本文主要是介绍超超长篇 - 手把手带你用python玩转Excel,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- pandas库读取excel
- 1、按行读取 Excel 文件
- 2、按列读取 Excel 文件
- 3、总结示例
- openpyxl操作excel
- 1、基础使用
- 创建一个新的 Excel 工作簿
- 打开一个现有的 Excel 文件
- 写入数据到工作表
- 读取工作表中的数据
- 操作行和列
- 合并和拆分单元格
- 2、按行写入Excel
- 3、按列写入Excel
- 4、追加写入
- 5、按行读取Excel
- 6、按列读取Excel
- 7、认识sheet
- 遍历sheet的值
- 8、样式大全介绍
- 1. 设置字体(Font)
- 2. 设置填充(Fill)
- 3. 设置边框(Border)
- Side 类
- Border 类
- 边框代码示列
- 4. 设置对齐方式(Alignment)
- 作用
- 5. 设置数字格式(Number Format)
- 6. 设置单元格保护(Protection)
- 7.设置列宽
- 8、设置行高
- 9、样式组合使用封装
- 10、复制他表数据到新的sheet页
- 11、复制他表数据到新的sheet页-保留样式
本文配套代码及笔记地址:
gitee:https://gitee.com/xiaozai-van-liu/mwj_utils
github:https://github.com/Lvan826199/mwj_utils
求star,求star,求star ~
pandas库读取excel
使用 pandas 库读取 Excel 文件时,可以按行或按列读取数据。以下是分别实现这两种读取方式的方法。
1、按行读取 Excel 文件
按行读取 Excel 文件通常是指读取整个工作表并按行处理数据。以下是一个示例方法:
import pandas as pddef read_excel_by_rows(file_path, sheet_name=0):"""按行读取 Excel 文件。参数:- file_path (str): Excel 文件路径- sheet_name (str or int): 工作表名称或索引,默认读取第一个工作表返回:- DataFrame: 包含 Excel 数据的 DataFrame"""# 读取 Excel 文件df = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=sheet_name)# 按行处理数据for index, row in df.iterrows():print(f"Row {index}: {row.to_dict()}")return df# 示例使用
file_path = 'example.xlsx'
df_rows = read_excel_by_rows(file_path)
2、按列读取 Excel 文件
按列读取 Excel 文件通常是指读取整个工作表并按列处理数据。以下是一个示例方法:
import pandas as pddef read_excel_by_columns(file_path, sheet_name=0):"""按列读取 Excel 文件。参数:- file_path (str): Excel 文件路径- sheet_name (str or int): 工作表名称或索引,默认读取第一个工作表返回:- DataFrame: 包含 Excel 数据的 DataFrame"""# 读取 Excel 文件df = pd.read_excel(file_path, sheet_name=sheet_name)# 按列处理数据for column in df.columns:print(f"Column {column}: {df[column].tolist()}")return df# 示例使用
file_path = 'example.xlsx'
df_columns = read_excel_by_columns(file_path)
- 按行处理数据:
- 使用
df.iterrows()方法按行迭代 DataFrame。 - 在每次迭代中,
index是行索引,row是包含该行数据的 Series。 - 示例中使用
row.to_dict()将每行数据转换为字典格式并打印。
- 使用
- 按列处理数据:
- 遍历
df.columns获取每一列的名称。 - 使用
df[column]获取列数据,并使用tolist()将列数据转换为列表格式并打印。
- 遍历
3、总结示例
假设 example.xlsx 文件包含以下数据:
| Name | Age | City |
|---|---|---|
| 梦小仔 | 30 | 深圳 |
| 无矶 | 25 | 上海 |
| 无妨 | 35 | 北京 |
运行上述代码后:
-
按行读取 方法将输出每一行的数据:
Row 0: {'Name': '梦小仔', 'Age': 30, 'City': '深圳'} Row 1: {'Name': '无矶', 'Age': 25, 'City': '上海'} Row 2: {'Name': '无妨', 'Age': 35, 'City': '北京'} -
按列读取 方法将输出每一列的数据:
Column Name: ['梦小仔', '无矶', '无妨'] Column Age: [30, 25, 35] Column City: ['深圳', '上海', '北京']
openpyxl操作excel
openpyxl 是一个用于读写 Excel 文件(xlsx/xlsm/xltx/xltm 格式)的 Python 库。
安装openpyxl库
pip install openpyxl
1、基础使用
导入openpyxl库
import openpyxl
创建一个新的 Excel 工作簿
# 1、创建一个新的工作簿
wb = openpyxl.Workbook()# 2、获取当前激活的工作表
ws = wb.active# 3、给工作表命名
ws.title = "Sheet1"# 4、保存工作簿
wb.save("excelPath/demo1.xlsx")
打开一个现有的 Excel 文件
# 打开一个已存在的工作簿
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook("excelPath/demo1.xlsx")# 获取活跃的工作表
ws = wb.active# 或者通过名称获取工作表
ws = wb["Sheet1"]
写入数据到工作表
# 写入单个单元格
ws['A1'] = "Hello"
ws['B1'] = "World"# 写入多个单元格
data = [["Name", "Age", "City"],["雷神", 30, "稻妻"],["申鹤", 25, "我家"],["凝光", 35, "璃月"]
]for row in data:ws.append(row)# 保存工作簿
wb.save("excelPath/demo1.xlsx")
读取工作表中的数据
读取单个单元格
print(ws['A1'].value)
读取多个单元格
for row in ws.iter_rows(min_row=1, max_row=4, min_col=1, max_col=3):for cell in row:print(cell.value, end=" ")print()
读取所有数据
for row in ws.iter_rows(values_only=True):print(row)
操作行和列
插入行
ws.insert_rows(1)
删除行
ws.delete_rows(1)
插入列
ws.insert_cols(1)
删除列
ws.delete_cols(1)
合并和拆分单元格
这个用的比较少,我在工作中反正是没有用到过。
# 合并单元格
ws.merge_cells('A1:C1')
ws['A1'] = "Merged Cell"# 拆分单元格
ws.unmerge_cells('A1:C1')# 保存工作簿
wb.save("excelPath/demo1.xlsx")
样式的操作我们放到后面讲,并且我们开始一边写一边封装,这样以后需要使用就不用看教程,直接CV代码就可以啦。
2、按行写入Excel
按照我们基础使用的步骤走:
1、创建表
2、指定sheet页
3、写入数据
4、保存表
示列
def write_rows_to_excel(file_path, rows):"""按行写入数据到Excel文件。:param file_path: (str)Excel文件路径:param rows :(list of list)要写入的行数据,每行是一个列表"""# 创建一个新的工作簿wb = Workbook()ws = wb.active# 按行写入数据for row in rows:ws.append(row)# 保存工作簿wb.save(file_path)
直接封装成一个方法,后续可以直接调用。
if __name__ == '__main__':# 示例使用file_path = 'excelPath/demo2.xlsx'rows = [['Name', 'Age', 'City'],['无矶', 30, '黄山'],['无妨', 25, '泰山'],['无妨游志', 35, '华山']]write_rows_to_excel(file_path, rows)print(f"文件已保存到 {file_path}")
3、按列写入Excel
一列一列写入excel里面,我们可以字典的格式写入,也可以使用列表的格式写入。
- 字典格式:使用字典,键为列标,值为该列的数据列表。适合已知列标的情况。
- 列表格式:使用嵌套列表,每个内部列表代表一列的数据。适合动态生成列标的情况。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2024/6/5 17:55
@Email : Lvan826199@163.com
@公众号 : 梦无矶的测试开发之路
@File : 03_按列写入Excel.py
"""
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"import openpyxl
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letterdef write_data_by_column(data, filename):"""将数据按列写入 Excel 文件。:param data: (dict): 包含列标和对应数据的字典,或者包含列数据的嵌套列表。:param filename: (str): 要保存的文件名。"""# 创建一个新的工作簿wb = openpyxl.Workbook()ws = wb.activews.title = "Sheet1"# 检查数据类型并写入数据if isinstance(data, dict):for col, values in data.items():for row, value in enumerate(values, start=1):ws[f'{col}{row}'] = valueelif isinstance(data, list):for col_idx, col_data in enumerate(data, start=1):col_letter = get_column_letter(col_idx)for row_idx, value in enumerate(col_data, start=1):ws[f'{col_letter}{row_idx}'] = valueelse:raise ValueError("数据格式不正确,请提供字典或嵌套列表。")# 保存工作簿wb.save(filename)
使用示列
if __name__ == '__main__':data_dict = {'A': ["Name", "梦无矶", "小仔", "沐默"],'B': ["Age", 30, 25, 35],'C': ["City", "潮汕", "银川", "台北"]}data_list = [["Name", "梦无矶", "小仔", "沐默"],["Age", 30, 25, 35],["City", "香港", "璃月", "阿尔及利亚"]]# 使用字典数据写入write_data_by_column(data_dict, "excelPath/demo3_dict.xlsx")# 使用列表数据写入write_data_by_column(data_list, "excelPath/demo3_list.xlsx")
4、追加写入
假设你有一个已经存在的Excel文件demo1.xlsx(使用的是前面的excel),你想在其中追加一些新的行数据。
首先我们要理清楚步骤,再根据步骤一步步写代码:
1、加载现有excel
2、获取需要写入的sheet页
3、追加行数据
4、保存excel
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2024/6/5 18:21
@Email : Lvan826199@163.com
@公众号 : 梦无矶的测试开发之路
@File : 04_追加写入.py
"""
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import load_workbookdef append_rows_to_excel(file_path, rows, sheet_name=None):"""追加行数据到现有的Excel文件。:param:file_path: (str): Excel文件路径:param:rows: (list of list): 要追加的行数据,每行是一个列表:param:sheet_name: (str): 要追加数据的表格名称,可选参数,默认为None,表示追加到当前活动表格"""# 加载现有的工作簿wb = load_workbook(file_path)if sheet_name:# 检查工作表是否存在if sheet_name in wb.sheetnames:ws = wb[sheet_name]else:raise ValueError(f"工作表 '{sheet_name}' 不存在")else:# 获取活动工作表ws = wb.active# 追加行数据for row in rows:ws.append(row)# 保存工作簿wb.save(file_path)
示列使用
if __name__ == '__main__':file_path = 'excelPath/demo1.xlsx'rows = [['申鹤', 40, '成都'],['甘雨', 28, '哈尔滨']]append_rows_to_excel(file_path, rows)print(f"数据已追加到 {file_path}")
假设demo1.xlsx文件最初包含以下数据:
| Name | Age | City |
|---|---|---|
| 雷神 | 30 | 稻妻 |
| 申鹤 | 25 | 我家 |
| 凝光 | 35 | 璃月 |
运行上述代码后,文件将被更新为:
| Name | Age | City |
|---|---|---|
| 雷神 | 30 | 稻妻 |
| 申鹤 | 25 | 我家 |
| 凝光 | 35 | 璃月 |
| 申鹤 | 40 | 成都 |
| 甘雨 | 28 | 哈尔滨 |
5、按行读取Excel
1、加载对应工作簿(表)
2、加载对应sheet页
3、遍历sheet[row]
from openpyxl import load_workbookdef read_row(file_path, sheet_name, row):wb = load_workbook(file_path)sheet = wb[sheet_name]row_values = []for cell in sheet[row]:row_values.append(cell.value)return row_values
示列:
if __name__ == '__main__':# 调用方法读取特定行的数据file_path = 'excelPath/demo1.xlsx'sheet_name = 'Sheet1'row_number = 3 # 假设要读取第3行row_data = read_row(file_path, sheet_name, row_number)print(row_data)
输出:
['雷神', 30, '稻妻']
6、按列读取Excel
1、加载对应工作簿(表)
2、加载对应sheet页
3、遍历sheet[column]
from openpyxl import load_workbookdef read_column(file_path, sheet_name, column):wb = load_workbook(file_path)sheet = wb[sheet_name]column_values = []for cell in sheet[column]:column_values.append(cell.value)return column_values
示列:
if __name__ == '__main__':# 调用方法读取特定列的数据file_path = 'excelPath/demo1.xlsx'sheet_name = 'Sheet1'column_letter = 'A' # 假设要读取A列column_data = read_column(file_path, sheet_name, column_letter)print(column_data)
输出:
if __name__ == '__main__':# 调用方法读取特定列的数据file_path = 'excelPath/demo1.xlsx'sheet_name = 'Sheet1'column_letter = 'A' # 假设要读取A列column_data = read_column(file_path, sheet_name, column_letter)print(column_data)
注意事项:
- sheet[row]、sheet[column],这个参数是A、B、C就代表是列,参数是数字就代表行,行是1开始。
7、认识sheet
我们直接wb = load_workbook(file_path),再sheet= wb[sheet_name],之后使用sheet的时候会发现不能自动点出属性,这里引入一个知识点,解决不自动联想属性。
解决方案:
1、我们可以直接print(sheet),发现是<Worksheet "Sheet1">,由此我们知道这个sheet是Worksheet实例
2、那么我们就可以引入这个实例(直接在代码里面写Worksheet,鼠标放上去会然你导入,直接点击就会自动导入对应的类)
3、并且给sheet声明是属于这个实例,之后我们使用sheet的时候就可以自动联想出它所有的属性了。
4、声明格式,属性:类型,sheet: Worksheet,效果如下代码。

遍历sheet的值
wb = load_workbook(file_path)sheet: Worksheet = wb[sheet_name]for i in sheet.values:print(i)
输出:
('Merged Cell', None, None)
('Name', 'Age', 'City')
('雷神', 30, '稻妻')
('申鹤', 25, '我家')
('凝光', 35, '璃月')
('申鹤', 40, '成都')
('甘雨', 28, '哈尔滨')
8、样式大全介绍
可以用来设置 Excel 单元格的字体、颜色、边框、对齐方式等。下面介绍一些常见的Excel样式操作,至于在工作中用不用得到,纯看你需不需要花里胡哨的表。
1. 设置字体(Font)
你可以设置字体的名称、大小、粗体、斜体、下划线等属性。
字体样式:
name: 字体名称,如'Arial'。size: 字体大小,如14。bold: 是否加粗,布尔值。italic: 是否斜体,布尔值。underline: 下划线样式,如'single'。strike: 是否删除线,布尔值。color: 字体颜色。
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Fontwb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active# 设置字体
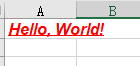
font = Font(name='Arial', size=12, bold=True, italic=True, underline='single', color='FF0000')
ws['A1'].font = font
ws['A1'] = "Hello, World!"wb.save("excelPath/demo08.xlsx")
效果展示:
2. 设置填充(Fill)
设置单元格的背景颜色。
填充模式:
- 填充模式 (
fill_type),如solid、pattern等
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import PatternFillwb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
# 设置填充
fill = PatternFill(start_color='FFFF00', end_color='FFFF00', fill_type='solid')
ws['A2'].fill = fill
ws['A2'] = "Background Color"wb.save("excelPath/demo08_2.xlsx")

在源码里面openpyxl->styles->fills.py里面有所有参数,想深入研究的可以看源码。
FILL_NONE = 'none'
FILL_SOLID = 'solid'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKDOWN = 'darkDown'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKGRAY = 'darkGray'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKGRID = 'darkGrid'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKHORIZONTAL = 'darkHorizontal'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKTRELLIS = 'darkTrellis'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKUP = 'darkUp'
FILL_PATTERN_DARKVERTICAL = 'darkVertical'
FILL_PATTERN_GRAY0625 = 'gray0625'
FILL_PATTERN_GRAY125 = 'gray125'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTDOWN = 'lightDown'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTGRAY = 'lightGray'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTGRID = 'lightGrid'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTHORIZONTAL = 'lightHorizontal'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTTRELLIS = 'lightTrellis'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTUP = 'lightUp'
FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTVERTICAL = 'lightVertical'
FILL_PATTERN_MEDIUMGRAY = 'mediumGray'fills = (FILL_SOLID, FILL_PATTERN_DARKDOWN, FILL_PATTERN_DARKGRAY,FILL_PATTERN_DARKGRID, FILL_PATTERN_DARKHORIZONTAL, FILL_PATTERN_DARKTRELLIS,FILL_PATTERN_DARKUP, FILL_PATTERN_DARKVERTICAL, FILL_PATTERN_GRAY0625,FILL_PATTERN_GRAY125, FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTDOWN, FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTGRAY,FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTGRID, FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTHORIZONTAL,FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTTRELLIS, FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTUP, FILL_PATTERN_LIGHTVERTICAL,FILL_PATTERN_MEDIUMGRAY)
3. 设置边框(Border)
在 openpyxl 中,边框样式通过 Border 和 Side 类来定义。每个边框可以分别设置顶部、底部、左侧和右侧的样式和颜色。
Side 类
Side 类用于定义边框的样式和颜色。它的主要参数包括:
border_style: 边框的样式。常见的样式有:"thin": 细边框"medium": 中等宽度边框"thick": 厚边框"dashed": 虚线边框"dotted": 点线边框"double": 双线边框"hair": 极细边框"mediumDashed": 中等宽度虚线边框"dashDot": 虚线点边框"mediumDashDot": 中等宽度虚线点边框"dashDotDot": 双点虚线边框"mediumDashDotDot": 中等宽度双点虚线边框"slantDashDot": 斜虚线点边框
color: 边框的颜色,使用 RGB 颜色代码表示,例如"FF0000"表示红色。
Border 类
Border 类用于组合各个边框(左、右、上、下、对角线)的 Side 实例。它的主要参数包括:
left: 左侧边框的Side实例。right: 右侧边框的Side实例。top: 顶部边框的Side实例。bottom: 底部边框的Side实例。diagonal: 对角线边框的Side实例。diagonal_direction: 对角线方向,取值可以是0(无对角线)、1(从左上到右下)、2(从右上到左下)。
边框代码示列
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2024/6/6 18:56
@Email : Lvan826199@163.com
@公众号 : 梦无矶测开实录
@File : 08_样式大全_03设置边框.py
"""
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Border, Side# 创建一个新的工作簿和工作表
workbook = Workbook()
sheet = workbook.active# 定义不同的边框样式
thin_border = Border(left=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),right=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),top=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),bottom=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000")
)thick_border = Border(left=Side(border_style="thick", color="FF0000"),right=Side(border_style="thick", color="FF0000"),top=Side(border_style="thick", color="FF0000"),bottom=Side(border_style="thick", color="FF0000")
)dashed_border = Border(left=Side(border_style="dashed", color="00FF00"),right=Side(border_style="dashed", color="00FF00"),top=Side(border_style="dashed", color="00FF00"),bottom=Side(border_style="dashed", color="00FF00")
)double_border = Border(left=Side(border_style="double", color="0000FF"),right=Side(border_style="double", color="0000FF"),top=Side(border_style="double", color="0000FF"),bottom=Side(border_style="double", color="0000FF")
)# 应用边框样式到不同的单元格
sheet["A1"].value = "Thin Border"
sheet["A1"].border = thin_bordersheet["B1"].value = "Thick Border"
sheet["B1"].border = thick_bordersheet["C1"].value = "Dashed Border"
sheet["C1"].border = dashed_bordersheet["D1"].value = "Double Border"
sheet["D1"].border = double_border# 保存工作簿
workbook.save("excelPath/demo08_3.xlsx")
- 创建 Side实例:
- Side(border_style=“thin”, color=“000000”): 创建一个细边框,颜色为黑色。
- Side(border_style=“thick”, color=“FF0000”): 创建一个厚边框,颜色为红色。
- Side(border_style=“dashed”, color=“00FF00”): 创建一个虚线边框,颜色为绿色。
- Side(border_style=“double”, color=“0000FF”): 创建一个双线边框,颜色为蓝色。
- 创建 Border 实例:
- Border(left=…, right=…, top=…, bottom=…): 将 Side 实例组合成一个 Border`实例,分别设置左、右、上、下四个边框。
- 应用边框样式到单元格:
- sheet[“A1”].border = thin_border: 将细边框应用到单元格
A1。 - sheet[“B1”].border = thick_border: 将厚边框应用到单元格
B1。 - sheet[“C1”].border = dashed_border: 将虚线边框应用到单元格
C1。 - sheet[“D1”].border = double_border: 将双线边框应用到单元格
D1。
- sheet[“A1”].border = thin_border: 将细边框应用到单元格
效果如下:

4. 设置对齐方式(Alignment)
设置单元格的水平和垂直对齐方式。
对齐方式:
- 缩进 (
indent) - 换行 (
wrap_text),在表格里面是自动换行,如果你代码写入的时候强制换行只需要使用\n即可。- 当
wrap_text设置为True时,单元格中的文本会根据单元格的宽度自动换行,以便在单元格中完全显示内容。
- 当
作用
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2024/6/7 11:26
@Email : Lvan826199@163.com
@公众号 : 梦无矶测开实录
@File : 08_样式大全_04对齐方式.py
"""
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Alignmentwb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
# 设置对齐方式
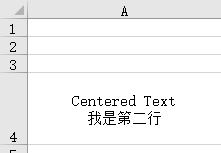
alignment = Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', wrap_text=True)
ws['A4'].alignment = alignment
ws['A4'] = "Centered Text\n我是第二行"# 保存工作簿
wb.save("excelPath/demo08_4.xlsx")效果如下:
5. 设置数字格式(Number Format)
可以设置单元格的数字格式,比如日期、货币等。
数字格式:
- 格式化数字、日期、时间等 (
number_format),如'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'。
- 常规数字格式:
- 整数:
'0' - 小数:
'0.00' - 千分位:
'#,##0' - 百分比:
'0%' - 科学计数法:
'0.00E+00'
- 整数:
- 日期和时间格式:
- 日期(年-月-日):
'yyyy-mm-dd' - 日期(月/日/年):
'mm/dd/yyyy' - 时间(小时:分钟:秒):
'hh:mm:ss' - 日期和时间:
'yyyy-mm-dd hh:mm:ss'
- 日期(年-月-日):
- 货币格式:
- 美元:
'$#,##0.00' - 欧元:
'€#,##0.00' - 人民币:
'¥#,##0.00'
- 美元:
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import Workbookwb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active# 设置数字格式
ws['A5'].number_format = 'YYYY-MM-DD'
ws['A5'] = '2024-06-05'wb.save("excelPath/demo08_5.xlsx")
6. 设置单元格保护(Protection)
你可以设置单元格是否锁定和隐藏。
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.styles import Protectionwb = Workbook()
ws = wb.active
# 设置单元格保护
protection = Protection(locked=True, hidden=False)
ws['A6'].protection = protection
ws['A6'] = "Protected Cell"wb.save("excelPath/demo08_6.xlsx")
7.设置列宽
设置A列宽20,B列宽10,C列宽30
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"from openpyxl import load_workbookcolumn_widths = {'A': 20, 'B': 10, 'C': 30} # 设置列宽file_path = "excelPath/demo1.xlsx"
# 加载现有的工作簿
wb = load_workbook(file_path)
ws = wb.active
# 设置列宽
for col, width in column_widths.items():ws.column_dimensions[col].width = width
# 保存工作簿
wb.save(file_path)
8、设置行高
将第 1 行的高度设置为 30,第 2 行的高度设置为 50)
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"import openpyxl# 打开 Excel 文件
workbook = openpyxl.load_workbook('excelPath/demo1.xlsx')# 选择一个工作表
sheet = workbook.active# 设置行高 (将第 1 行的高度设置为 30)
sheet.row_dimensions[1].height = 30
# 设置行高 (将第 2 行的高度设置为 50)
sheet.row_dimensions[2].height = 50# 保存修改后的 Excel 文件
workbook.save('excelPath/demo1.xlsx')
9、样式组合使用封装
将上述样式组合使用来设置单元格的样式。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@Time : 2024/6/7 11:46
@Email : Lvan826199@163.com
@公众号 : 梦无矶测开实录
@File : 09_样式组合使用封装.py
"""
__author__ = "梦无矶小仔"import os
from copy import copyimport openpyxl
from openpyxl import Workbook
from openpyxl.worksheet.worksheet import Worksheet
from openpyxl.styles import Font, PatternFill, Alignment, Border, Side
from typing import List, Optionalclass ExcelWriter:def __init__(self, filename):self.filename: str = filenameself.workbook: Workbook = Workbook()self.sheet: Worksheet = self.workbook.activedef save(self):self.workbook.save(self.filename)def create_excel(self):# 新建一个空表格self.save()def create_excel_with_row(self, row_data: list, has_title=True, styles=None):"""新建一个带有标题的表格,单行写入:param row_data:list[]:param has_title::param styles::return:"""self.append_row(row_data, has_title=has_title, styles=styles)def create_excel_with_rows(self, rows_data: list, has_title=True, styles=None):"""新建一个带有标题的表格,多行写入:param rows_data: list[[],[],[]...]:param has_title::param styles::return:"""self.append_rows(rows_data, has_title=has_title, styles=styles)def verfiy_row_data(self, row_data: list, excel_title):"""校验行数据长度:param row_data::param excel_title::return:"""if len(row_data) != len(excel_title):raise ValueError(f"{row_data}写入行的数据长度必须和标题行长度一致!")def append_row(self, row_data: list, has_title: bool = False, styles=None):"""写入或追加一行数据并设置样式:param row_data: list[]:param has_title: 是否带有标题:param styles::return:"""if has_title:for col_num, value in enumerate(row_data, 1):cell = self.sheet.cell(row=1, column=col_num, value=value)self.write_with_styles(1, col_num, cell, styles)self.save()else:row_num = self.sheet.max_row + 1for col_num, value in enumerate(row_data, 1):cell = self.sheet.cell(row=row_num, column=col_num, value=value)self.write_with_styles(row_num, col_num, cell, styles)self.save()def append_rows(self, rows_data: list, has_title: bool = False, styles=None):"""写入或追加多行数据并设置样式:param row_data: list[[],[],[]...]:param has_title: 是否带有标题:param styles::return:"""if has_title and isinstance(rows_data[0], list):for col_num, value in enumerate(rows_data[0], 1):cell = self.sheet.cell(row=1, column=col_num, value=value)self.write_with_styles(1, col_num, cell, styles)self.save()for row_data in rows_data[1:]:row_num = self.sheet.max_row + 1for col_num, value in enumerate(row_data, 1):cell = self.sheet.cell(row=row_num, column=col_num, value=value)self.write_with_styles(row_num, col_num, cell, styles)self.save()else:for row_data in rows_data:row_num = self.sheet.max_row + 1for col_num, value in enumerate(row_data, 1):cell = self.sheet.cell(row=row_num, column=col_num, value=value)self.write_with_styles(row_num, col_num, cell, styles)self.save()def copy_excel_to_sheet(self, source_excel_path, sheet_name):"""复制表数据不包含样式到指定sheet页:param source_excel_path::param sheet_name::return:"""# 打开源文件和目标文件source_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(source_excel_path)destination_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.filename)# 获取源文件中的第一个 sheetsource_sheet = source_wb.active# 在目标文件中创建一个新的 sheetnew_sheet = destination_wb.create_sheet(title=sheet_name)# 遍历源 sheet 中的所有单元格,并将其值复制到新 sheet 中for row in source_sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True):new_sheet.append(row)# 保存目标文件destination_wb.save(self.filename)run_dir = os.getcwd()excel_path = os.path.join(run_dir, self.filename)print(f"生成结果表格路径:{excel_path}")def copy_excel_to_sheet_with_styles(self, source_excel_path, sheet_name):"""复制表数据包含样式到指定sheet页:param source_excel_path::param sheet_name::return:"""# 打开源文件和目标文件source_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(source_excel_path)destination_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.filename)# 获取源文件中的第一个 sheetsource_sheet = source_wb.active# 在目标文件中创建一个新的 sheetnew_sheet = destination_wb.create_sheet(title=sheet_name)# 复制单元格的值和样式for row in source_sheet.iter_rows():for cell in row:new_cell = new_sheet.cell(row=cell.row, column=cell.col_idx, value=cell.value)# 复制样式if cell.has_style:new_cell.font = copy(cell.font)new_cell.border = copy(cell.border)new_cell.fill = copy(cell.fill)new_cell.number_format = copy(cell.number_format)new_cell.protection = copy(cell.protection)new_cell.alignment = copy(cell.alignment)# 复制列宽for col in source_sheet.column_dimensions:new_sheet.column_dimensions[col].width = source_sheet.column_dimensions[col].width# 复制行高for row in source_sheet.row_dimensions:new_sheet.row_dimensions[row].height = source_sheet.row_dimensions[row].height# 保存目标文件destination_wb.save(self.filename)run_dir = os.getcwd()excel_path = os.path.join(run_dir, self.filename)print(f"生成结果表格路径:{excel_path}")def write_with_styles(self, row_num, col_num, cell, styles=None):"""对行的指定列进行样式设置,不支持多行不同列样式设置:param row_num::param col_num::param cell::param styles::return:"""# 设置默认样式cell.font = Font(color="000000")cell.fill = PatternFill(start_color="FFFFFF", end_color="FFFFFF", fill_type="solid")cell.alignment = Alignment(wrap_text=True, horizontal="center", vertical="center")cell.border = Border(left=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),right=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),top=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"),bottom=Side(border_style="thin", color="000000"))# 如果提供了样式,则应用样式if styles and col_num in styles:print(f"styles:{row_num},{col_num},{cell}")style = styles[col_num]if 'font_color' in style:cell.font = Font(color=style['font_color'])if 'bg_color' in style:cell.fill = PatternFill(start_color=style['bg_color'], end_color=style['bg_color'], fill_type="solid")if 'alignment' in style:cell.alignment = Alignment(wrap_text=style['alignment'].get('wrap_text', True),horizontal=style['alignment'].get('horizontal', "center"),vertical=style['alignment'].get('vertical', "center"),indent=style['alignment'].get('indent', 0))if 'width' in style:self.sheet.column_dimensions[cell.column_letter].width = style['width']if 'height' in style:self.sheet.row_dimensions[row_num].height = style['height']if 'border' in style:cell.border = Border(left=Side(border_style=style['border'].get('left', 'thin'), color=style['border'].get('left_color', '000000')),right=Side(border_style=style['border'].get('right', 'thin'), color=style['border'].get('right_color', '000000')),top=Side(border_style=style['border'].get('top', 'thin'), color=style['border'].get('top_color', '000000')),bottom=Side(border_style=style['border'].get('bottom', 'thin'), color=style['border'].get('bottom_color', '000000')))if 'font' in style:cell.font = Font(name=style['font'].get('name', 'Calibri'),size=style['font'].get('size', 11),bold=style['font'].get('bold', False),italic=style['font'].get('italic', False),underline=style['font'].get('underline', 'none'),strike=style['font'].get('strike', False),color=style['font'].get('color', '000000'))if 'number_format' in style:cell.number_format = style['number_format']if __name__ == '__main__':# 示例使用row_data = [["姓名", "年龄", "性别", "职业", "城市", "语言"],["张三", 25, "男", "工程师", "北京", "中文"],["李四", 30, "女", "设计师", "上海", "英文"],["王五", 35, "男", "教师", "广州", "粤语"],["赵六", 40, "女", "医生", "深圳", "国语"],["钱七", 45, "男", "律师", "杭州", "英语"], ["孙八", 50, "女", "护士", "南京", "国语"]]styles = {1: {'font_color': 'FF0000','bg_color': 'FFFF00','alignment': {'horizontal': 'left', 'vertical': 'top', 'wrap_text': True, 'indent': 1},'width': 20,'height': 30,'border': {'left': 'thick', 'left_color': 'FF0000'},'font': {'name': 'Arial', 'size': 14, 'bold': True, 'italic': True, 'underline': 'single', 'strike': True, 'color': 'FF0000'}},3: {'font_color': '0000FF','bg_color': '00FF00','alignment': {'horizontal': 'center', 'vertical': 'center', 'wrap_text': True},'width': 15,'border': {'bottom': 'dashed', 'bottom_color': '00FF00'}},5: {'font_color': '00FF00','bg_color': 'FF00FF','alignment': {'horizontal': 'right', 'vertical': 'bottom', 'wrap_text': True},'height': 25,'border': {'top': 'double', 'top_color': '0000FF'},'number_format': 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'}}# 多行写入excel_writer = ExcelWriter("excelPath/demo09_多行写入.xlsx")excel_writer.create_excel_with_rows(row_data, True, styles)# 单行写入row_data2 = ["姓名", "年龄", "性别", "职业", "城市", "语言"]excel_writer2 = ExcelWriter("excelPath/demo09_单行写入.xlsx")excel_writer2.create_excel_with_row(row_data2, True, styles)
效果展示:

10、复制他表数据到新的sheet页
已封装到第九小节中
def copy_excel_to_sheet(self, source_excel_path, sheet_name):# 打开源文件和目标文件source_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(source_excel_path)destination_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.filename)# 获取源文件中的第一个 sheetsource_sheet = source_wb.active# 在目标文件中创建一个新的 sheetnew_sheet = destination_wb.create_sheet(title=sheet_name)# 遍历源 sheet 中的所有单元格,并将其值复制到新 sheet 中for row in source_sheet.iter_rows(values_only=True):new_sheet.append(row)# 保存目标文件destination_wb.save(self.filename)run_dir = os.getcwd()excel_path = os.path.join(run_dir, self.filename)print(f"生成结果表格路径:{excel_path}")
11、复制他表数据到新的sheet页-保留样式
已封装到第九小节中
def copy_excel_to_sheet_with_styles(self, source_excel_path, sheet_name):"""复制表数据包含样式到指定sheet页:param source_excel_path::param sheet_name::return:"""# 打开源文件和目标文件source_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(source_excel_path)destination_wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(self.filename)# 获取源文件中的第一个 sheetsource_sheet = source_wb.active# 在目标文件中创建一个新的 sheetnew_sheet = destination_wb.create_sheet(title=sheet_name)# 复制单元格的值和样式for row in source_sheet.iter_rows():for cell in row:new_cell = new_sheet.cell(row=cell.row, column=cell.col_idx, value=cell.value)# 复制样式if cell.has_style:new_cell.font = copy(cell.font)new_cell.border = copy(cell.border)new_cell.fill = copy(cell.fill)new_cell.number_format = copy(cell.number_format)new_cell.protection = copy(cell.protection)new_cell.alignment = copy(cell.alignment)# 复制列宽for col in source_sheet.column_dimensions:new_sheet.column_dimensions[col].width = source_sheet.column_dimensions[col].width# 复制行高for row in source_sheet.row_dimensions:new_sheet.row_dimensions[row].height = source_sheet.row_dimensions[row].height# 保存目标文件destination_wb.save(self.filename)run_dir = os.getcwd()excel_path = os.path.join(run_dir, self.filename)print(f"生成结果表格路径:{excel_path}")
好,基本就这些了,有啥新的需求或者想法欢迎留言 ~
这篇关于超超长篇 - 手把手带你用python玩转Excel的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




