本文主要是介绍代码解读 | Hybrid Transformers for Music Source Separation[04],希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、背景
0、Hybrid Transformer 论文解读
1、代码复现|Demucs Music Source Separation_demucs架构原理-CSDN博客
2、Hybrid Transformer 各个模块对应的代码具体在工程的哪个地方
3、Hybrid Transformer 各个模块的底层到底是个啥(初步感受)?
4、Hybrid Transformer 各个模块处理后,数据的维度大小是咋变换的?
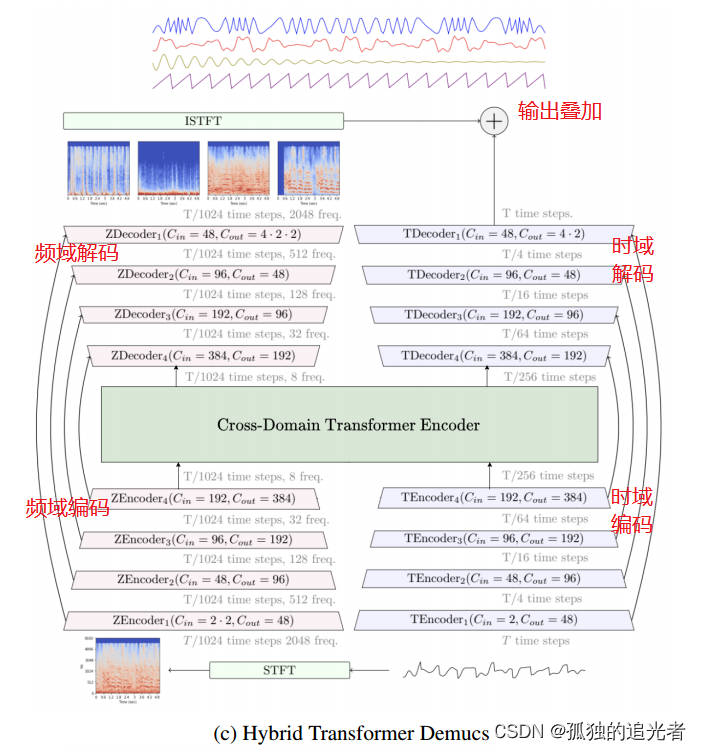
从模块上划分,Hybrid Transformer Demucs 共包含 (STFT模块、时域编码模块、频域编码模块、Cross-Domain Transformer Encoder模块、时域解码模块、频域解码模块、ISTFT模块)7个模块。
本篇目标:拆解STFT模块的底层。
二、拆解STFT模块底层
2.1 torch.stft
import torch as thdef spectro(x, n_fft=512, hop_length=None, pad=0):*other, length = x.shapex = x.reshape(-1, length)is_mps = x.device.type == 'mps'if is_mps:x = x.cpu()z = th.stft(x,n_fft * (1 + pad),hop_length or n_fft // 4,window=th.hann_window(n_fft).to(x),win_length=n_fft,normalized=True,center=True,return_complex=True,pad_mode='reflect')_, freqs, frame = z.shapereturn z.view(*other, freqs, frame)核心代码,长上面这样。
简单说一下为啥使用短时傅里叶变换(STFT),而不直接使用傅里叶变换(FT)。原因:傅立叶变换只能告诉我们信号当中有哪些频率成分。当我们还想知道各个成分出现的时间的时候,就得用到STFT了(这也就是时频分析。所谓时频分析,就是既要考虑到频率特征,又要考虑到时间序列变化)。

上述公式就是torch.stft的底层公式,一句话总结:首先窗函数×时域信号,然后进行傅里叶变换。其中,表示频率,
表示滑动窗口的下标,input是一个时间序列,hop_length表示窗移大小,win_length表示窗长,window表示窗函数。
具体的,torch.stft函数中各个参数的意义如下所示。
| 参数名称 | 说明 |
| input (Tensor):the input tensor | 输入 |
| n_fft (int): size of Fourier transform | 傅里叶变换大小(决定频率分辨率) |
| hop_length (int, optional): the distance between neighboring sliding window frames. Default: ``None`` (treated as equal to ``floor(n_fft / 4)``) | 窗移,默认大小floor(n_fft / 4) |
| win_length (int, optional): the size of window frame and STFT filter. Default: ``None`` (treated as equal to :attr:`n_fft`) | 窗长,默认大小n_fft |
| window (Tensor, optional): the optional window function. Default: ``None`` (treated as window of all :math:`1` s) | 窗函数 |
| center (bool, optional): whether to pad :attr:`input` on both sides so that the :math:`t`-th frame is centered at time :math:`t \times \text{hop\_length}`. Default: ``True`` | 是否对input两侧进行填充, 以至于在t帧的是居中的 |
| pad_mode (string, optional): controls the padding method used when :attr:`center` is ``True``. Default: ``"reflect"`` | 填充模式 |
| normalized (bool, optional): controls whether to return the normalized STFT results Default: ``False`` | 是否归一化 |
| onesided (bool, optional): controls whether to return half of results to avoid redundancy for real inputs. Default: ``True`` for real :attr:`input` and :attr:`window`, ``False`` otherwise. | 控制是否返回一半结果 |
| return_complex (bool, optional): whether to return a complex tensor, or a real tensor with an extra last dimension for the real and imaginary components. | 返回值是否设置为复数 |
n_fft关注的是频率分辨率,即能够分辨的最小频率间隔。n_fft越大,频率分辨率越高,但计算量也越大。win_length关注的是时间分辨率,即能够分辨的最小时间间隔。win_length越大,时间分辨率越低,但可以更好地捕捉到低频信号的特征。
2.2 STFT整个模块干了啥
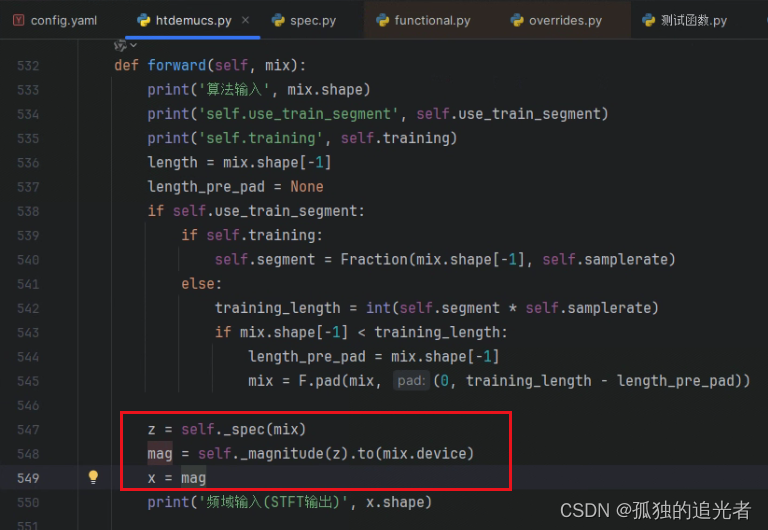
上图是htdemucs调用STFT模块的入口。

1、为了保持输出大小=输入大小/hop_length,先对输入信息进行填充(使用pad1d函数),然后进行STFT变换(核心代码见2.1)。
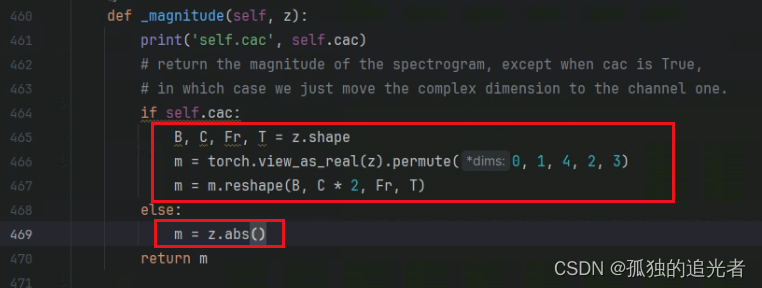
2、拿到STFT结果后,进入_magnitude函数。当cac为True的时候,_magnitude函数把复数维度移动到通道维度。当cac为False的时候,_magnitude函数计算出幅度值。
done,STFT模块讲解完成。
感谢阅读,最近开始写公众号(分享好用的AI工具),欢迎大家一起见证我的成长(桂圆学AI)
这篇关于代码解读 | Hybrid Transformers for Music Source Separation[04]的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






