本文主要是介绍排序——冒泡、归并、快速、选择、插入、堆,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
冒泡排序,O(n²)
原理:遍历集合多次,比较相邻的两个元素,将较大或者较小的元素向后移动,类似于“气泡”一样向上浮动。
/*** * <p>Title: 基础原理</p>* <p>author : xukai</p>* <p>date : 2017年5月16日 下午2:51:22</p>* @param array*/public static void bubbleSort1(int[] array) {// 1.外层循环,次数为(length-1)for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {// 2.遍历集合,比较相邻元素大小for (int j = 0; j < array.length - i; j++) {if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {swap(array, j, j + 1);}}System.out.print("第" + i + "次循环执行之后:");print(array);}}
优化:假如在外层循环中,某次循环一次都没有执行swap操作,说明集合已经排序完毕,无需再遍历
/*** * <p>Title: 某次遍历没有swap(排序完成),那么下一次也不需要遍历</p>* <p>author : xukai</p>* <p>date : 2017年5月16日 下午3:10:03</p>* @param array*/private static void bubbleSort2(int[] array) {boolean needNextPass = true;for (int i = 1; i < array.length && needNextPass; i++) {// 1.假设集合排序完毕needNextPass = false;for (int j = 0; j < array.length - i; j++) {if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {swap(array, j, j + 1);// 2.假如未被执行,集合排序完毕,外层循环结束needNextPass = true;}}System.out.print("第" + i + "次循环执行之后:");print(array);}}
归并排序,O(nlog(n))
原理:1.将集合平均拆分为两个子集合,对子集合进行归并排序。2.直到子集合中有且仅有一个元素,对两个子集合排序。
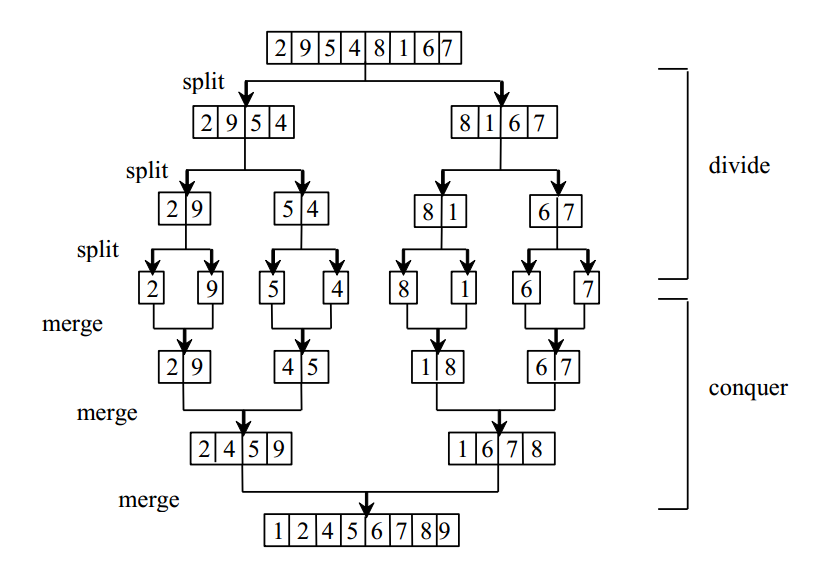
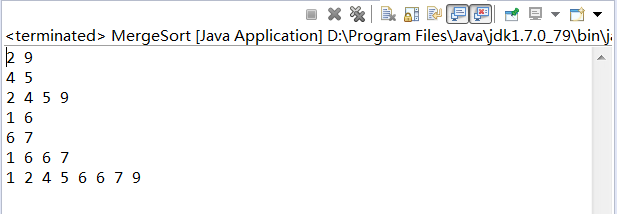
public class MergeSort {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = { 2, 9, 5, 4, 1, 6, 7, 6 };mergeSort(array);}/*** * <p>Title: 1.递归拆除数组</p>* <p>author : xukai</p>* <p>date : 2017年5月17日 下午5:51:16</p>* @param array*/public static void mergeSort(int[] array) {if (array.length > 1) {// 1.左侧数组int[] arrayLeft = new int[array.length / 2];System.arraycopy(array, 0, arrayLeft, 0, array.length / 2);mergeSort(arrayLeft);// 2.右侧数组int arrayRightLength = array.length - arrayLeft.length;int[] arrayRight = new int[arrayRightLength];System.arraycopy(array, array.length / 2, arrayRight, 0, arrayRightLength);mergeSort(arrayRight);// 3.左右侧数组合并int[] temp = merge(arrayLeft, arrayRight);print(temp);// 4.返回已经排序完毕的子数组System.arraycopy(temp, 0, array, 0, temp.length);} else {return;}}/*** * <p>Title: 合并两个数组</p>* <p>author : xukai</p>* <p>date : 2017年5月17日 下午5:51:33</p>* @param arrayLeft* @param arrayRight* @return*/private static int[] merge(int[] arrayLeft, int[] arrayRight) {int[] temp = new int[arrayLeft.length + arrayRight.length];int indexOfLeft = 0;int indexOfRight = 0;int indexOfTemp = 0;while (indexOfLeft < arrayLeft.length && indexOfRight < arrayRight.length) {if (arrayLeft[indexOfLeft] < arrayRight[indexOfRight]) {temp[indexOfTemp++] = arrayLeft[indexOfLeft++];} else {temp[indexOfTemp++] = arrayRight[indexOfRight++];}}while (indexOfLeft < arrayLeft.length) {// 左侧未遍历完temp[indexOfTemp++] = arrayLeft[indexOfLeft++];}while (indexOfRight < arrayRight.length) {// 右侧未遍历完temp[indexOfTemp++] = arrayRight[indexOfRight++];}return temp;}private static void print(int[] array) {for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}System.out.print("\n");}
}
这里需要注意一点代码中的第4步,temp数组为已经排好序的数组,一定要复制给原数组
快速排序,O(nlog(n))
原理:任意选择主元元素(默认index=0),将数组分为两部分,左侧元素小于或等于主元,右侧元素大于主元。对左右两部分递归此操作。
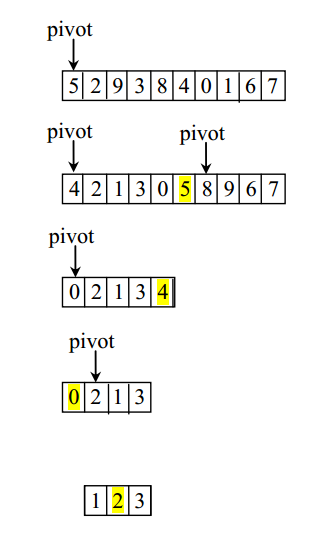
/*** @moudle: QuickSort* @version:v1.0* @Description: 快速排序:任意选择主元元素(默认index=0),将数组分为两部分,左侧元素小于或等于主元,右侧元素大于主元。递归此规则。* @author: xukai* @date: 2017年5月17日 下午6:21:08**/
public class QuickSort {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = { 5, 2, 9, 3, 8, 5, 0, 1, 6, 7 };quickSort(array);print(array);}public static void quickSort(int[] array) {quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);}private static void quickSort(int[] array, int firstIndex, int lastIndex) {if (firstIndex < lastIndex) {int pivotIndex = partition(array, firstIndex, lastIndex);quickSort(array, firstIndex, pivotIndex - 1);quickSort(array, pivotIndex + 1, lastIndex);}}/*** * <p>Title: partition</p>* <p>author : xukai</p>* <p>date : 2017年5月20日 上午11:39:50</p>* @param array* @param firstIndex* @param lastIndex* @return*/private static int partition(int[] array, int firstIndex, int lastIndex) {int pivot = array[firstIndex]; // 主元int low = firstIndex + 1; // 向前下标int high = lastIndex; // 向后下标while (low < high) {// 当前元素小于等于主元,nextwhile (low <= high && array[low] <= pivot)low++;// 当前元素大于主元,prenextwhile (high >= low && array[high] > pivot)high--;// low,high未移动,array[low]>pivot && array[high] <= pivotif (low < high)swap(array, low, high);}// TODO/*** case:* 1.(array[high]==pivot)=true,next* 2.lastIndex - firstIndex == 1*/while (high > firstIndex && array[high] >= pivot)high--; if (array[high] < pivot) {// pivot放在中间array[firstIndex] = array[high];array[high] = pivot;return high; // 返回主元新下标} else {return firstIndex; // 主元下标}}private static void print(int[] array) {for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {System.out.print(array[i] + " ");}System.out.print("\n");}private static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {int temp = array[i];array[i] = array[j];array[j] = temp;}
}
***我一直没看懂代码中TODO标签下的while循环有什么作用,为什么不删除掉… ***
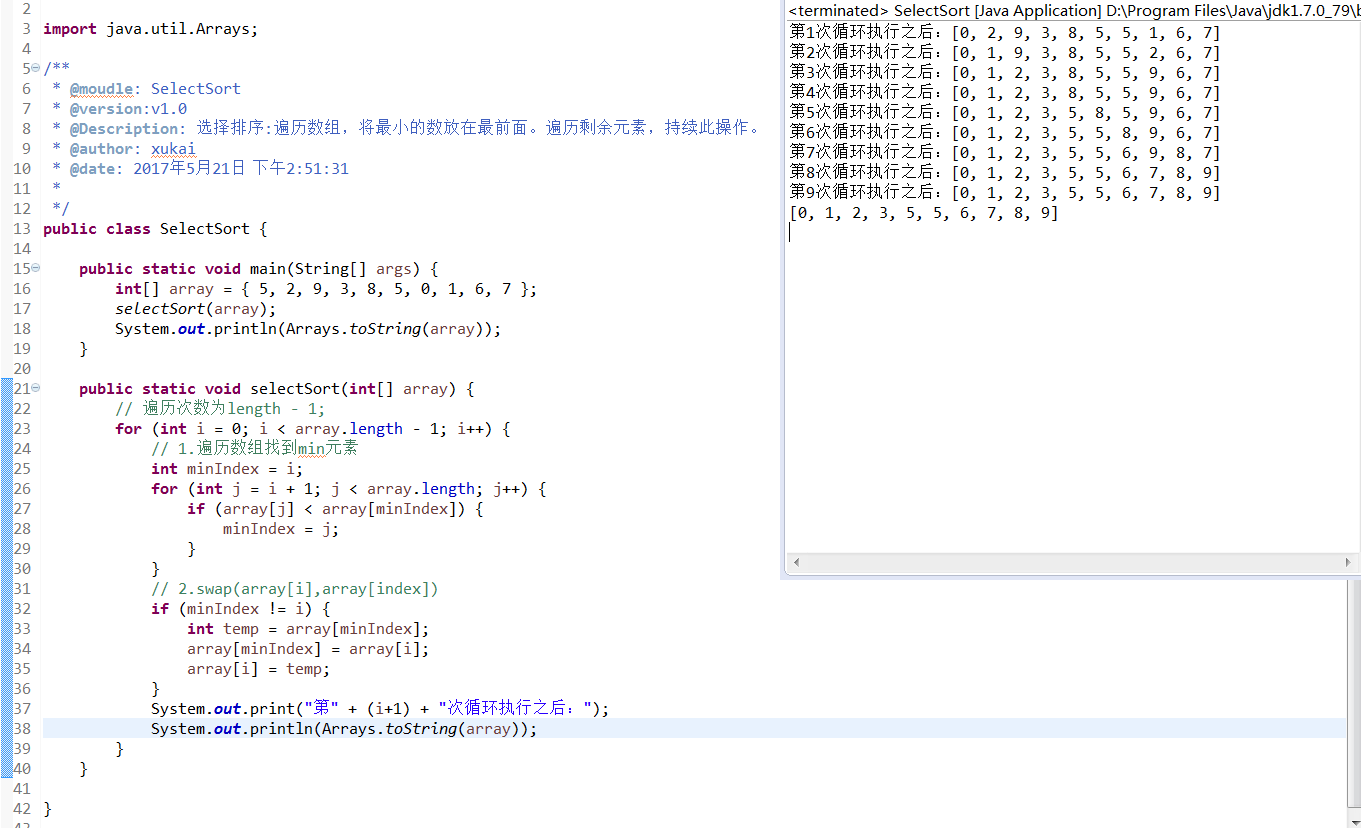
选择排序,O(n²)
原理:遍历数组,将最小的数放在最前面。遍历剩余元素,持续此操作。
/*** @moudle: SelectSort* @version:v1.0* @Description: 选择排序:遍历数组,将最小的数放在最前面。遍历剩余元素,持续此操作。* @author: xukai* @date: 2017年5月21日 下午2:51:31**/
public class SelectSort {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array = { 5, 2, 9, 3, 8, 5, 0, 1, 6, 7 };selectSort(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}public static void selectSort(int[] array) {// 遍历次数为length - 1;for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {// 1.遍历数组找到min元素int minIndex = i;for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) {minIndex = j;}}// 2.swap(array[i],array[index])if (minIndex != i) {int temp = array[minIndex];array[minIndex] = array[i];array[i] = temp;}}}}
插入排序,O(n²)
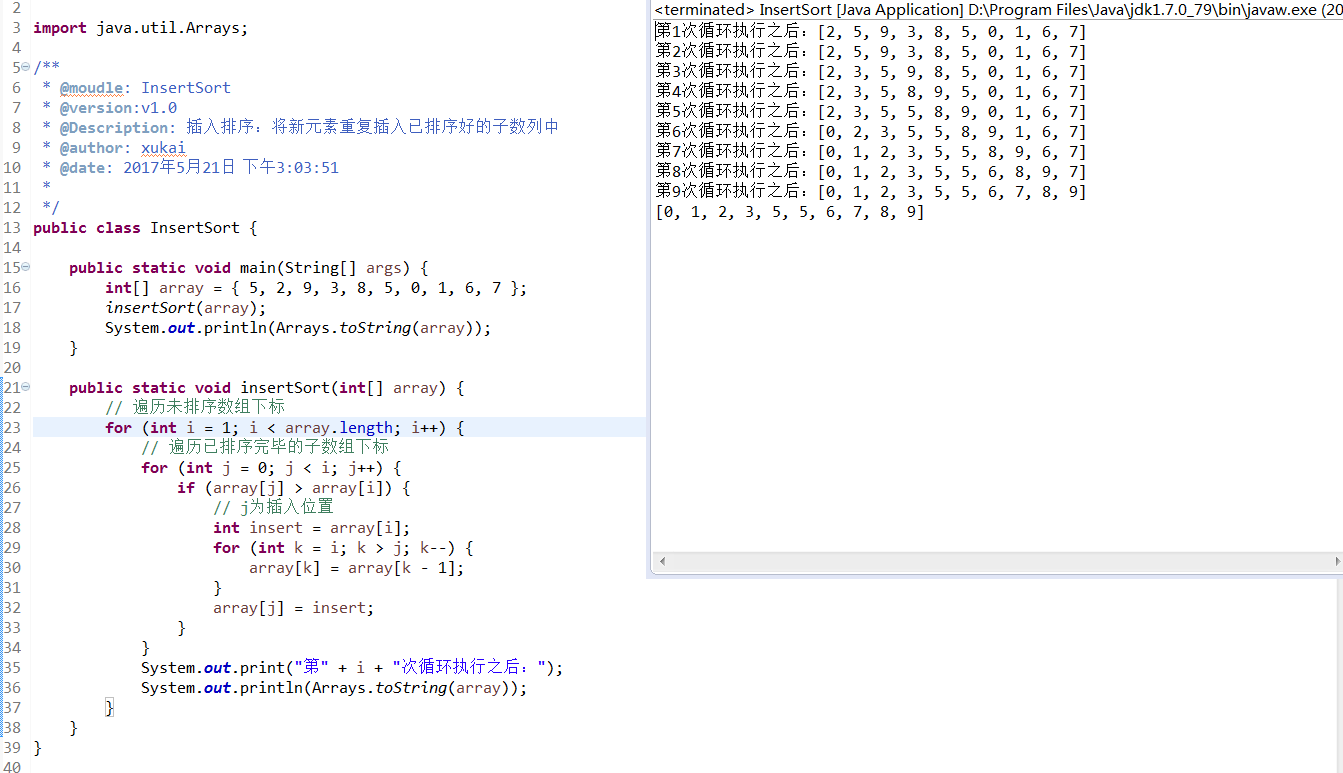
原理:将新元素重复插入已排序好的子数列中
public static void insertSort(int[] array) {// 遍历未排序数组下标for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) {// 遍历已排序完毕的子数组下标for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {if (array[j] > array[i]) {// j为插入位置int insert = array[i];for (int k = i; k > j; k--) {array[k] = array[k - 1];}array[j] = insert;}}System.out.print("第" + i + "次循环执行之后:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}}
堆排序,O(nlog(n))
堆特性:
- 一颗完整的二叉树(除了最后一层未满且叶子偏左,或每层都是满的)
- 每个结点大于或者等于它的子节点
添加结点原理:
- 将新元素放置进内部List集合
- 将新元素下标作为游标,开始遍历其父结点
- 如果大于父结点,swap(子节点,父结点),执行2和3,直到遍历树完毕。
删除结点原理:
- 判断是否为空树,if(true) return null
- 将最后的元素放置在index=0(根),并移除原先元素,temp=root
- 遍历树,游标从根开始,找到左右子树中最大值的下标maxIndex
- 比较游标和maxIndex的值大小,如果list(cursor)<maxIndex,那么swap
- cursor=maxIndex,依旧向下遍历树。直到无swap执行
import java.util.ArrayList;/*** @moudle: 堆类:1.每个结点大于它的所有子结点。2.完全二叉树* @version:v1.0* @Description: TODO* @author: xukai* @date: 2017年5月21日 下午1:58:16** @param <E>*/
public class Heap<E extends Comparable<E>> {private ArrayList<E> list = new ArrayList<>();public Heap() {}public Heap(E[] objects) {for (int i = 0; i < objects.length; i++) {add(objects[i]);}}public void add(E object) {list.add(object);// 1.新元素下标int currentIndex = list.size() - 1;while (currentIndex > 0) {int parentIndex = (currentIndex - 1) / 2; // 当前结点的父结点// 2.新元素大于其父结点,swapif (list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(parentIndex)) > 0) {E temp = list.get(currentIndex);list.set(currentIndex, list.get(parentIndex));list.set(parentIndex, temp);} else {break;}// 3.向上遍历树currentIndex = parentIndex;}}public E remove() {// 1.判断是否为空树,if(true) return nullif (list.size() == 0)return null;// 2.将最后的元素放置在index=0(根),并移除原先元素E removeObject = list.get(0);list.set(0, list.get(list.size() - 1));list.remove(list.size() - 1);// 3.从头遍历树int currentIndex = 0;while (currentIndex < list.size()) {// 3.1 maxIndex(left,right)int leftChildIndex = 2 * currentIndex + 1;int rightChildIndex = leftChildIndex + 1;if (leftChildIndex >= list.size())break; // 超出范围int maxIndex = leftChildIndex; // 默认为左子结点,右子节点可能为空if (rightChildIndex < list.size())if (list.get(maxIndex).compareTo(list.get(rightChildIndex)) < 0) maxIndex = rightChildIndex;// 3.2 if(current<maxIndex) swap(current, maxIndex)if (list.get(currentIndex).compareTo(list.get(maxIndex)) < 0) {E temp = list.get(maxIndex);list.set(maxIndex, list.get(currentIndex));list.set(currentIndex, temp);currentIndex = maxIndex;} else {break;}}// 4.返回被删除元素return removeObject;}public int getSize() {return list.size();}
}
排序原理:执行堆的删除操作,即获得堆中最大值。
/*** @moudle: HeapSort * @version:v1.0* @Description: 堆排序* @author: xukai* @date: 2017年5月21日 下午2:38:36**/
public class HeapSort {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] array = {5, 2, 9, 3, 8, 5, 0, 1, 6, 7};heapSort(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}public static Integer[] heapSort(Integer[] array) {// 1.创建一个堆对象,并初始化完毕Heap<Integer> heap = new Heap<>(array);// 2.反向遍历数组,从头开始删除for (int i = array.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {array[i] = heap.remove();}return array;}
}
总结
JDK中有很多的排序方法实现,例如:Arrays里面的sort方法。
查看代码
动画演示
这篇关于排序——冒泡、归并、快速、选择、插入、堆的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








