本文主要是介绍Go反射四讲---第一讲:什么是反射,反射常用的API,反射三原则以及注意事项,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
反射-引入
这是我们反射四讲的第一讲,本次主要向大家介绍一下反射的基础概念以及相关的API。
在计算机科学中,反射是指计算机程序能够在运行时可以访问,检测和修改本身状态或者行为的一种能力。
简单的来说,反射就是程序在运行时能够动地查看自己的状态,并允许修改自身的行为。
首先,要明白对于一个类型变量。它有两层含义,一是类型是什么,二是存储的值是什么。类型决定了变量的存储方式,支持的操作和方法等。值无外乎是读与写,在存储是以0,1格式存放,并使用类型加以约束。类型和值不是孤立存在的。
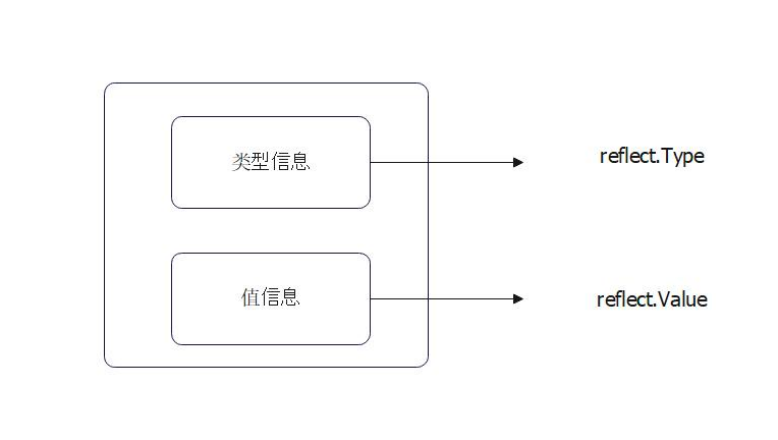
反射的相关API都在 reflect 包中,最核心的就是reflect.Value和reflect.Type。
其中,reflect.Value用于操作值,部分值是可以被反射修改的。reflect.Type用于操作类型信息。类型信息是只能读取的。
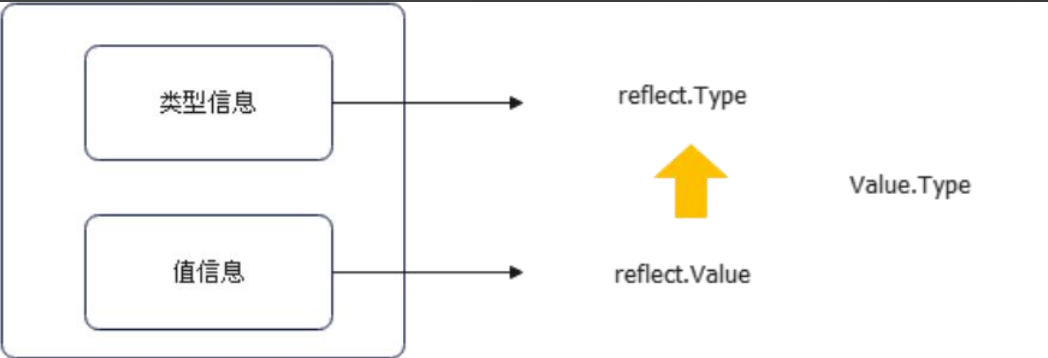
注意:reflect.Type可以通过reflect.Value得到,但是反过来不行。

reflect.Type
func TypeOf(i any) Type
//type any = interface{}
形参是一个空接口类型,返回值是一个 Type 接口类型。
注意:reflect包有一个很强的的假设,我们必须我们要操作的是什么Kind。
Kind是一个枚举值,用来判断操作的对应类型。例如是否是指针,是否是数组,是否是切片等。
如果使用不当就会引起 panic。so,在调用API之前,我们一定要先读注释,确认什么情况下可以使用!!!
接下来,讲解一下 Type 接口提供的主要通用方法。
类型的通用方法
// Name returns the type's name within its package for a defined type.
Name() string// Kind returns the specific kind of this type.
Kind() Kind// Implements reports whether the type implements the interface type u.
Implements(u Type) bool// AssignableTo reports whether a value of the type is assignable to type u.
AssignableTo(u Type) bool// ConvertibleTo reports whether a value of the type is convertible to type u.
ConvertibleTo(u Type) bool// Comparable reports whether values of this type are comparable.
Comparable() bool// NumMethod returns the number of methods accessible using Method.
NumMethod() int// Method returns the i'th method in the type's method set.
Method(int) Method// MethodByName returns the method with that name in the type's
// method set and a boolean indicating if the method was found.
MethodByName(string) (Method, bool)// PkgPath returns a defined type's package path, that is, the import path
PkgPath() string// Size returns the number of bytes needed to store
Size() uintptr
类型的专有方法
type Type interface {
// Elem returns a type's element type.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Array, Chan, Map, Pointer, or Slice.
Elem() Type// Bits returns the size of the type in bits.
Bits() int// Len returns an array type's length.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Array.
Len() int// struct 专有的方法// NumField returns a struct type's field count.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Struct.
NumField() int// Field returns a struct type's i'th field.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Struct.
// It panics if i is not in the range [0, NumField()).
Field(i int) StructField// FieldByIndex returns the nested field corresponding
// to the index sequence. It is equivalent to calling Field
// successively for each index i.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Struct.
FieldByIndex(index []int) StructField// FieldByName returns the struct field with the given name
// and a boolean indicating if the field was found.
// If the returned field is promoted from an embedded struct,
// then Offset in the returned StructField is the offset in
// the embedded struct.
FieldByName(name string) (StructField, bool)// FieldByNameFunc returns the struct field with a name
// that satisfies the match function and a boolean indicating if
// the field was found.
FieldByNameFunc(match func(string) bool) (StructField, bool)// func 专有的方法// IsVariadic reports whether a function type's final input parameter
// IsVariadic panics if the type's Kind is not Func.
IsVariadic() bool// In returns the type of a function type's i'th input parameter.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Func.
// It panics if i is not in the range [0, NumIn()).
In(i int) Type// NumIn returns a function type's input parameter count.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Func.
NumIn() int// NumOut returns a function type's output parameter count.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Func.
NumOut() int// map 专有的方法// Key returns a map type's key type.
// It panics if the type's Kind is not Map.
Key() Type
}
reflect.Value
reflect.Value 表示的是实例的值信息。reflect.Value是一个 struct,并且提供了一系列的 method 。
func ValueOf(i any) Value
//type Value struct {
// typ_ *abi.Type //值的指针类型typ
// ptr unsafe.Pointer // 指向值的指针ptr
// flag //标记字段
//}
注意:这里一定要搞清与Type的区别,Type 直接返回接口,Value 返回的是结构体,而在结构体上绑定了一些方法。
下面我们介绍几个常用的在 Value 结构体上绑定的方法。
// CanAddr reports whether the value's address can be obtained with [Value.Addr].
func (v Value) CanAddr() bool {}// Addr returns a pointer value representing the address of v.
func (v Value) Addr() Value {}// CanSet reports whether the value of v can be changed.
func (v Value) CanSet() bool {}// Elem returns the value that the interface v contains
// or that the pointer v points to.
func (v Value) Elem() Value {}// Field returns the i'th field of the struct v.
func (v Value) Field(i int) Value {}// Bool returns v's underlying value.
func (v Value) Bool() bool {}// Bytes returns v's underlying value.
func (v Value) Bytes() []byte {} // Index returns v's i'th element.
func (v Value) Index(i int) Value {}
这里方法我们没有讲解全面,如果想了解源码内容,可以去 reflect 包下的 value.go 下查看。
反射的原则
下图展示了实例,Type与Value三者之间的关系。
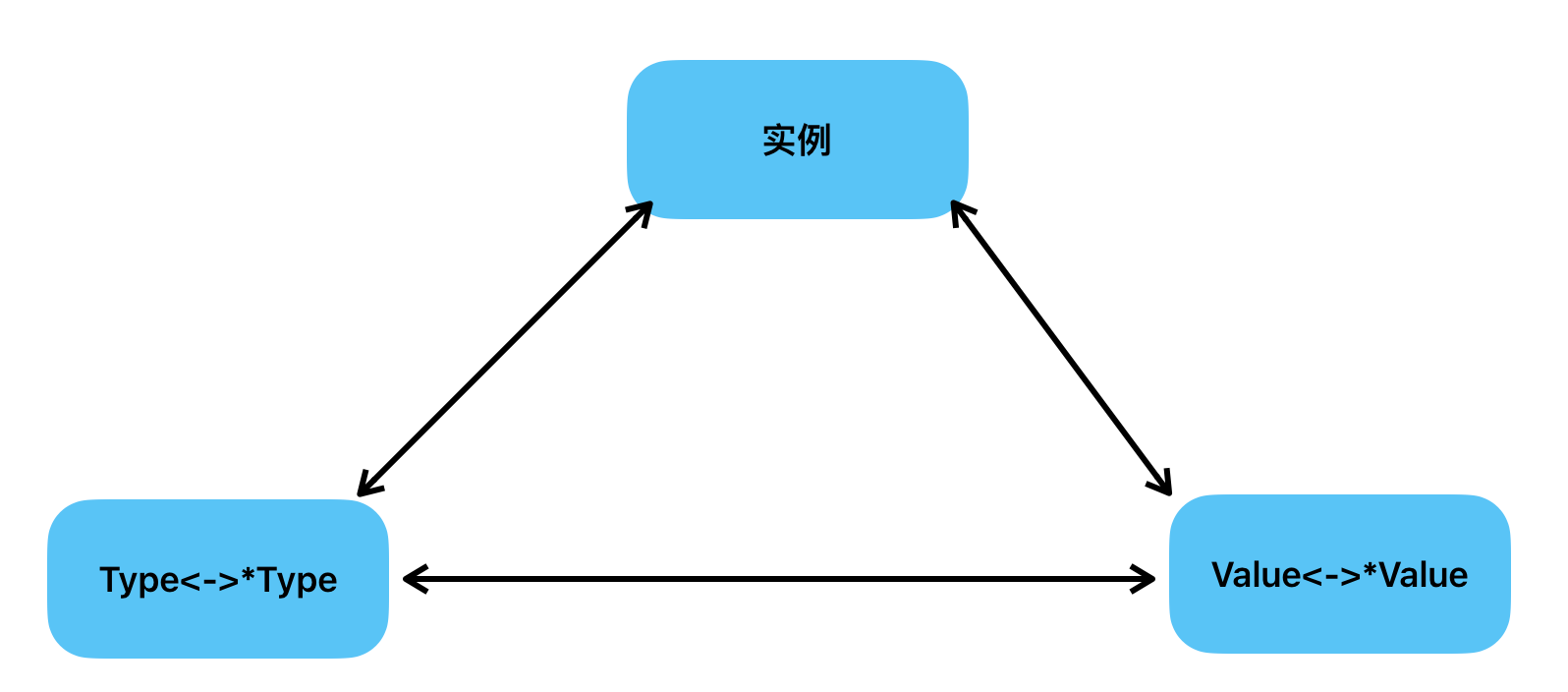
API使用总结:
-
实例到
Value。使用实例获取对象的Value,直接使用reflect.ValueOf()函数。 -
实例到
Type。使用实例获取对象的Type, 直接使用reflect.TypeOf()函数。 -
Type到Value。无法直接从一个Type接口变量获取实例的Value。一般先使用Type构建一个新的实例Value。第一种,使用
func New(typ Type) Value创建一个Value,Value的Type是一个指定的typ的指针类型。第二种,使用
func Zero(typ Type) Value创建一个Value,注意此时的Value不能寻址,意味着值不可以变。第三种,如果知道一个值的底层存放地址,可以使用
func NewAt(typ Type, p unsafe.Pointer) Value来恢复Value。此处的typ是实例类型,p是实例的地址。 -
Value到Type。直接可以调用Value结构体上绑定的func (v Value) Type() Type {}方法。 -
Value到实例。可以使用通用方法func (v Value) Interface() (i any) {}直接返回实例。 -
Value指针到值。使用func (v Value) Elem() Value {}返回值。注意:如果类型是接口,则Elem()返回接口绑定的实例的Value,如果类型是指针,则返回指针值的Value,否则引起panic。 -
Type指针到Type值。使用Elem() Type返回子元素的Type。 -
Type值到Type指针。使用func PtrTo(t Type) Type {},返回指向t的指针类型Type。 -
值的可修改性。可以使用
func (v Value) CanSet() bool {}去判断一个值是否可以修改,如果可以修改返回true。接着可以使用func (v Value) Set(x Value)去设置一个值。
总结
本次,带领大家了解反射的基本概念,如何使用等。待熟悉相关的API之后,下一次,我们将展示给您如何在实战中使用reflect包。
参考
- 《Go语言核心编程》-- 李文塔
- https://pkg.go.dev/reflect
这篇关于Go反射四讲---第一讲:什么是反射,反射常用的API,反射三原则以及注意事项的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


