本文主要是介绍一文读懂Kubernetes Scheduler扩展功能,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
Scheduler是Kubernetes组件中功能&逻辑相对单一&简单的模块,它主要的作用是:watch kube-apiserver,监听PodSpec.NodeName为空的pod,并利用预选和优选算法为该pod选择一个最佳的调度节点,最终将pod与该节点进行绑定,使pod调度在该节点上运行
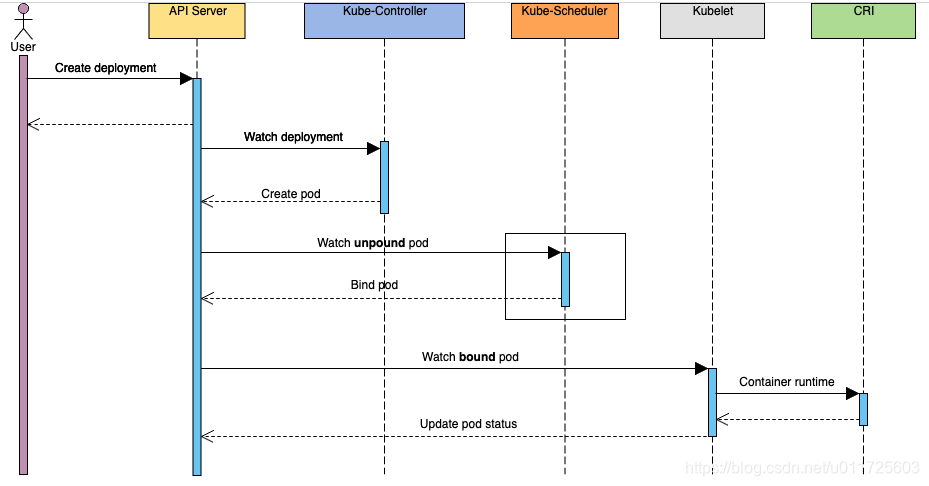
展开上述调用流程中的scheduler部分,内部细节调用(参考Kubernetes Scheduler)如图所示:
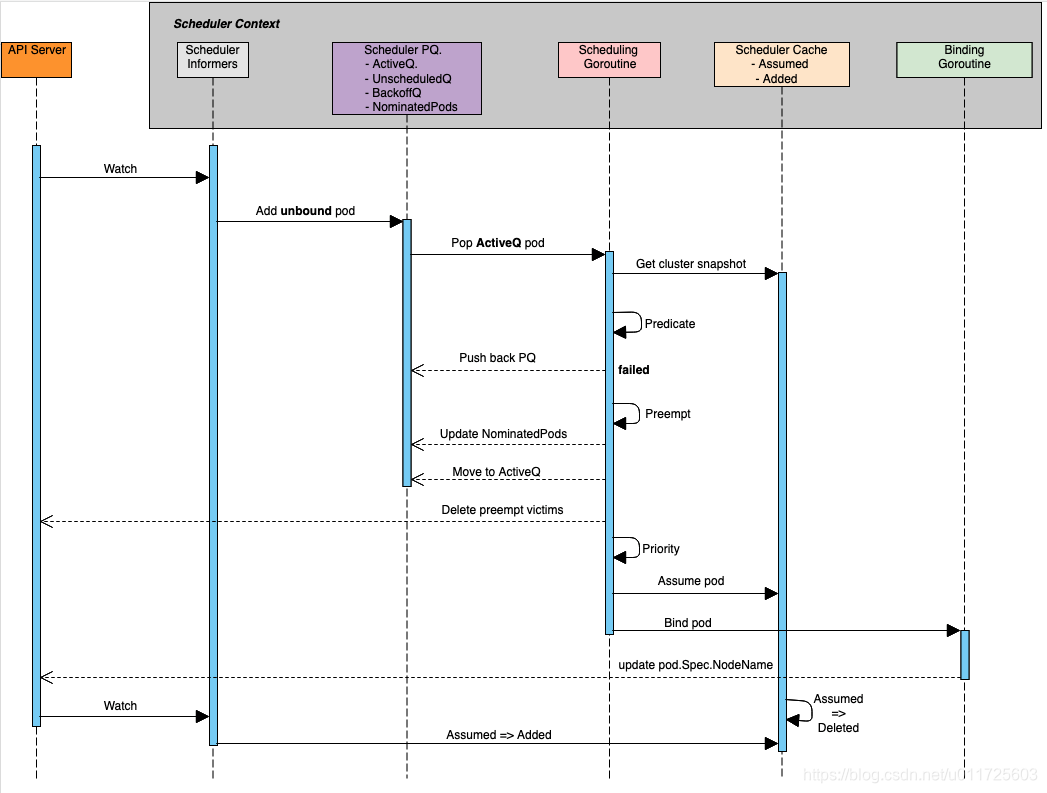
scheduler内部预置了很多预选和优选算法(参考scheduler_algorithm),比如预选:NoDiskConflict,PodFitsResources,MatchNodeSelector,CheckNodeMemoryPressure等;优选:LeastRequestedPriority,BalancedResourceAllocation,CalculateAntiAffinityPriority,NodeAffinityPriority等。但是在实际生产环境中我们常常会需要一些特殊的调度策略,比如批量调度(aka coscheduling or gang scheduling),这是kubernetes默认调度策略所无法满足的,这个时候就需要我们对scheduler进行扩展来实现这个功能了
scheduler扩展方案
目前Kubernetes支持四种方式实现客户自定义的调度算法(预选&优选),如下:
- default-scheduler recoding: 直接在Kubernetes默认scheduler基础上进行添加,然后重新编译kube-scheduler
- standalone: 实现一个与kube-scheduler平行的custom scheduler,单独或者和默认kube-scheduler一起运行在集群中
- scheduler extender: 实现一个"scheduler extender",kube-scheduler会调用它(http/https)作为默认调度算法(预选&优选&bind)的补充
- scheduler framework: 实现scheduler framework plugins,重新编译kube-scheduler,类似于第一种方案,但是更加标准化,插件化
下面分别展开介绍这几种方式的原理和开发指引
default-scheduler recoding
这里我们先分析一下kube-scheduler调度相关入口:
- 设置默认预选&优选策略
见defaultPredicates以及defaultPriorities(k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/defaults.go):
func init() {registerAlgorithmProvider(defaultPredicates(), defaultPriorities())
}func defaultPredicates() sets.String {return sets.NewString(predicates.NoVolumeZoneConflictPred,predicates.MaxEBSVolumeCountPred,predicates.MaxGCEPDVolumeCountPred,predicates.MaxAzureDiskVolumeCountPred,predicates.MaxCSIVolumeCountPred,predicates.MatchInterPodAffinityPred,predicates.NoDiskConflictPred,predicates.GeneralPred,predicates.PodToleratesNodeTaintsPred,predicates.CheckVolumeBindingPred,predicates.CheckNodeUnschedulablePred,)
}func defaultPriorities() sets.String {return sets.NewString(priorities.SelectorSpreadPriority,priorities.InterPodAffinityPriority,priorities.LeastRequestedPriority,priorities.BalancedResourceAllocation,priorities.NodePreferAvoidPodsPriority,priorities.NodeAffinityPriority,priorities.TaintTolerationPriority,priorities.ImageLocalityPriority,)
}func registerAlgorithmProvider(predSet, priSet sets.String) {// Registers algorithm providers. By default we use 'DefaultProvider', but user can specify one to be used// by specifying flag.scheduler.RegisterAlgorithmProvider(scheduler.DefaultProvider, predSet, priSet)// Cluster autoscaler friendly scheduling algorithm.scheduler.RegisterAlgorithmProvider(ClusterAutoscalerProvider, predSet,copyAndReplace(priSet, priorities.LeastRequestedPriority, priorities.MostRequestedPriority))
}const (// DefaultProvider defines the default algorithm provider name.DefaultProvider = "DefaultProvider"
)
- 注册预选和优选相关处理函数
注册预选函数(k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/register_predicates.go):
func init() {...// Fit is determined by resource availability.// This predicate is actually a default predicate, because it is invoked from// predicates.GeneralPredicates()scheduler.RegisterFitPredicate(predicates.PodFitsResourcesPred, predicates.PodFitsResources)
}
注册优选函数(k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithmprovider/defaults/register_priorities.go):
func init() {...// Prioritizes nodes that have labels matching NodeAffinityscheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.NodeAffinityPriority, priorities.CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityMap, priorities.CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityReduce, 1)
}
- 编写预选和优选处理函数
PodFitsResourcesPred对应的预选函数如下(k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithm/predicates/predicates.go):
// PodFitsResources checks if a node has sufficient resources, such as cpu, memory, gpu, opaque int resources etc to run a pod.
// First return value indicates whether a node has sufficient resources to run a pod while the second return value indicates the
// predicate failure reasons if the node has insufficient resources to run the pod.
func PodFitsResources(pod *v1.Pod, meta Metadata, nodeInfo *schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo) (bool, []PredicateFailureReason, error) {node := nodeInfo.Node()if node == nil {return false, nil, fmt.Errorf("node not found")}var predicateFails []PredicateFailureReasonallowedPodNumber := nodeInfo.AllowedPodNumber()if len(nodeInfo.Pods())+1 > allowedPodNumber {predicateFails = append(predicateFails, NewInsufficientResourceError(v1.ResourcePods, 1, int64(len(nodeInfo.Pods())), int64(allowedPodNumber)))}// No extended resources should be ignored by default.ignoredExtendedResources := sets.NewString()var podRequest *schedulernodeinfo.Resourceif predicateMeta, ok := meta.(*predicateMetadata); ok && predicateMeta.podFitsResourcesMetadata != nil {podRequest = predicateMeta.podFitsResourcesMetadata.podRequestif predicateMeta.podFitsResourcesMetadata.ignoredExtendedResources != nil {ignoredExtendedResources = predicateMeta.podFitsResourcesMetadata.ignoredExtendedResources}} else {// We couldn't parse metadata - fallback to computing it.podRequest = GetResourceRequest(pod)}if podRequest.MilliCPU == 0 &&podRequest.Memory == 0 &&podRequest.EphemeralStorage == 0 &&len(podRequest.ScalarResources) == 0 {return len(predicateFails) == 0, predicateFails, nil}allocatable := nodeInfo.AllocatableResource()if allocatable.MilliCPU < podRequest.MilliCPU+nodeInfo.RequestedResource().MilliCPU {predicateFails = append(predicateFails, NewInsufficientResourceError(v1.ResourceCPU, podRequest.MilliCPU, nodeInfo.RequestedResource().MilliCPU, allocatable.MilliCPU))}if allocatable.Memory < podRequest.Memory+nodeInfo.RequestedResource().Memory {predicateFails = append(predicateFails, NewInsufficientResourceError(v1.ResourceMemory, podRequest.Memory, nodeInfo.RequestedResource().Memory, allocatable.Memory))}if allocatable.EphemeralStorage < podRequest.EphemeralStorage+nodeInfo.RequestedResource().EphemeralStorage {predicateFails = append(predicateFails, NewInsufficientResourceError(v1.ResourceEphemeralStorage, podRequest.EphemeralStorage, nodeInfo.RequestedResource().EphemeralStorage, allocatable.EphemeralStorage))}for rName, rQuant := range podRequest.ScalarResources {if v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(rName) {// If this resource is one of the extended resources that should be// ignored, we will skip checking it.if ignoredExtendedResources.Has(string(rName)) {continue}}if allocatable.ScalarResources[rName] < rQuant+nodeInfo.RequestedResource().ScalarResources[rName] {predicateFails = append(predicateFails, NewInsufficientResourceError(rName, podRequest.ScalarResources[rName], nodeInfo.RequestedResource().ScalarResources[rName], allocatable.ScalarResources[rName]))}}if klog.V(10) {if len(predicateFails) == 0 {// We explicitly don't do klog.V(10).Infof() to avoid computing all the parameters if this is// not logged. There is visible performance gain from it.klog.Infof("Schedule Pod %+v on Node %+v is allowed, Node is running only %v out of %v Pods.",podName(pod), node.Name, len(nodeInfo.Pods()), allowedPodNumber)}}return len(predicateFails) == 0, predicateFails, nil
}
优选NodeAffinityPriority对应的Map与Reduce函数(k8s.io/kubernetes/pkg/scheduler/algorithm/priorities/node_affinity.go)如下:
// CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityMap prioritizes nodes according to node affinity scheduling preferences
// indicated in PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution. Each time a node matches a preferredSchedulingTerm,
// it will get an add of preferredSchedulingTerm.Weight. Thus, the more preferredSchedulingTerms
// the node satisfies and the more the preferredSchedulingTerm that is satisfied weights, the higher
// score the node gets.
func CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityMap(pod *v1.Pod, meta interface{}, nodeInfo *schedulernodeinfo.NodeInfo) (framework.NodeScore, error) {node := nodeInfo.Node()if node == nil {return framework.NodeScore{}, fmt.Errorf("node not found")}// default is the podspec.affinity := pod.Spec.Affinityif priorityMeta, ok := meta.(*priorityMetadata); ok {// We were able to parse metadata, use affinity from there.affinity = priorityMeta.affinity}var count int32// A nil element of PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution matches no objects.// An element of PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution that refers to an// empty PreferredSchedulingTerm matches all objects.if affinity != nil && affinity.NodeAffinity != nil && affinity.NodeAffinity.PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution != nil {// Match PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution term by term.for i := range affinity.NodeAffinity.PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution {preferredSchedulingTerm := &affinity.NodeAffinity.PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution[i]if preferredSchedulingTerm.Weight == 0 {continue}// TODO: Avoid computing it for all nodes if this becomes a performance problem.nodeSelector, err := v1helper.NodeSelectorRequirementsAsSelector(preferredSchedulingTerm.Preference.MatchExpressions)if err != nil {return framework.NodeScore{}, err}if nodeSelector.Matches(labels.Set(node.Labels)) {count += preferredSchedulingTerm.Weight}}}return framework.NodeScore{Name: node.Name,Score: int64(count),}, nil
}// CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityReduce is a reduce function for node affinity priority calculation.
var CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityReduce = NormalizeReduce(framework.MaxNodeScore, false)
- 相关使用
接下来我们看一下kube-scheduler调度算法(预选&优选)是如何与上述这些操作结合起来的:
// Fit is determined by resource availability.
// This predicate is actually a default predicate, because it is invoked from
// predicates.GeneralPredicates()
scheduler.RegisterFitPredicate(predicates.PodFitsResourcesPred, predicates.PodFitsResources)...
// RegisterFitPredicate registers a fit predicate with the algorithm
// registry. Returns the name with which the predicate was registered.
func RegisterFitPredicate(name string, predicate predicates.FitPredicate) string {return RegisterFitPredicateFactory(name, func(AlgorithmFactoryArgs) predicates.FitPredicate { return predicate })
}...
// RegisterFitPredicateFactory registers a fit predicate factory with the
// algorithm registry. Returns the name with which the predicate was registered.
func RegisterFitPredicateFactory(name string, predicateFactory FitPredicateFactory) string {schedulerFactoryMutex.Lock()defer schedulerFactoryMutex.Unlock()validateAlgorithmNameOrDie(name)fitPredicateMap[name] = predicateFactoryreturn name
}...
// Prioritizes nodes that have labels matching NodeAffinity
scheduler.RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(priorities.NodeAffinityPriority, priorities.CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityMap, priorities.CalculateNodeAffinityPriorityReduce, 1)...
// RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction registers a priority function with the algorithm registry. Returns the name,
// with which the function was registered.
func RegisterPriorityMapReduceFunction(name string,mapFunction priorities.PriorityMapFunction,reduceFunction priorities.PriorityReduceFunction,weight int) string {return RegisterPriorityConfigFactory(name, PriorityConfigFactory{MapReduceFunction: func(AlgorithmFactoryArgs) (priorities.PriorityMapFunction, priorities.PriorityReduceFunction) {return mapFunction, reduceFunction},Weight: int64(weight),})
}...
// RegisterPriorityConfigFactory registers a priority config factory with its name.
func RegisterPriorityConfigFactory(name string, pcf PriorityConfigFactory) string {schedulerFactoryMutex.Lock()defer schedulerFactoryMutex.Unlock()validateAlgorithmNameOrDie(name)priorityFunctionMap[name] = pcfreturn name
}...
// (g.predicates)
// podFitsOnNode checks whether a node given by NodeInfo satisfies the given predicate functions.
// For given pod, podFitsOnNode will check if any equivalent pod exists and try to reuse its cached
// predicate results as possible.
// This function is called from two different places: Schedule and Preempt.
// When it is called from Schedule, we want to test whether the pod is schedulable
// on the node with all the existing pods on the node plus higher and equal priority
// pods nominated to run on the node.
// When it is called from Preempt, we should remove the victims of preemption and
// add the nominated pods. Removal of the victims is done by SelectVictimsOnNode().
// It removes victims from meta and NodeInfo before calling this function.
func (g *genericScheduler) podFitsOnNode(ctx context.Context,state *framework.CycleState,pod 这篇关于一文读懂Kubernetes Scheduler扩展功能的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




