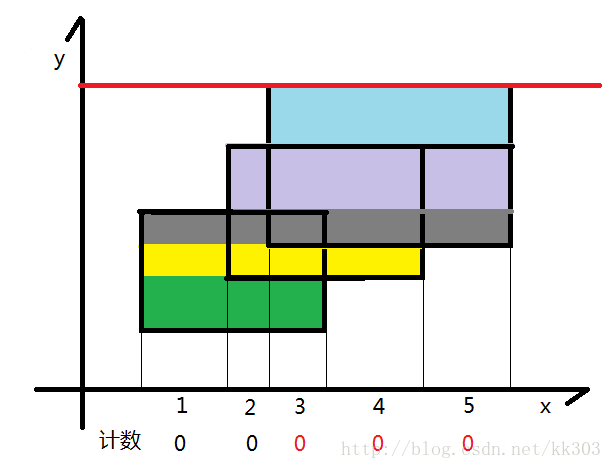
现在假设我们有一根线,从下往上开始扫描
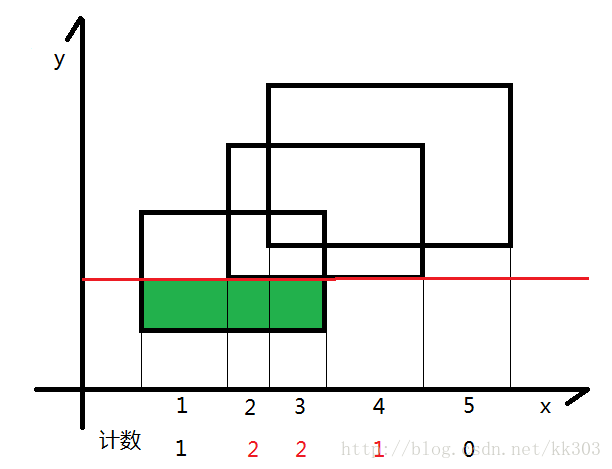
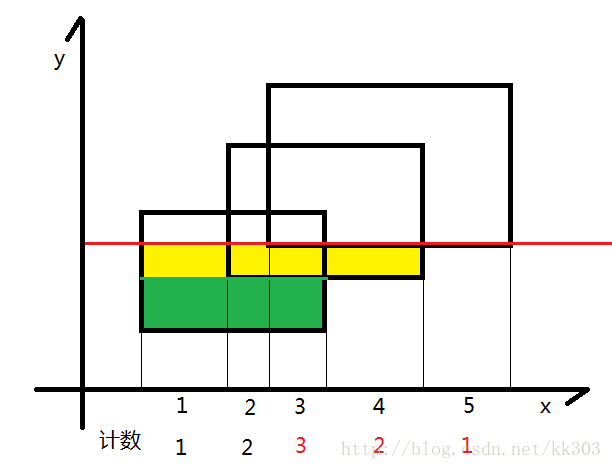
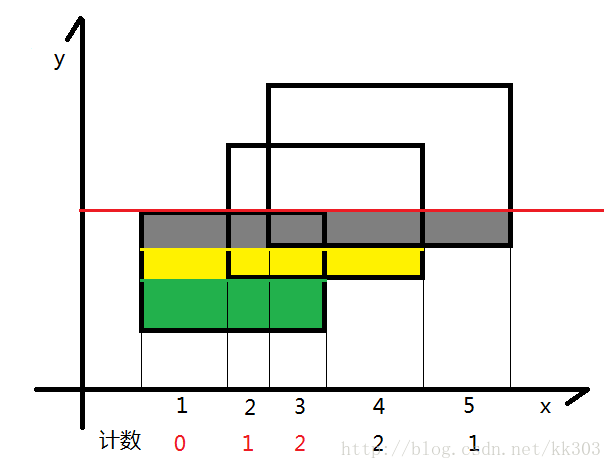
- 如图所示,我们可以把整个矩形分成如图各个颜色不同的小矩形,那么这个小矩形的高就是我们扫过的距离,那么剩下了一个变量,那就是矩形的长一直在变化。
- 我们的线段树就是为了维护矩形的长,我们给每一个矩形的上下边进行标记,下面的边标记为1,上面的边标记为-1,每遇到一个矩形时,我们知道了标记为1的边,我们就加进来这一条矩形的长,等到扫描到-1时,证明这一条边需要删除,就删去,利用1和-1可以轻松的到这种状态。
- 还要注意这里的线段树指的并不是线段的一个端点,而指的是一个区间,所以我们要计算的时候r+1和r-1
- 再提一下离散化,离散化就是把一段很大的区间映射到一个小区间内,这样会节省大量空间,要进行离散化,我们先对端点进行排序,然后去重,然后二分找值就可以了
具体的请结合代码分析:
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define N 220
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
#define lson l,m,rt<<1
#define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1
struct Seg
{double l,r,h;int f;Seg() {}Seg(double a,double b,double c,int d):l(a),r(b),h(c),f(d) {}bool operator < (const Seg &cmp) const{return h<cmp.h;}
} e[N];
struct node
{int cnt;double len;
} t[N<<2];
double X[N];
void pushdown(int l,int r,int rt)
{if(t[rt].cnt)//当前的边被标记,就把当前的长度加上t[rt].len=X[r+1]-X[l];else if(l==r)//当为一个点的时候长度为0t[rt].len=0;else//其他情况把左右两个区间的值加上t[rt].len=t[rt<<1].len+t[rt<<1|1].len;
}
void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt,int val)
{if(L<=l&&r<=R){t[rt].cnt+=val;//加上标记的值pushdown(l,r,rt);//像下更新节点return;}int m=(l+r)>>1;if(L<=m) update(L,R,lson,val);if(R>m) update(L,R,rson,val);pushdown(l,r,rt);
}
int main()
{int n,q=1;double a,b,c,d;while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n){mem(t,0);int num=0;for(int i=0; i<n; i++){scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c,&d);X[num]=a;e[num++]=Seg(a,c,b,1);//矩形下面用1来标记吗X[num]=c;e[num++]=Seg(a,c,d,-1);//上面用-1来标记}sort(X,X+num);//用于离散化sort(e,e+num);//把矩形的边的纵坐标从小到大排序int m=unique(X,X+num)-X;double ans=0;for(int i=0; i<num; i++){int l=lower_bound(X,X+m,e[i].l)-X;//找出离散化以后的值int r=lower_bound(X,X+m,e[i].r)-X-1;update(l,r,0,m,1,e[i].f);ans+=t[1].len*(e[i+1].h-e[i].h);}printf("Test case #%d\nTotal explored area: %.2lf\n\n",q++,ans);}return 0;
}这篇关于POJ1151 Atlantis(线段树,扫描线,离散化,矩形面积并)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!