本文主要是介绍【C++】日期类函数(时间计数器)从无到有实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

欢迎来到Harper·Lee的学习笔记!
博主主页传送门:Harper·Lee的博客主页
个人语录:他强任他强,清风拂山岗!

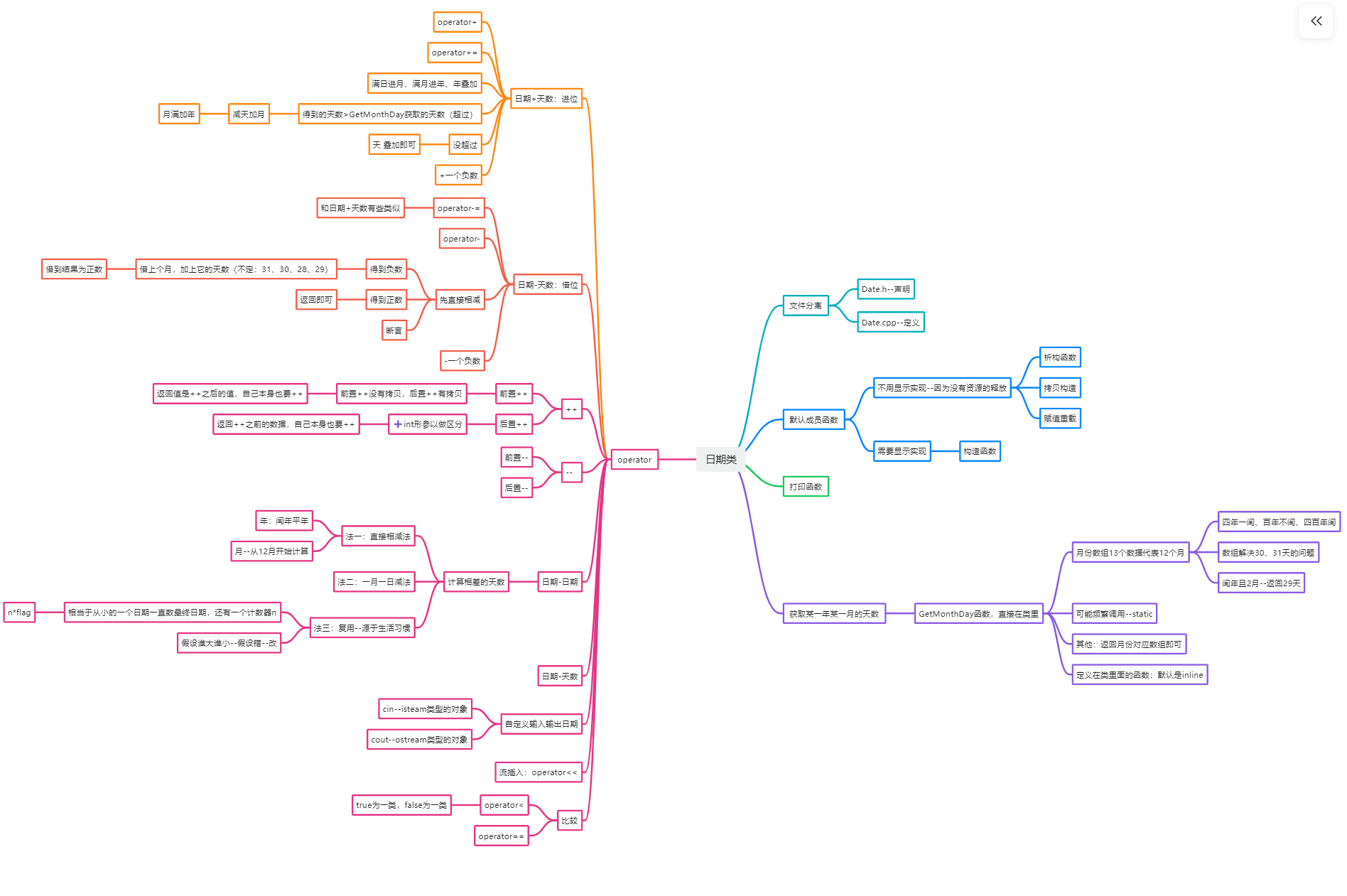
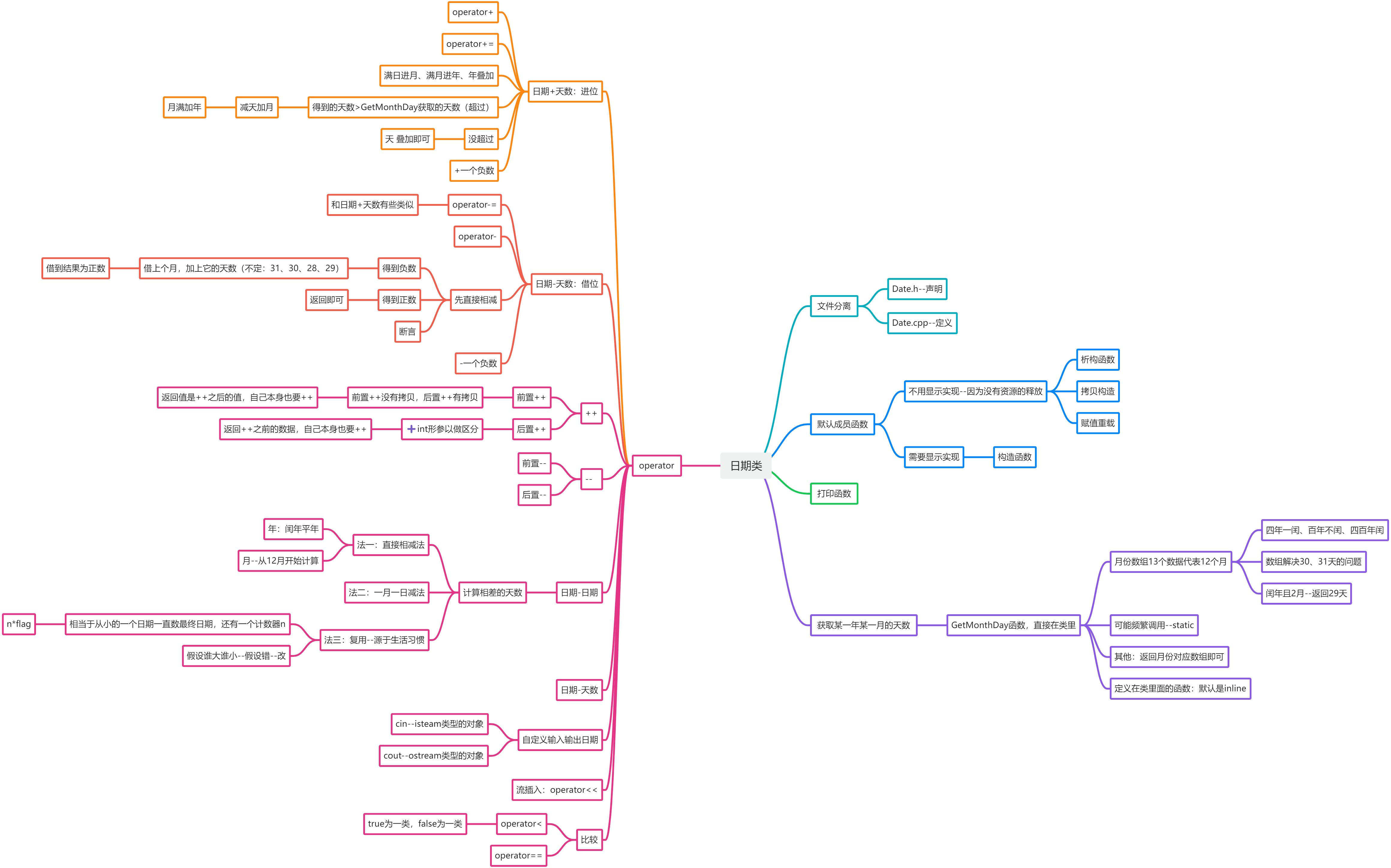
一、前期准备
1.1 检查构造的日期是否合法
bool Date::CheckDate()
{if (_month < 1 || _month > 12|| _day < 1 || _day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){return false;}else{return true;}
}Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;//防止构造的日期有问题if (!CheckDate()){cout << "非法日期:" << endl;Print();}
}
1.2 获取某年的某月的总天数
- 建议直接写在类里面作为成员函数:定义在类里面的成员函数默认是内联
inline,而且该函数不仅短小,还会被频繁调用;
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month){assert(month > 0 && month < 13);//避免出现非法月份??????static int GetMonthDayArray[13] = { -1,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))//先判断是否为2月{return 29;//闰年}return GetMonthDayArray[month];}
1.3 打印函数
void Date::Print()
{cout << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl;
}
二、日期+天数
2.1 operator+=
- 进位:
时间在向前先直接相加,日期不合法,减天加月,月满加年,直至日期合法。 - 返回值:返回
*this,所以使用引用返回。 - 注意:这里是
+=,而不是+。a+1:a本身不变;a+=1:a本身是会变的。
//日期+天数:d1+=100
Date& Date::operator+= (int day)
{//正常+:2024/7/12+10=2024/7/22_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))//判断日期是否非法{//时间在前进:_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//先减天++_month;//再加月,判断是否满月,满月进年if (_month == 13){_year++;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}
2.2 operator+
- 传值返回
- 直接写:
//d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+ (int day)
{Date tmp = *this;//这里拷贝一份出来tmp._day += day;while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)){tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);++tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 13){tmp._year++;tmp._month = 1;}}return tmp;//这里就不能使用引用返回了,局部对象,出作用域就会销毁
}
- 上面的是直接写的,也可以在写了
operator+=后,+复用+=:
//d1 + 100
Date Date::operator+ (int day)
{Date tmp = *this;//这里拷贝一份出来tmp += day;//复用+=return tmp;//这里就不能使用引用返回了,局部对象,出作用域就会销毁
}
三、日期-天数
3.1 operator-=
//d1 -= 100
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0)//判断出非法日期{--_month;//先借月if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//加上借来的}return *this;
}
3.2 operator-
- 直接实现:
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day<=0){--tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 0){tmp._month = 12;--tmp._year;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}return tmp;
}
-复用-=
//d1 - 100
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;tmp -= day;return tmp;
}
3.3 两种复用对比
-复用-=(相对较好)
//d1 -= 100
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;//拷贝1tmp -= day;return tmp;//拷贝2
}Date& Date::operator-=(int day)//无拷贝
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0)//判断出非法日期{--_month;//先借月if (_month == 0){_month = 12;--_year;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);//加上借来的}return *this;
}
-=复用-
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{Date tmp = *this;//拷贝1tmp._day -= day;while (tmp._day<=0){--tmp._month;if (tmp._month == 0){tmp._month = 12;--tmp._year;}tmp._day += GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month);}return tmp;//拷贝2
}Date& Date::operator-=(int day)//一次赋值拷贝
{/*Date tmp = *this - day;*this = tmp;*/*this = *this - day;//赋值也是一种拷贝return *this;
}
// 拷贝的次数比第一种多
- 两种
operator-的拷贝次数一样; - 第一种的
-=是自己实现的,全程无拷贝;但是第二种-=复用-:前面-的两次拷贝再加上自己本身的一次赋值拷贝。因此第一种相对较好。
四、日期比较
4.1 operator<
//d1 < d2
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d)
{//true为一类if (_year < d._year){return true;}else if (_year == d._year){if (_month < d._month){return true;}else if (_month == d._month){if (_day < d._day){return true;}}}//false为一类return false;
}
4.2 operator==
//d1 == d2
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day;
}
4.3 其他关系比较
在写了operator<(或者operator>)和operator=两个之后,就可以根据去翻等个侯总逻辑关系表示出其他的关系符。
//d1 <= d2
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d)
{//在写了前面两个之后:return *this < d || *this == d;
}bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{return !(*this <= d);
}bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this < d);
}bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d)
{return !(*this == d);
}
五、++
- 前置++用的比较多,而且拷贝比较少。
- 重载++运算符时,有前置++和后置++,运算符重载函数名都是``operator++
,无法很好的区分。C++规定,后置++重载时,增加一个int`形参,跟前置++构成函数重载,方便区分。
5.1 前置++
//1.前置++:d1.operator++()
Date Date::operator++()//没有拷贝
{//Date tmp = *this;*this += 1;return *this;//使用引用返回
}
5.2 后置++
//2.后置++:d1.operator++(0)(括号里面只要求整数)
Date& Date::operator++(int)//有拷贝
{Date tmp = *this;*this += 1;return tmp;
}
六、-- (和++相似)
6.1 前置–
//1.前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{//Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return *this;
}
6.2 后置–
//2.后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date tmp = *this;*this -= 1;return tmp;
}
八、所有代码
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;class Date
{
public:// 获取某年某月的天数int GetMonthDay(int year, int month) const{assert(month > 0 && month < 13);// 因为该函数会经常调用,但是数组的值一直是不需要变化的,因此可以使用静态数组// 好处是在静态区只会创建一份变量static int GetMonthDayArray[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };if ((month == 2) && ((year % 400 == 0) || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)))return 29;return GetMonthDayArray[month];}// 构造函数Date(int year, int month, int day);// 拷贝构造函数// d2(d1)Date(const Date& d);// 赋值运算符重载// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)// >运算符重载bool operator>(const Date& d) const;// ==运算符重载bool operator==(const Date& d) const;// >=运算符重载bool operator >= (const Date& d) const;// <运算符重载bool operator < (const Date& d) const;// <=运算符重载bool operator <= (const Date& d) const;// !=运算符重载bool operator != (const Date& d) const;// 操作赋值操作符Date& operator=(const Date& d);// 日期+=天数Date& operator+=(int day);// 日期+天数Date operator+(int day) const;// 日期-天数Date operator-(int day) const;// 日期-=天数Date& operator-=(int day);// 前置++Date& operator++();// 后置++Date operator++(int);// 后置--Date operator--(int);// 前置--Date& operator--();// 日期-日期 返回天数int operator-(const Date& d) const;
private:int _year;int _month;int _day;
};
Date.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Date.h"// 构造函数
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{_year = year;_month = month;_day = day;
}
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;
}
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{_year = d._year;_month = d._month;_day = d._day;return *this;
}// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{if (_year > d._year)return true;else if (_year == d._year){if (_month > d._month)return true;else if (_month == d._month){if (_day > d._day)return true;}}return false;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{return _year == d._year&& _month == d._month&& _day == d._day;
}
// >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d) const
{return *this > d || *this == d;
}
// <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d) const
{return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d) const
{return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d) const
{return !(*this == d);
}// 日期+=天数
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{_day += day;while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);++_month;if (_month == 13){++_year;_month = 1;}}return *this;
}
// 日期+天数 ---使用前面实现的+=运算符重载实现
//Date Date::operator+(int day) const
//{
// Date temp(*this);
// temp += day;
// return temp;
//}// 日期+天数 ---直接实现
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{Date temp(*this);temp._day += day;while (temp._day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)){temp._day -= GetMonthDay(temp._year, temp._month);++temp._month;if (temp._month == 13){++temp._year;temp._month = 1;}}return temp;
}
// 日期-=天数
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{_day -= day;while (_day <= 0){--_month;if (_month == 0){--_year;_month = 12;}_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);}return *this;
}
// 日期-天数 ---使用前面-=运算符重载实现
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{//Date temp(*this);Date temp(*this);temp -= day;return temp;
}//日期-天数 ---直接实现
//Date Date::operator-(int day) const
//{
// //Date temp(*this);
// Date temp(*this);
// temp._day -= day;
// while (temp._day <= 0)
// {
// --temp._month;
// if (temp._month == 0)
// {
// --temp._year;
// temp._month = 12;
// }
// temp._day += GetMonthDay(temp._year, temp._month);
// }
// return temp;
//}// 前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{*this += 1;return *this;
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int)
{Date temp(*this);*this += 1;return temp;
}
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{Date temp(*this);*this -= 1;return temp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{*this -= 1;return *this;
}// 日期-日期 返回天数
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{int flag = 1;Date max = *this;Date min = d;if (*this < d){flag = -1;max = d;min = *this;}int n = 0;while (min != max){min++;n++;}return n * flag;
}
喜欢的uu记得三连支持一下哦!

这篇关于【C++】日期类函数(时间计数器)从无到有实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






