本文主要是介绍C语言基础(三十三),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、链表排序之归并排序与线性搜索
测试代码:
#include "date.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>// 链表节点结构体
typedef struct Node {int data;struct Node *next;
} Node;// 插入节点到链表末尾
Node* insertNode(Node *head, int data) {Node *newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = data;newNode->next = NULL;if (head == NULL) {head = newNode;} else {Node *current = head;while (current->next != NULL) {current = current->next;}current->next = newNode;}return head;
}// 归并排序
Node* merge(Node *head) {if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {return head;}// 分割链表Node *slow = head, *fast = head->next;while (fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL) {slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}Node *head2 = slow->next;slow->next = NULL;// 合并排序head = merge(head);head2 = merge(head2);Node dummy;Node *ptr = &dummy;while (head != NULL && head2 != NULL) {if (head->data < head2->data) {ptr->next = head;head = head->next;} else {ptr->next = head2;head2 = head2->next;}ptr = ptr->next;}ptr->next = (head != NULL) ? head : head2;return dummy.next;
}// 遍历链表
void printList(Node *head) {Node *current = head;while (current != NULL) {printf("Data: %d, Address: %p\n", current->data, (void*)current);current = current->next;}
}// 线性搜索
int linearSearch(Node *head, int target, Node **foundNodes) {int count = 0;Node *current = head;while (current != NULL) {if (current->data == target) {foundNodes[count] = current;count++;}current = current->next;}return count;
}int main() {int times = getTime();int n;printf("Enter the number of random numbers: ");scanf("%d", &n);Node *head = NULL;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {int randomNumber = rand() % 100; // 生成0-99范围内的随机数head = insertNode(head, randomNumber);}printf("Before sorting:\n");printList(head);head = merge(head);printf("After sorting:\n");printList(head);int target;printf("Enter the element to search for: ");scanf("%d", &target);Node *foundNodes[n];int count = linearSearch(head, target, foundNodes);if (count > 0) {printf("Found %d elements:\n", count);for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {printf("Data: %d, Address: %p\n", foundNodes[i]->data, (void*)foundNodes[i]);}} else {printf("Element not found.\n");}return 0;
}运行结果如下:
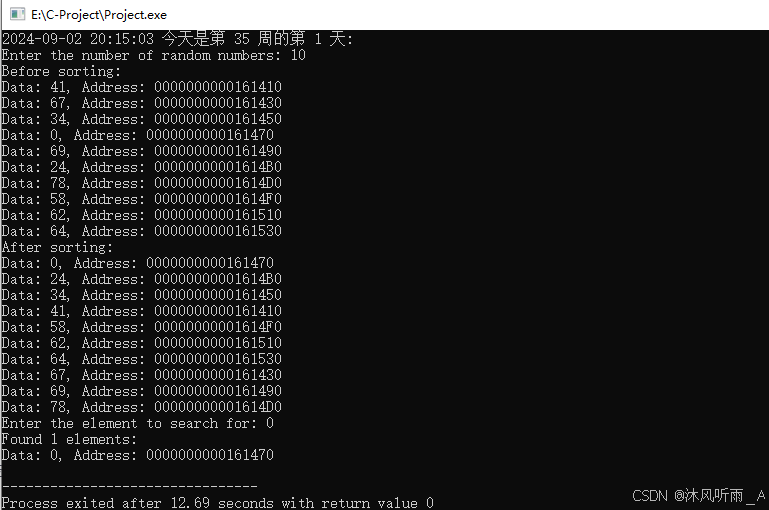
2、 链表排序之插入排序与二分搜索:
测试代码:
#include "date.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef struct Node {int data;struct Node* next;
} Node;// 插入排序
void insertSort(Node** head) {if (*head == NULL || (*head)->next == NULL) {return;}Node* sorted = NULL;Node* current = *head;while (current != NULL) {Node* next = current->next;if (sorted == NULL || current->data < sorted->data) {current->next = sorted;sorted = current;} else {Node* temp = sorted;while (temp->next != NULL && temp->next->data < current->data) {temp = temp->next;}current->next = temp->next;temp->next = current;}current = next;}*head = sorted;
}// 输出链表
void printList(Node* head) {Node* current = head;while (current != NULL) {printf("Data: %d, Address: %p\n", current->data, (void*)current);current = current->next;}
}// 二分搜索
Node* binarySearch(Node* head, int target) {Node* left = head;Node* right = NULL;// 获取链表结尾for (Node* curr = head; curr != NULL; curr = curr->next) {right = curr;}while (left != right) {Node* mid = left;int len = 0;while (mid != right) {len++;mid = mid->next;}len /= 2;mid = left;for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {mid = mid->next;}if (mid->data == target) {return mid;} else if (mid->data < target) {left = mid->next;} else {right = mid;}}return NULL;
}int main() {int times = getTime();int n;printf("Enter the number of elements: ");scanf("%d", &n);Node* head = NULL;// 生成随机数并添加到链表for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {Node* newNode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newNode->data = rand();newNode->next = head;head = newNode;}printf("Unsorted List:\n");printList(head);// 对链表进行插入排序insertSort(&head);printf("\nSorted List:\n");printList(head);// 二分搜索指定的元素int target;printf("\nEnter the element to search: ");scanf("%d", &target);Node* result = binarySearch(head, target);if (result != NULL) {printf("Element found - Data: %d, Address: %p\n", result->data, (void*)result);} else {printf("Element not found\n");}return 0;
}运行结果如下;
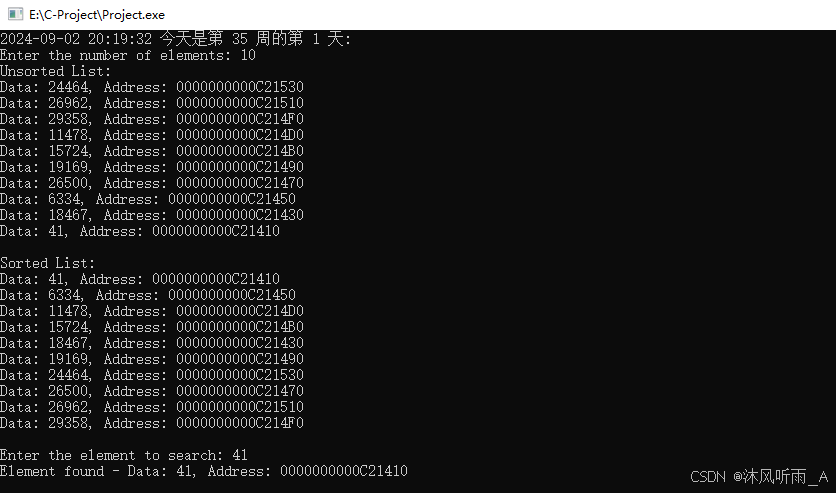
这篇关于C语言基础(三十三)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






