本文主要是介绍python 判断点和线段相交,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
python 判断点和线段相交
import numpy as np
import cv2
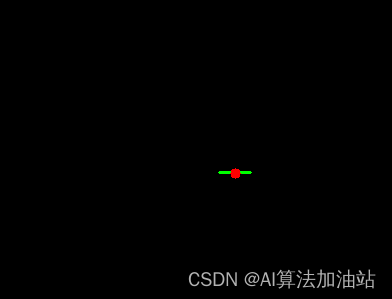
import numpy as npdef point_to_line_distance(points, line_segments):# line_segments = [[549, 303], [580, 303]]# points = [565, 304]x0, y0, x1, y1=line_segments[0][0], line_segments[0][1], line_segments[1][0], line_segments[1][1]px,py=points[0],points[1]"""计算点到线段的距离"""line_mag = np.sqrt((x1 - x0) ** 2 + (y1 - y0) ** 2)if line_mag < 1e-6:return np.sqrt((px - x0) ** 2 + (py - y0) ** 2)u = ((px - x0) * (x1 - x0) + (py - y0) * (y1 - y0)) / (line_mag ** 2)if u < 0.0 or u > 1.0:# 最近点在线段外ix = min(max(x0, x1), max(min(x0, x1), px))iy = min(max(y0, y1), max(min(y0, y1), py))else:# 最近点在线段上ix = x0 + u * (x1 - x0)iy = y0 + u * (y1 - y0)return np.sqrt((px - ix) ** 2 + (py - iy) ** 2)def show_dis(line_segments,points):# 定义线段和点# line_segments = [[584, 284], [645, 279]]# points = [612, 317]# 创建一个黑色图像image = np.zeros((600, 800, 3), dtype=np.uint8)start_point = tuple(line_segments[0])end_point = tuple(line_segments[1])color = (0, 255, 0) # 绿色thickness = 2cv2.line(image, start_point, end_point, color, thickness)# 绘制点center = tuple(points)color = (0, 0, 255) # 红色radius = 5thickness = -1 # 实心圆cv2.circle(image, center, radius, color, thickness)# 显示图像cv2.imshow('dis', image)cv2.waitKey(0)# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':line_segments = [[549, 303], [580, 303]]point = [565, 304]show_dis(line_segments, point)distance = point_to_line_distance(point, line_segments)print(f"点 ({point[0]}, {point[1]}) 到线段 的距离: {distance}")这篇关于python 判断点和线段相交的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






