本文主要是介绍Spring(十三)JDBC相关概念、事务隔离级别、事务传播属性、事务管理及Spring整合JDBC,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
数据库系统提供了四种事务隔离级别供用户选择。不同的隔离级别采用不同的锁类型来实现,在四种隔离级别中,Serializable的隔离级别最高,Read Uncommited的隔离级别最低。大多数据库默认的隔离级别为Read Commited,如SQL Server,当然也有少部分数据库默认的隔离级别为Repeatalbe Read,如MySQL
- Read Uncommited:读未提交数据(会出现脏读,不可重复读和幻读)
- Read Commited:读已提交数据(会出现不可重复读和幻读)
- Repeatable Read:可重复读(会出现幻读)
- Serializable:串行化
不可重复读:在同一事务中,多次读取同一数据返回的结果有所不同。换句话说就是,后续读取可以读到另一事务已提交的更新数据。相反,“可重复读”在同一事务中多次读取数据时,能够保证所读数据一样,也就是,后续读取不能读到另一事务已提交的更新数据。
幻读:一个事务读取到另一事务已提交的insert数据。
事务传播属性
- REQUIRED:业务方法需要在一个事务中运行。如果方法运行时,已经处在一个事务中,那么加入到该事务,否则为自己创建一个新的事务。
- NOT_SUPPORTED:声明方法不需要事务。如果方法没有关联到一个事务,容器不会为它开启事务。如果方法在一个事务中被调用,该事务会被挂起,在方法调用结束后,原先的事务便会恢复执行。
- REQUIRESNEW:属性表明不管是否存在事务,业务方法总会为自己发起一个新的事务。如果方法已经运行在一个事务中,则原有事务会被挂起,新的事务会被创建,直到方法执行结束,新事务才算结束,原先的事务才会恢复执行。
- MANDATORY:该属性指定业务方法只能在一个已经存在的事务中执行,业务方法不能发起自己的事务。如果业务方法在没有事务的环境下调用,容器就会抛出例外。
- SUPPORTS:这一事务属性表明,如果业务方法在某个事务范围内被调用,则方法成为该事务的一部分。如果业务方法在事务范围外被调用,则方法在没有事务的环境下执行。
- Never:指定业务方法绝对不能在事务范围内执行。如果业务方法在某个事务中执行,容器会抛出例外,只有业务方法没有关联到任何事务,才能正常执行。
- NESTED:如果一个活动的事务存在,则运行在一个嵌套的事务中,如果没有活动事务,则按REQUIRED属性执行,它使用了一个单独的事务,这个事务拥有多个可以回滚的保存点。内部事务的回滚不会对外部事务造成影响。它只对DataSourceTransactionManager事务管理器起效。
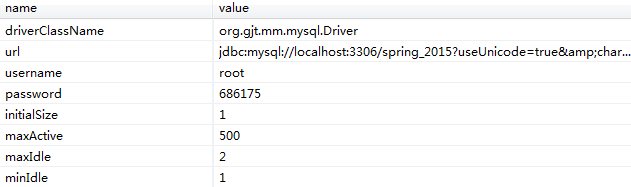
做开发不连接数据库怎么行!Spring整合JDBC过程中,数据源可以直接都在beans.xml里配置,也可以把数据单独放在一个properties文件里,方便维护。
首先放入各种jar包,连接MySQL当然要放数据驱动文件。
jar包什么的对照项目截图,切面aspect和cglib在这个工程没用到,jar包可以不添加进来
beans.xml,在头文件加上tx事务相关的引用,其他要注意的在文件的注释里基本都点到了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beanshttp://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/contexthttp://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-2.5.xsdhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/txhttp://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd"><!-- 加上classpath明确指定配置文件在类路径底下 --><context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties" /><bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"destroy-method="close"><!-- 可以把这些配置信息放在同一个配置文件里面 --><!-- <property name="driverClassName" value="org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver" /> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_2015?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="686175"/> <property name="initialSize" value="1" /> <property name="maxActive" value="500"/> <property name="maxIdle" value="2"/> <property name="minIdle" value="1"/> --><property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}" /><property name="url" value="${url}" /><property name="username" value="${username}" /><property name="password" value="${password}" /><property name="initialSize" value="${initialSize}" /><property name="maxActive" value="${maxActive}" /><property name="maxIdle" value="${maxIdle}" /><property name="minIdle" value="${minIdle}" /></bean><bean id="txManager"class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" /></bean><!-- 采用@Transaction注解方式使用事务 --><tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager" /><!-- 将PersonServiceImpl交给Spring管理 --><bean id="personService" class="test.spring.service.impl.PersonServiceImpl"><!-- 通过xml的方式对数据源进行注入 --><property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property></bean>
</beans>
jdbc.properties
driverClassName=org.gjt.mm.mysql.Driver
url=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/spring_2015?useUnicode\=true&characterEncoding\=UTF-8
username=root
password=686175
initialSize=1
maxActive=500
maxIdle=2
minIdle=1
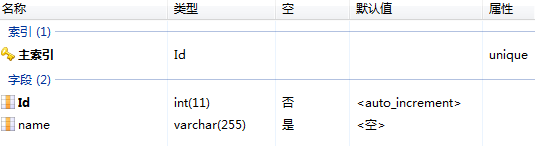
测试用到的数据库spring_2015,表person
实体类
package test.spring.entity;public class Person {private Integer id;private String name;public Person() {}public Person(String name) {super();this.name = name;}public Integer getId() {return id;}public void setId(Integer id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubreturn "[Person:id = " + id + ",name = " + name + "]";}}
package test.spring.service.impl;import java.util.List;import javax.sql.DataSource;import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;import test.spring.entity.Person;
import test.spring.service.PersonService;@Transactional
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {// private DataSource dataSource;private JdbcTemplate jTemplate;public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {// this.dataSource = dataSource;this.jTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);}@Overridepublic void save(Person person) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubjTemplate.update("insert into person(name) values(?)",new Object[] { person.getName() },new int[] { java.sql.Types.VARCHAR });}@Overridepublic void update(Person person) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubjTemplate.update("update person set name=? where id=?", new Object[] {person.getName(), person.getId() }, new int[] {java.sql.Types.VARCHAR, java.sql.Types.INTEGER });}@Overridepublic Person getPerson(Integer personId) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubPerson person = (Person) jTemplate.queryForObject("select * from person where id=?", new Object[] { personId },new int[] { java.sql.Types.INTEGER }, new PersonRowMapper());return person;}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")@Overridepublic List<Person> getPersons() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubList<Person> persons = jTemplate.query("select * from person",new PersonRowMapper());return persons;}@Overridepublic void delete(Integer personId) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubjTemplate.update("delete from person where id=?",new Object[] { personId },new int[] { java.sql.Types.INTEGER });}}
各个方法的测试
package test.spring.junit;import static org.junit.Assert.*;import java.util.List;import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;import test.spring.entity.Person;
import test.spring.service.PersonService;public class SpringAndJDBCTest {private static PersonService pService;@BeforeClasspublic static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception {AbstractApplicationContext aContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");pService = (PersonService) aContext.getBean("personService");}@Testpublic void testSave() {pService.save(new Person("LinDL"));}@Testpublic void testGetPerson() {Person person = pService.getPerson(1);System.out.println(person.getName());}@Testpublic void testGetPersons() {List<Person> list = pService.getPersons();for (Person person : list) {System.out.println(person);}}@Testpublic void testUpdate() {Person person = pService.getPerson(1);person.setName("张大春");pService.update(person);}@Testpublic void testDelete() {pService.delete(1);}}
这篇关于Spring(十三)JDBC相关概念、事务隔离级别、事务传播属性、事务管理及Spring整合JDBC的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!