本文主要是介绍代理设计模式之JDK动态代理CGLIB动态代理原理与源码剖析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
代理设计模式
代理模式(Proxy),为其它对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。如下图
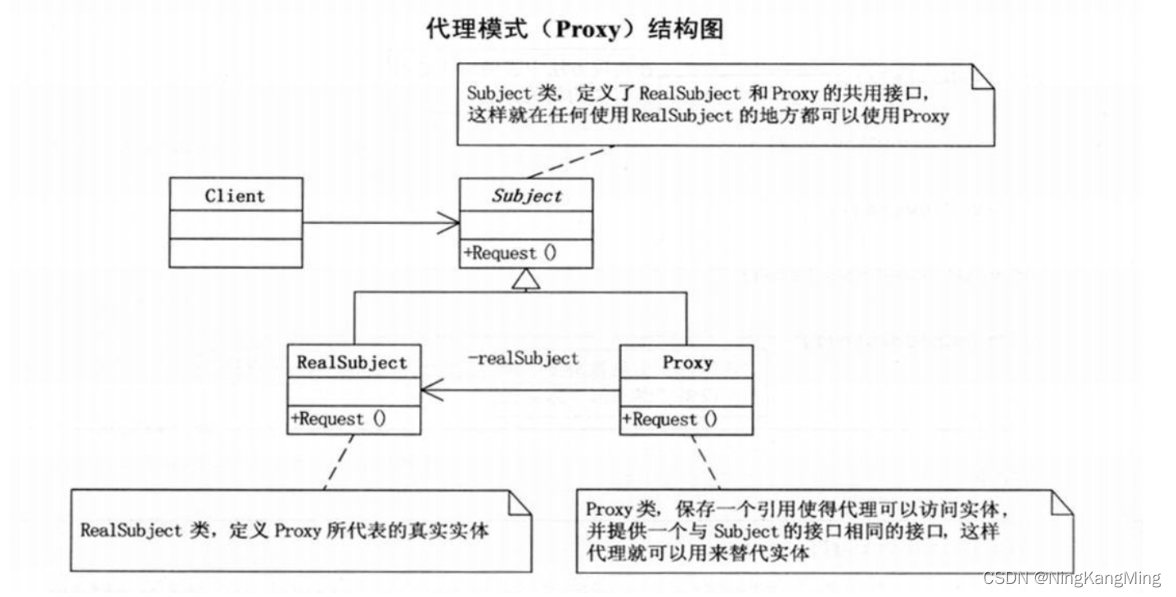
从上面的类图可以看出,通过代理模式,客户端访问接口时的实例实际上是Proxy对象,Proxy对象持有RealSubject的引用,这样一来Proxy在可以在实际执行RealSubject前后做一些操作,相当于是对RealSubject的Reques方法做了增强。
/*** @author kangming.ning* @date 2021/5/8 9:51*/
public class Client {public static void main(String[] args) {Subject subject = new Proxy();subject.request();}
}Proxy类对RealSubject的request方法进行了增强
/*** @author kangming.ning* @date 2021/5/8 9:49*/
public class Proxy implements Subject {private RealSubject realSubject;public Proxy() {realSubject = new RealSubject();}@Overridepublic void request() {System.out.println("proxy do something before");realSubject.request();System.out.println("proxy do something after");}
}代理设计模式就是这么简单,但却很好用。像上面这种提前设计好的代理可以称为静态代理,因为它是针对某个需要增强的接口直接进行编码设计的。这种方式事实上用的很少,因为它需要针对每个需要增强的接口添加代理类,试想类似于mybatis的Mapper代理如果都是静态代理,是不是会导致我们编写大量代理类,实在麻烦。所以项目中通常都是使用动态代理,所谓动态代理,可以简单理解为代理类可以在运行时动态创建并加载到JVM中,下面做详细介绍。
动态代理
动态代理:从 JVM 角度来说,动态代理是在运行时动态生成类字节码,并加载到 JVM 中的。
其本质和静态代理是一样的,只不过被设计为可以动态生成代理类,使用更加方便,在实际的开发中有大量应用。比如spring的AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming) 切面编程这种唬人的技术,其本质不过就是利用代理模式对方法进行增强。当然spring aop用的是动态代理技术,再具体就是利用JDK动态代理或CGLIB动态代理对针对接口或类生成动态代理类,然后实际执行方法时,实际执行的代理类的逻辑,代理类可以在方法前后做一些操作(增强)。
JDK动态代理
JDK动态代理Proxy是JDK提供的一个用于创建动态代理的一个工具类。下面用一个简单例子说明如何应用JDK动态代理
首先还是需要有被代理的接口,自定股票买卖行为
/*** 股票接口* @author kangming.ning* @date 2024-01-19 16:40* @since 1.0**/
public interface StockService {/*** 购买股票接口* @param stockName 买的哪个股票* @param totalMoney*/void buyStock(String stockName,double totalMoney);/*** 卖出股票接口* @param stockName 卖的哪个股票* @param totalMoney*/void sellStock(String stockName,double totalMoney);
}接口的实现 ,即买卖股票需要做的一些事情。
/*** @author kangming.ning* @date 2024-01-19 16:54* @since 1.0**/
public class StockServiceImpl implements StockService {@Overridepublic void buyStock(String stockName, double totalMoney) {System.out.println("成功购买了股票" + stockName + " 共" + totalMoney + "元");}@Overridepublic void sellStock(String stockName, double totalMoney) {System.out.println("成功卖出了股票" + stockName + " 共" + totalMoney + "元");}
}没有代理的情况,买卖这些事情是需要股民自己去做的
/*** 没有代理的情况** @author kangming.ning* @date 2024-01-22 09:50* @since 1.0**/
public class StockDirectClient {public static void main(String[] args) {StockService stockService = new StockServiceImpl();stockService.buyStock("001", 100);stockService.sellStock("002", 200);}
}而有代理的情况,通常表现为,我们买卖的基金,其背后实际是大部分是股票(偏股基金),基金经理可以认为是我们的代理。
/*** 韭菜侠(又称为基民)* @author kangming.ning* @date 2024-01-19 16:57* @since 1.0**/
public class FragrantFloweredGarlicMan {public static void main(String[] args) {//韭菜侠发现投资商机,基金好像跌到底部了,果断去抄底StockService stockService = new StockServiceImpl();StockService proxy = (StockService)Proxy.newProxyInstance(//目标类的类加载器stockService.getClass().getClassLoader(),stockService.getClass().getInterfaces(),new StockInvocationHandler(stockService));proxy.buyStock("003",100);proxy.sellStock("004",200);}
}StockInvocationHandler如下
/*** @author kangming.ning* @date 2024-01-19 17:06* @since 1.0**/
public class StockInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {/*** 代理中的真实对象*/private final Object target;public StockInvocationHandler(Object target) {this.target = target;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {//调用方法之前,我们可以添加自己的操作System.out.println("before method " + method.getName());//执行被代理对象原方法Object invoke = method.invoke(target, args);//调用方法之后,我们同样可以添加自己的操作System.out.println("after method " + method.getName());return invoke;}
}上面的打印结果类似
before method buyStock
成功购买了股票003 共100.0元
after method buyStock
before method sellStock
成功卖出了股票004 共200.0元
after method sellStock可以看出,通过动态代理,对原接口调用前后都分别处理了额外的逻辑,和静态代理实现的效果是一致的。只是动态代理不需要事先编辑好相关代理类,而是在执行过程中动态生成代理类,这样一来,接口变动我们也不必修改代理类,所有调整适配工作都在InvocationHandler的实现类里处理。
JDK动态代理原理
通过上面的案例,我们知道怎么去使用JDK代理了。下面探讨一下其实现原理。Proxy创建动态代理的方法如下
/*** Returns an instance of a proxy class for the specified interfaces* that dispatches method invocations to the specified invocation* handler.** <p>{@code Proxy.newProxyInstance} throws* {@code IllegalArgumentException} for the same reasons that* {@code Proxy.getProxyClass} does.** @param loader the class loader to define the proxy class* @param interfaces the list of interfaces for the proxy class* to implement* @param h the invocation handler to dispatch method invocations to* @return a proxy instance with the specified invocation handler of a* proxy class that is defined by the specified class loader* and that implements the specified interfaces* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any of the restrictions on the* parameters that may be passed to {@code getProxyClass}* are violated* @throws SecurityException if a security manager, <em>s</em>, is present* and any of the following conditions is met:* <ul>* <li> the given {@code loader} is {@code null} and* the caller's class loader is not {@code null} and the* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission* s.checkPermission} with* {@code RuntimePermission("getClassLoader")} permission* denies access;</li>* <li> for each proxy interface, {@code intf},* the caller's class loader is not the same as or an* ancestor of the class loader for {@code intf} and* invocation of {@link SecurityManager#checkPackageAccess* s.checkPackageAccess()} denies access to {@code intf};</li>* <li> any of the given proxy interfaces is non-public and the* caller class is not in the same {@linkplain Package runtime package}* as the non-public interface and the invocation of* {@link SecurityManager#checkPermission s.checkPermission} with* {@code ReflectPermission("newProxyInPackage.{package name}")}* permission denies access.</li>* </ul>* @throws NullPointerException if the {@code interfaces} array* argument or any of its elements are {@code null}, or* if the invocation handler, {@code h}, is* {@code null}*/@CallerSensitivepublic static O这篇关于代理设计模式之JDK动态代理CGLIB动态代理原理与源码剖析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





