本文主要是介绍C语言基础(十六),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
C语言中的结构体(Struct)是一种用户自定义的数据类型,允许将不同类型的数据项组合成一个单一的类型:
测试代码1:
#include "date.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // 定义衣服结构体
struct Clothes { char name[50]; // 衣服名称 char color[20]; // 衣服颜色 int size; // 尺码 float price; // 价格
}; int main() { int time = getTime();// 创建衣服结构体数组 struct Clothes clothes[3]; // 使用"."访问并设置每件衣服的信息 strcpy(clothes[0].name, "衬衫"); strcpy(clothes[0].color, "白色"); clothes[0].size = 39; clothes[0].price = 59.99; strcpy(clothes[1].name, "牛仔裤"); strcpy(clothes[1].color, "蓝色"); clothes[1].size = 32; clothes[1].price = 99.99; strcpy(clothes[2].name, "外套"); strcpy(clothes[2].color, "黑色"); clothes[2].size = 42; clothes[2].price = 159.99; // 遍历数组并打印每件衣服的信息 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { printf("衣服名称: %s\n", clothes[i].name); printf("衣服颜色: %s\n", clothes[i].color); printf("尺码: %d\n", clothes[i].size); printf("价格: %.2f\n\n", clothes[i].price); } return 0;
}运行结果如下:
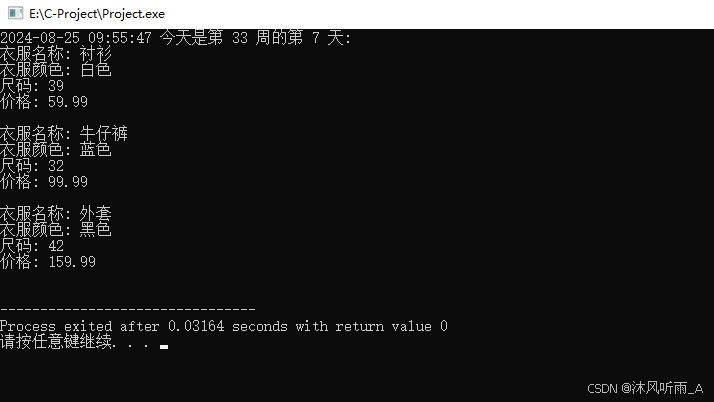
测试代码2:
#include"date.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h> // 定义衣服结构体
struct Clothes { char name[50]; // 衣服名称 char color[20]; // 衣服颜色 int size; // 尺码(假设用整数表示不同尺码) float price; // 价格
}; int main() { int time = getTime();// 创建衣服结构体变量 struct Clothes shirt; // 使用"."访问并设置shirt的成员 strcpy(shirt.name, "衬衫"); strcpy(shirt.color, "白色"); shirt.size = 39; shirt.price = 59.99; // 打印shirt的信息 printf("衣服名称: %s\n", shirt.name); printf("衣服颜色: %s\n", shirt.color); printf("尺码: %d\n", shirt.size); printf("价格: %.2f\n", shirt.price); // 定义一个指向衣服的指针 struct Clothes *ptr = &shirt; // 使用"->"访问并打印ptr指向的衣服的信息 printf("通过指针访问的衣服名称: %s\n", ptr->name); printf("通过指针访问的衣服颜色: %s\n", ptr->color); printf("通过指针访问的尺码: %d\n", ptr->size); printf("通过指针访问的价格: %.2f\n", ptr->price); return 0;
}运行结果如下:
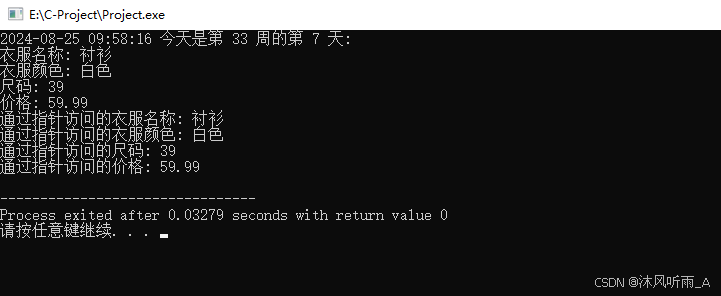
测试代码3:
#include "date.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <limits.h>
// 定义运动员结构体
typedef struct { int id; char name[50]; float height; float weight;
} Athlete; bool read_integer(const char *prompt, int *value) { while (true) { printf("%s", prompt); if (scanf("%d", value) == 1) { // 成功读取一个整数 return true; } // 清除输入缓冲区中的错误输入 int c; while ((c = getchar()) != EOF && c != '\n'); // 提示重新输入 printf("输入无效,请输入一个整数:"); }
} bool read_float(const char *prompt, float *value) { while (true) { printf("%s", prompt); if (scanf("%f", value) == 1) { // 成功读取一个浮点数 return true; } // 清除输入缓冲区中的错误输入 int c; while ((c = getchar()) != EOF && c != '\n'); // 提示重新输入 printf("输入无效,请输入一个浮点数:"); }
} bool read_string(const char *prompt, char *buffer, size_t bufsize) { printf("%s", prompt); if (fgets(buffer, bufsize, stdin) == NULL) { // fgets失败return false; } // 去除字符串末尾的换行符(如果有的话) size_t len = strlen(buffer); if (len > 0 && buffer[len - 1] == '\n') { buffer[len - 1] = '\0'; } // fgets总是读取一行 // 如果需要验证字符串内容(比如非空),可以在这里实现。 return true;
} int main() { int time = getTime();Athlete athlete; int n; if (!read_integer("请输入运动员数量: ", &n) || n <= 0) { fprintf(stderr, "无效的运动员数量。\n"); return 1; } for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { printf("请输入第 %d 个运动员的信息:\n", i + 1); if (!read_integer(" ID: ", &athlete.id)) { fprintf(stderr, "无法读取运动员ID。\n"); continue; // 或者退出循环/程序 } if (!read_float(" 身高(米): ", &athlete.height) || athlete.height < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "无效的身高值。\n"); continue; } if (!read_float(" 体重(公斤): ", &athlete.weight) || athlete.weight < 0) { fprintf(stderr, "无效的体重值。\n"); continue; } if (!read_string(" 姓名: ", athlete.name, sizeof(athlete.name))) { fprintf(stderr, "无法读取运动员姓名。\n"); continue; } // 打印运动员信息或将其添加到数据结构中 printf("运动员ID: %d, 姓名: %s, 身高: %.2f米, 体重: %.2f公斤\n", athlete.id, athlete.name, athlete.height, athlete.weight); } return 0;
}运行结果如下:
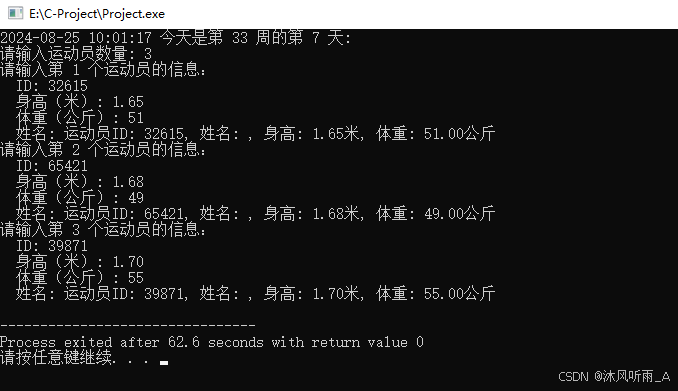
这篇关于C语言基础(十六)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




