关于softmax回归
看过最清晰的关于softmax回归的文档来源自UFLDL,简单摘录如下。
softmax用于多分类问题,比如0-9的数字识别,共有10个输出,而且这10个输出的概率和加起来应该为1,所以可以用一个softmax操作归一化这10个输出。进一步一般化,假如共有k个输出,softmax的假设可以形式化表示为:
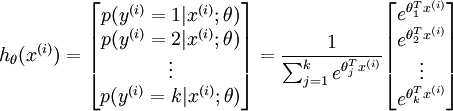
然后给这个假设定义一个loss function,就是softmax回归的loss function咯,形式化如下:
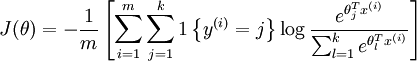
也很直观,对于某个样本i,他对应的gt label是j,那么对于loss function来说,显然只需要关心第k路是否是一个概率很大的值,所以就用一个l{·}的示性函数来表示只关心第 y(i) y(i)路(即label对应的那一路),其他路都忽略为0。然后log的部分其实就是第k路的概率值取log。最后需要注意到前面还有一个负号。
所以总的来说,这个loss function的意思是说,对于某个样本,我只看他gt对应的那个路子输出的概率,然后取一个-log从最大化概率变成最小化能量。
然后softmax可以求梯度,梯度的公式是:
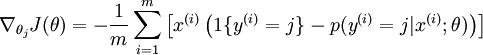
然后在实际应用中,一般还是要加上一个正则项,或者在UFLDL教程中被称为权重衰减项,于是loss function和回传梯度都多出了一项,变成了:
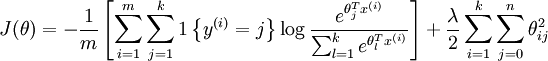
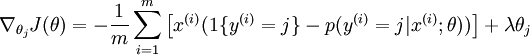
然后softmax回归就介绍完了,感觉不懂的话具体还是看UFLDL的教程比较好。
Caffe中的实现
注意这里贴的代码是基于笔者所使用的caffe版本的,大概是2015年初的吧,跟目前的最新caffe版本可能有所出入。
在实现细节上,train时候在最后接上SoftmaxWithLossLayer,test的时候换成SoftmaxLayer即可。这里可以看loss_layer.hpp的注释:
1 2 3 4 | * This layer should be preferred over separate * SoftmaxLayer + MultinomialLogisticLossLayer * as its gradient computation is more numerically stable. * At test time, this layer can be replaced simply by a SoftmaxLayer. |
先看softmax_layer.cpp,由于只会用到他的forward,所以只看forward就好了。代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | template <typename Dtype> void SoftmaxLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) { const Dtype* bottom_data = bottom[0]->cpu_data(); Dtype* top_data = (*top)[0]->mutable_cpu_data(); Dtype* scale_data = scale_.mutable_cpu_data(); int num = bottom[0]->num(); int channels = bottom[0]->channels(); int dim = bottom[0]->count() / bottom[0]->num(); int spatial_dim = bottom[0]->height() * bottom[0]->width(); caffe_copy(bottom[0]->count(), bottom_data, top_data); // We need to subtract the max to avoid numerical issues, compute the exp, // and then normalize. for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { // initialize scale_data to the first plane caffe_copy(spatial_dim, bottom_data + i * dim, scale_data); for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < spatial_dim; k++) { scale_data[k] = std::max(scale_data[k], bottom_data[i * dim + j * spatial_dim + k]); } } // subtraction caffe_cpu_gemm<Dtype>(CblasNoTrans, CblasNoTrans, channels, spatial_dim, 1, -1., sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), scale_data, 1., top_data + i * dim); // exponentiation caffe_exp<Dtype>(dim, top_data + i * dim, top_data + i * dim); // sum after exp caffe_cpu_gemv<Dtype>(CblasTrans, channels, spatial_dim, 1., top_data + i * dim, sum_multiplier_.cpu_data(), 0., scale_data); // division for (int j = 0; j < channels; j++) { caffe_div(spatial_dim, top_data + (*top)[0]->offset(i, j), scale_data, top_data + (*top)[0]->offset(i, j)); } } } |
可以看出基本就是softmax的假设时候的实现公式,即这条。
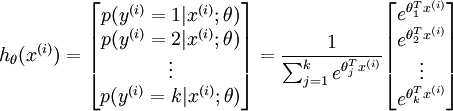
不同之处是先求取max然后所有值先减去了这个max,目的作者也给了注释是数值问题,毕竟之后是要接上e为底的指数运算的,所以值不可以太大,这个操作相当合理。
然后就到了softmax_loss_layer.cpp了,总共代码不超100行,就全贴在下面了:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 | #include <algorithm> #include <cfloat> #include <vector> #include "caffe/layer.hpp" #include "caffe/util/math_functions.hpp" #include "caffe/vision_layers.hpp" namespace caffe { template <typename Dtype> void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp( const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) { LossLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(bottom, top); softmax_bottom_vec_.clear(); softmax_bottom_vec_.push_back(bottom[0]); softmax_top_vec_.clear(); softmax_top_vec_.push_back(&prob_); softmax_layer_->SetUp(softmax_bottom_vec_, &softmax_top_vec_); } template <typename Dtype> void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape( const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) { LossLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(bottom, top); softmax_layer_->Reshape(softmax_bottom_vec_, &softmax_top_vec_); if (top->size() >= 2) { // softmax output (*top)[1]->ReshapeLike(*bottom[0]); } } template <typename Dtype> void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Forward_cpu( const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* top) { // The forward pass computes the softmax prob values. softmax_layer_->Forward(softmax_bottom_vec_, &softmax_top_vec_); const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data(); const Dtype* label = bottom[1]->cpu_data(); int num = prob_.num(); int dim = prob_.count() / num; int spatial_dim = prob_.height() * prob_.width(); Dtype loss = 0; for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < spatial_dim; j++) { loss -= log(std::max(prob_data[i * dim + static_cast<int>(label[i * spatial_dim + j]) * spatial_dim + j], Dtype(FLT_MIN))); } } (*top)[0]->mutable_cpu_data()[0] = loss / num / spatial_dim; if (top->size() == 2) { (*top)[1]->ShareData(prob_); } } template <typename Dtype> void SoftmaxWithLossLayer<Dtype>::Backward_cpu(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top, const vector<bool>& propagate_down, vector<Blob<Dtype>*>* bottom) { if (propagate_down[1]) { LOG(FATAL) << this->type_name() << " Layer cannot backpropagate to label inputs."; } if (propagate_down[0]) { Dtype* bottom_diff = (*bottom)[0]->mutable_cpu_diff(); const Dtype* prob_data = prob_.cpu_data(); caffe_copy(prob_.count(), prob_data, bottom_diff); const Dtype* label = (*bottom)[1]->cpu_data(); int num = prob_.num(); int dim = prob_.count() / num; int spatial_dim = prob_.height() * prob_.width(); for (int i = 0; i < num; ++i) { for (int j = 0; j < spatial_dim; ++j) { bottom_diff[i * dim + static_cast<int>(label[i * spatial_dim + j]) * spatial_dim + j] -= 1; } } // Scale gradient const Dtype loss_weight = top[0]->cpu_diff()[0]; caffe_scal(prob_.count(), loss_weight / num / spatial_dim, bottom_diff); } } #ifdef CPU_ONLY STUB_GPU(SoftmaxWithLossLayer); #endif INSTANTIATE_CLASS(SoftmaxWithLossLayer); } // namespace caffe |
其实这个函数挺好懂的,总结起来大致是:
- 首先这里直接内置了一个SoftmaxLayer,利用它直接得到概率值prob_
- 之后的forward和backward都很直观了,就是没有正则项的loss function和梯度的实现方式。(这里为啥没有考虑正则项,是因为正则项的代码不是写在这这里的,而是在更新梯度时候再一起考虑的,具体可以看layer的更新代码,会发现考虑了一个叫decay的东西)
- 这里有了spatial_dim的概念后,就可以直接支持做全图的softmax了,具体来可以参考FCN一文中最后做20类分类的概率图的那个全图softmax