本文主要是介绍FFmpeg源码:AV_RB32宏定义分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、AV_RB32宏定义的作用
AV_RB32是FFmpeg源码中经常出现的一个宏,其定义如下:
#ifndef AV_RB32
# define AV_RB32(p) AV_RB(32, p)
#endif该宏定义有多层。把它简化为函数,其函数声明可以等价于:
uint32_t AV_RB32(uint8_t *data);该函数作用是:按照大端模式 读取形参data指向的缓冲区的前四个字节,并返回。
形参data:输入型参数。指向某个缓冲区。
返回值:按照大端模式 读取到的 “形参data指向的缓冲区的前四个字节”。
二、AV_RB32宏定义的内部实现
FFmpeg源码目录下的libavutil/intreadwrite.h 中存在如下宏定义:
#ifndef AV_RB32
# define AV_RB32(p) AV_RB(32, p)
#endif#ifndef AV_RN32
# define AV_RN32(p) AV_RN(32, p)
#endif# define AV_RB(s, p) av_bswap##s(AV_RN##s(p))# define AV_RN(s, p) (((const union unaligned_##s *) (p))->l)union unaligned_32 { uint32_t l; } __attribute__((packed)) av_alias;libavutil/attributes.h 中存在如下宏定义:
#ifdef __GNUC__
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) (__GNUC__ > (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= (y))
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) (__GNUC__ < (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ <= (y))
#else
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) 0
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) 0
#endif#define av_alias __attribute__((may_alias))#ifndef av_always_inline
#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(3,1)
# define av_always_inline __attribute__((always_inline)) inline
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
# define av_always_inline __forceinline
#else
# define av_always_inline inline
#endif
#endif#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(2,6) || defined(__clang__)
# define av_const __attribute__((const))
#else
# define av_const
#endif所以 # define AV_RB32(p) AV_RB(32, p) 等价于 =>
# define AV_RB32(p) av_bswap32(AV_RN(32, p)) 等价于 =>
# define AV_RB32(p) av_bswap32((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l))
libavutil/bswap.h 中存在如下宏定义:
#define AV_BSWAP16C(x) (((x) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((x) >> 8 & 0x00ff))
#define AV_BSWAP32C(x) (AV_BSWAP16C(x) << 16 | AV_BSWAP16C((x) >> 16))#ifndef av_bswap32
static av_always_inline av_const uint32_t av_bswap32(uint32_t x)
{return AV_BSWAP32C(x);
}
#endif所以AV_BSWAP32C(x) 等价于 =>
(AV_BSWAP16C(x) << 16 | AV_BSWAP16C((x) >> 16)) 等价于 =>
( (((x) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((x) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) << 16 | ((((x) >> 16) << 8 & 0xff00) | (((x) >> 16) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) )
所以
static av_always_inline av_const uint32_t av_bswap32(uint32_t x)
{return AV_BSWAP32C(x);
}等价于 =>
static __attribute__((always_inline)) inline __attribute__((const)) uint32_t av_bswap32(uint32_t x)
{return ( (((x) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((x) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) << 16 | ((((x) >> 16) << 8 & 0xff00) | (((x) >> 16) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) );
}
所以 AV_RB32(p); 等价于 =>
av_bswap32((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l)); 等价于 =>
( ((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l)) << 8 & 0xff00) | (((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l)) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) << 16 | (((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l)) >> 16) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (p))->l)) >> 16) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) );三、编写测试例子,测试AV_RB32
main.c :
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>#ifdef __GNUC__
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) (__GNUC__ > (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ >= (y))
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) (__GNUC__ < (x) || __GNUC__ == (x) && __GNUC_MINOR__ <= (y))
#else
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(x,y) 0
# define AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_MOST(x,y) 0
#endif#define av_alias __attribute__((may_alias))#ifndef av_always_inline
#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(3,1)
# define av_always_inline __attribute__((always_inline)) inline
#elif defined(_MSC_VER)
# define av_always_inline __forceinline
#else
# define av_always_inline inline
#endif
#endif#if AV_GCC_VERSION_AT_LEAST(2,6) || defined(__clang__)
# define av_const __attribute__((const))
#else
# define av_const
#endif#define AV_BSWAP16C(x) (((x) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((x) >> 8 & 0x00ff))
#define AV_BSWAP32C(x) (AV_BSWAP16C(x) << 16 | AV_BSWAP16C((x) >> 16))#ifndef av_bswap32
static av_always_inline av_const uint32_t av_bswap32(uint32_t x)
{return AV_BSWAP32C(x);
}
#endifunion unaligned_32 { uint32_t l; } __attribute__((packed)) av_alias;# define AV_RN(s, p) (((const union unaligned_##s *) (p))->l)
# define AV_RB(s, p) av_bswap##s(AV_RN##s(p))#ifndef AV_RB32
# define AV_RB32(p) AV_RB(32, p)
#endif#ifndef AV_RN32
# define AV_RN32(p) AV_RN(32, p)
#endifint main()
{uint8_t *data = (uint8_t *)malloc(sizeof(uint8_t) * 8);if(data){data[0] = 0x12;data[1] = 0x34;data[2] = 0x56;data[3] = 0x78;data[4] = 0x9A;data[5] = 0xBC;data[6] = 0xDE;data[7] = 0xF0;printf("%lu\n", AV_RB32(data));printf("%lu\n", AV_RB32(data + 4));free(data);data = NULL;}return 0;
}Linux平台下使用gcc编译(我用的是CentOS 7.5,通过10.2.1版本的gcc编译)。输出为:
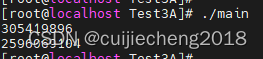
由于AV_RB32是按照大端模式读取。而data[0] = 0x12,data[1] = 0x34,data[2] = 0x56,data[3] = 0x78; 所以AV_RB32(data) 的值为0x12345678,换算成10进制就是305419896。
data[4] = 0x9A;data[5] = 0xBC;data[6] = 0xDE;data[7] = 0xF0;所以AV_RB32(data + 4) 的值为0x9ABCDEF0,换算成10进制就是2596069104。
AV_RB32(data) 将宏展开,实际就是:
( ((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (data))->l)) << 8 & 0xff00) | (((((const union unaligned_32 *) (data))->l)) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) << 16 | (((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (data))->l)) >> 16) << 8 & 0xff00) | ((((((const union unaligned_32 *) (data))->l)) >> 16) >> 8 & 0x00ff)) )四、参考文章
《大小端模式》
这篇关于FFmpeg源码:AV_RB32宏定义分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



