本文主要是介绍React中的 Scheduler,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
为什么需要调度
在 React 中,组件最终体现为 Fiber,并形成 FiberTree,Fiber 的目的是提高渲染性能,将原先的 React 渲染任务拆分为多个小的微任务,这样做的目的是可以灵活的让出主线程,可以随时打断渲染,后面再继续执行。由于需要让出主线程,需要将任务保存起来,一个个排队执行,需要的时候进行切换,为了实现排队、切换,就需要实现一个调度引擎,哪个任务先执行,哪个任务后执行,暂停之后怎么继续执行。
优先级队列
React 中,Scheduler.js 定义了定义了调度的核心逻辑,Task 包存在一个 PriorityQueue 中,优先级高的任务会先进行处理。
WorkLoop
React 中,WorkLoop 是指循环Fiber Tree 去找需要处理的任务,WorkLoop 分为同步和并发,这两个逻辑几乎一样,并发处理是,要检查是否要暂停并释放主线程给浏览器执行其他任务。
## 同步,不能中断
function workLoopSync() {while (workInProgress !== null) {performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);}
}
function workLoopConcurrent() {while (workInProgress !== null && !shouldYield()) {performUnitOfWork(workInProgress);}
}
shouldYield 大于 5 毫秒就会释放,打开 React Tools Profile 可以看到这个渲染过程
function shouldYieldToHost() {const timeElapsed = getCurrentTime() - startTime;if (timeElapsed < frameInterval) {// The main thread has only been blocked for a really short amount of time;// smaller than a single frame. Don't yield yet.return false;}
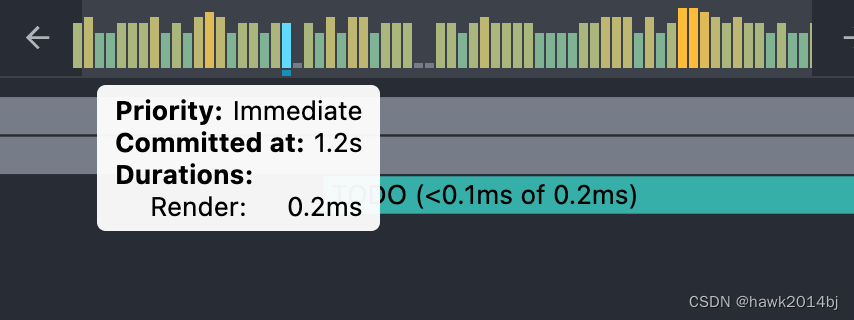
调度
首先,调度创建任务,任务通过 callback function 创建,源码 Sheduler.js -> unstable_scheduleCallback,可以看到,优先级是通过过期时间进行定义的,越早过期的优先级越高,正常的任务 5 秒过期,USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT 阻碍用户操作的任务 250 毫秒。
var timeout;switch (priorityLevel) {case ImmediatePriority:timeout = IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;case UserBlockingPriority:timeout = USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;case IdlePriority:timeout = IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;case LowPriority:timeout = LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;case NormalPriority:default:timeout = NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;break;}var expirationTime = startTime + timeout;var newTask = {id: taskIdCounter++,callback,priorityLevel,startTime,expirationTime,sortIndex: -1,};
任务加入队列并执行
if (startTime > currentTime) {// This is a delayed task.newTask.sortIndex = startTime;##########加入队列push(timerQueue, newTask);if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {// All tasks are delayed, and this is the task with the earliest delay.if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {// Cancel an existing timeout.cancelHostTimeout();} else {isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;}// Schedule a timeout.requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);}} else {newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime;##########加入队列push(taskQueue, newTask);if (enableProfiling) {markTaskStart(newTask, currentTime);newTask.isQueued = true;}// Schedule a host callback, if needed. If we're already performing work,// wait until the next time we yield.if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {isHostCallbackScheduled = true;requestHostCallback(flushWork);}
requestHostCallback 最终会调用 schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline,schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline会调用 performWorkUntilDeadline。
### 调用 schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline
function requestHostCallback(callback) {scheduledHostCallback = callback;if (!isMessageLoopRunning) {isMessageLoopRunning = true;schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();}
}
## 最终调用 performWorkUntilDeadline
let schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline;
if (typeof localSetImmediate === 'function') {// Node.js and old IE.// There's a few reasons for why we prefer setImmediate.//// Unlike MessageChannel, it doesn't prevent a Node.js process from exiting.// (Even though this is a DOM fork of the Scheduler, you could get here// with a mix of Node.js 15+, which has a MessageChannel, and jsdom.)// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/20756//// But also, it runs earlier which is the semantic we want.// If other browsers ever implement it, it's better to use it.// Although both of these would be inferior to native scheduling.schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {localSetImmediate(performWorkUntilDeadline);};
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined') {// DOM and Worker environments.// We prefer MessageChannel because of the 4ms setTimeout clamping.const channel = new MessageChannel();const port = channel.port2;channel.port1.onmessage = performWorkUntilDeadline;schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {port.postMessage(null);};
} else {// We should only fallback here in non-browser environments.schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {localSetTimeout(performWorkUntilDeadline, 0);};
}
scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime) ,通过上面的代码的定义可知scheduledHostCallback 就是flushWork,所以这里是调用 flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime)
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {const currentTime = getCurrentTime();// Keep track of the start time so we can measure how long the main thread// has been blocked.startTime = currentTime;const hasTimeRemaining = true;// If a scheduler task throws, exit the current browser task so the// error can be observed.//// Intentionally not using a try-catch, since that makes some debugging// techniques harder. Instead, if `scheduledHostCallback` errors, then// `hasMoreWork` will remain true, and we'll continue the work loop.let hasMoreWork = true;try {hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime);} finally {if (hasMoreWork) {// If there's more work, schedule the next message event at the end// of the preceding one.schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();} else {isMessageLoopRunning = false;scheduledHostCallback = null;}}} else {isMessageLoopRunning = false;}// Yielding to the browser will give it a chance to paint, so we can// reset this.needsPaint = false;
};
flushWork 在调用 workLoop, workLoop 是 scheduler 核心
function flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {// 省略一部分代码isPerformingWork = true;const previousPriorityLevel = currentPriorityLevel;try {if (enableProfiling) {try {return workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime);workLoop 是 Scheduler 的核心方法,当 currentTask 的 callback 是一个方法,这部分处理暂停任务,如果callback返回一个 function,那么在一次执行中还是执行当前任务,否则任务完成。
const callback = currentTask.callback;if (typeof callback === 'function') {currentTask.callback = null;currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;if (enableProfiling) {markTaskRun(currentTask, currentTime);}const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);currentTime = getCurrentTime();//**************是否是暂停任务if (typeof continuationCallback === 'function') {currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;if (enableProfiling) {markTaskYield(currentTask, currentTime);}} else {if (enableProfiling) {markTaskCompleted(currentTask, currentTime);currentTask.isQueued = false;}if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {pop(taskQueue);}}advanceTimers(currentTime);} else {pop(taskQueue);}
总结
React 调度是用来调度 fiber 任务的,任务可以暂停并将控制权交给浏览器,调度的核心是通过 Priority Queue 实现,根据重要程度进行排序,过期时间作为排序字段,先到期的先执行。
这篇关于React中的 Scheduler的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





