本文主要是介绍Linux内核下网卡硬件 MAC 和PHY分析笔记,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1 简介
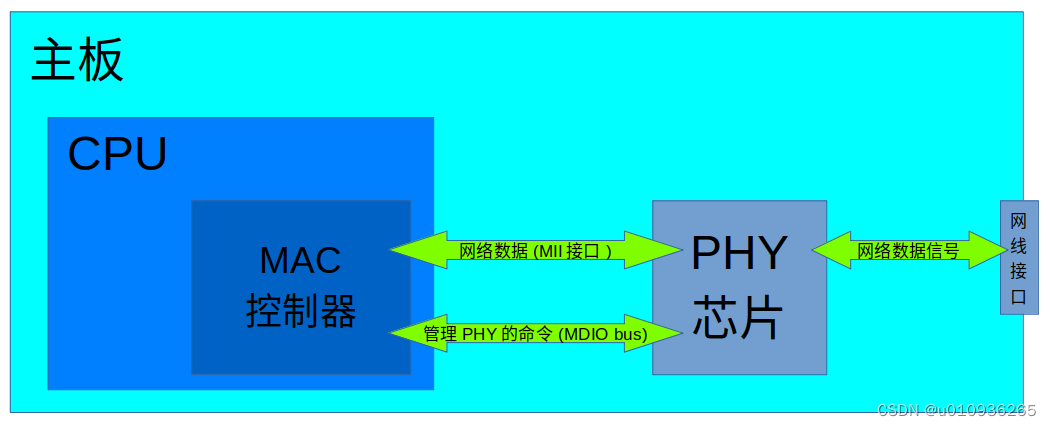
通常CPU自带的以太网接口是MAC控制器,为了实现完整的功能,外围硬件还需要增加一个PHY芯片。
PHY芯片在建立网络连接时负责协商确定网速、全双工 或者 半双工等。在正常通讯时负责在MAC控制器的MII信号 与 网线中的信号之间做转换。
本文的内核代码主要来自kernel-5.4.18
2 PHY芯片 和 MDIO bus
2.1 简介
Most network devices consist of set of registers which provide an interface to a MAC layer, which communicates with the physical connection through a PHY.
The PHY concerns itself with negotiating link parameters with the link partner on the other side of the network connection (typically, an ethernet cable), and provides a register interface to allow drivers to determine what settings were chosen, and to configure what settings are allowed.
《Documentation/networking/phy.rst》
2.2 驱动分析
2.2.1 数据结构
struct phy_device;
struct phy_driver;struct class mdio_bus_class;
struct bus_type mdio_bus_type;
struct mii_bus;
struct mdio_device;
struct mdio_driver;
2.2.2 mii_bus、phy_device 和 mdio_device 的初始化
mdiobus_register();-> __mdiobus_register(); -> mdiobus_scan(); -> get_phy_device();-> get_phy_id();-> mdiobus_read();-> phy_device_create();-> phy_device_register();-> mdiobus_register_device();struct mii_bus表示一个mdio bus,mdiobus_register()函数用来向内核注册一个mdio bus。在注册mdio bus时会扫描这个mdio bus上连接的所有phy芯片。
一个mdio bus上最多可以连接32个phy芯片,每个phy芯片都有一个唯一的总线地址。驱动代码会通过唯一的总线地址去读取phy芯片的ID,如果在某个总线地址上读到了ID,就意味着发现了一个phy芯片。
发现phy芯片后,会调用phy_device_create()函数创建struct phy_device和struct mdio_device对象,然后调用phy_device_register() 和 mdiobus_register_device()函数向内核注册device。
在注册phy_device后,会遍历内核中的phy_driver,通过结构体中成员变量phy_id来配对。
2.2.3 通⽤phy驱动
//drivers/net/phy/phy_device.c
static struct phy_driver genphy_driver = {.phy_id = 0xffffffff,.phy_id_mask = 0xffffffff,.name = "Generic PHY",.soft_reset = genphy_no_soft_reset,.get_features = genphy_read_abilities,.aneg_done = genphy_aneg_done,.suspend = genphy_suspend,.resume = genphy_resume,.set_loopback = genphy_loopback,
};
2.3 查看系统下的相关信息
2.3.1 查看设备和驱动的信息:/sys/bus/mdio_bus/
# ls /sys/bus/mdio_bus/drivers
'Broadcom BCM84881' 'Generic Clause 45 PHY' 'Generic PHY'2.3.2 设备类信息:/sys/class/phy/
2.3.3 mdio bus的统计信息:/sys/class/mdio_bus/<bus>/statistics/ (kernel-5.6以后的内核才有)
# ls /sys/class/mdio_bus/fixed-0/statistics/
errors errors_18 errors_28 reads reads_18 reads_28 transfers transfers_18 transfers_28 writes writes_18 writes_28
errors_0 errors_19 errors_29 reads_0 reads_19 reads_29 transfers_0 transfers_19 transfers_29 writes_0 writes_19 writes_29
errors_1 errors_2 errors_3 reads_1 reads_2 reads_3 transfers_1 transfers_2 transfers_3 writes_1 writes_2 writes_3
errors_10 errors_20 errors_30 reads_10 reads_20 reads_30 transfers_10 transfers_20 transfers_30 writes_10 writes_20 writes_30
errors_11 errors_21 errors_31 reads_11 reads_21 reads_31 transfers_11 transfers_21 transfers_31 writes_11 writes_21 writes_31
errors_12 errors_22 errors_4 reads_12 reads_22 reads_4 transfers_12 transfers_22 transfers_4 writes_12 writes_22 writes_4
errors_13 errors_23 errors_5 reads_13 reads_23 reads_5 transfers_13 transfers_23 transfers_5 writes_13 writes_23 writes_5
errors_14 errors_24 errors_6 reads_14 reads_24 reads_6 transfers_14 transfers_24 transfers_6 writes_14 writes_24 writes_6
errors_15 errors_25 errors_7 reads_15 reads_25 reads_7 transfers_15 transfers_25 transfers_7 writes_15 writes_25 writes_7
errors_16 errors_26 errors_8 reads_16 reads_26 reads_8 transfers_16 transfers_26 transfers_8 writes_16 writes_26 writes_8
errors_17 errors_27 errors_9 reads_17 reads_27 reads_9 transfers_17 transfers_27 transfers_9 writes_17 writes_27 writes_9文件内容说明:
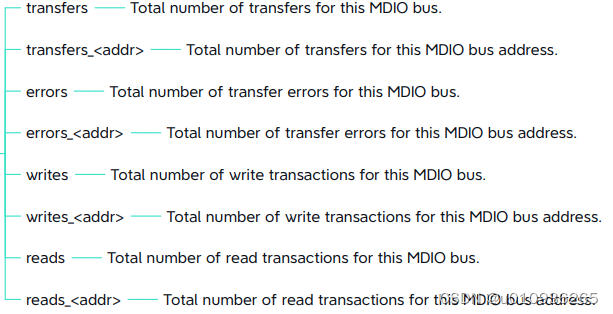
《Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-bus-mdio(kernel-5.6)》
2.4 mdio bus调试:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/mdio/mdio_access
__mdiobus_read();-> trace_mdio_access();__mdiobus_write();-> trace_mdio_access();3 MAC 与 PHY之间的网络数据接口(各种MII)
3.1 数据结构
//include/linux/phy.h
struct phy_device {......phy_interface_t interface;......
};//include/linux/phy.h
/* Interface Mode definitions */
typedef enum {PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_NA,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_INTERNAL,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_MII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_GMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_SGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_TBI,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_REVMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_ID,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_RXID,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_TXID,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RTBI,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_SMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_XGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_MOCA,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_QSGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_TRGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_1000BASEX,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_2500BASEX,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RXAUI,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_XAUI,/* 10GBASE-KR, XFI, SFI - single lane 10G Serdes */PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_10GKR,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_USXGMII,PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_MAX,
} phy_interface_t;3.2 在设备树中指定使用哪种MII
3.2.1 设备树属性“phy-mode” 和 “phy-connection-type”
可选的属性值
//Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-controller.yaml- internal- mii- gmii- sgmii- qsgmii- tbi- rev-mii- rmii# RX and TX delays are added by the MAC when required- rgmii# RGMII with internal RX and TX delays provided by the PHY,# the MAC should not add the RX or TX delays in this case- rgmii-id# RGMII with internal RX delay provided by the PHY, the MAC# should not add an RX delay in this case- rgmii-rxid# RGMII with internal TX delay provided by the PHY, the MAC# should not add an TX delay in this case- rgmii-txid- rtbi- smii- xgmii- trgmii- 1000base-x- 2500base-x- rxaui- xaui# 10GBASE-KR, XFI, SFI- 10gbase-kr- usxgmii
3.2.2 获取“phy-mode” 和 “phy-connection-type”属性的函数
of_get_phy_mode();-> of_property_read_string(np, "phy-mode", &pm);-> of_property_read_string(np, "phy-connection-type", &pm);3.3 RGMII信号中的 delay
The Reduced Gigabit Medium Independent Interface (RGMII) is a 12-pin
electrical signal interface using a synchronous 125Mhz clock signal and several
data lines. Due to this design decision, a 1.5ns to 2ns delay must be added
between the clock line (RXC or TXC) and the data lines to let the PHY (clock
sink) have enough setup and hold times to sample the data lines correctly. The
PHY library offers different types of PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII* values to let
the PHY driver and optionally the MAC driver, implement the required delay. The
values of phy_interface_t must be understood from the perspective of the PHY
device itself, leading to the following:* PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII: the PHY is not responsible for inserting any internal delay by itself, it assumes that either the Ethernet MAC (if capableor the PCB traces) insert the correct 1.5-2ns delay* PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_TXID: the PHY should insert an internal delayfor the transmit data lines (TXD[3:0]) processed by the PHY device* PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_RXID: the PHY should insert an internal delayfor the receive data lines (RXD[3:0]) processed by the PHY device* PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII_ID: the PHY should insert internal delays for both transmit AND receive data lines from/to the PHY deviceWhenever possible, use the PHY side RGMII delay for these reasons:* PHY devices may offer sub-nanosecond granularity in how they allow areceiver/transmitter side delay (e.g: 0.5, 1.0, 1.5ns) to be specified. Suchprecision may be required to account for differences in PCB trace lengths* PHY devices are typically qualified for a large range of applications(industrial, medical, automotive...), and they provide a constant and reliable delay across temperature/pressure/voltage ranges* PHY device drivers in PHYLIB being reusable by nature, being able toconfigure correctly a specified delay enables more designs with similar delayrequirements to be operate correctlyFor cases where the PHY is not capable of providing this delay, but the
Ethernet MAC driver is capable of doing so, the correct phy_interface_t value
should be PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII, and the Ethernet MAC driver should be
configured correctly in order to provide the required transmit and/or receive
side delay from the perspective of the PHY device. Conversely, if the Ethernet
MAC driver looks at the phy_interface_t value, for any other mode but
PHY_INTERFACE_MODE_RGMII, it should make sure that the MAC-level delays are
disabled.In case neither the Ethernet MAC, nor the PHY are capable of providing the
required delays, as defined per the RGMII standard, several options may be
available:* Some SoCs may offer a pin pad/mux/controller capable of configuring a givenset of pins'strength, delays, and voltage; and it may be a suitableoption to insert the expected 2ns RGMII delay.* Modifying the PCB design to include a fixed delay (e.g: using a specificallydesigned serpentine), which may not require software configuration at all.《Documentation/networking/phy.rst》
3.4 查看当前系统下MAC和PHY之间正在使用的是哪种MII
/sys/class/mdio_bus/<bus>/<device>/phy_interface
《Documentation/ABI/testing/sysfs-class-net-phydev》
3.5 特殊用法:两个MAC控制器通过MII直连,不经过PHY芯片
在这种情况下因为没有PHY芯片,硬件上无法通过协商确定网速、全/半双工等状态信息,需要通过其他方式来获取这些信息,请看下面的“fixed-link”相关的章节。
4 物理链路的状态
4.1 简介
网络物理链路状态在发生改变时,需要确定 UP/DOWN、网速、全双工还是半双工等关键状态信息。
多数时候网络物理链路的状态是通过phy硬件协商确定的,还有另一种方法就是直接指定物理链路的状态。
在某些特殊的硬件设计中,直接将两个MAC控制器的MII信号直连,不使用PHY芯片,这导致硬件无法协商确定物理链路状态,这种情况下也需要直接指定物理链路状态。
4.2 通过phy芯片获取物理链路状态
4.2.1 状态处理工作项
在创建phy_device时会创建工作项,处理函数是phy_state_machine();
phy_device_create();-> INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&dev->state_queue, phy_state_machine);
4.2.2 向内核添加工作项
轮训模式:
当phydev->irq == PHY_POLL时,采用轮训模式,轮训间隔是1秒,轮训间隔由宏 PHY_STATE_TIME 控制。
中断模式:
phy_request_interrupt();-> request_threaded_irq(phydev->irq, NULL, phy_interrupt, ...);phy_interrupt();
-> phy_trigger_machine();4.3 Fixed MDIO bus
4.3.1 简介
内核配置:CONFIG_FIXED_PHY
MDIO Bus/PHY emulation with fixed speed/link PHYs
Adds the platform "fixed" MDIO Bus to cover the boards that use PHYs that are not connected to the real MDIO bus.
drivers/net/phy/Kconfig
4.3.2 初始化
static int __init fixed_mdio_bus_init(void)
{struct fixed_mdio_bus *fmb = &platform_fmb;int ret;pdev = platform_device_register_simple("Fixed MDIO bus", 0, NULL, 0);......snprintf(fmb->mii_bus->id, MII_BUS_ID_SIZE, "fixed-0");fmb->mii_bus->name = "Fixed MDIO Bus";fmb->mii_bus->priv = fmb;fmb->mii_bus->parent = &pdev->dev;fmb->mii_bus->read = &fixed_mdio_read;fmb->mii_bus->write = &fixed_mdio_write;ret = mdiobus_register(fmb->mii_bus);......
}
module_init(fixed_mdio_bus_init);4.3.3 查看系统下的Fixed MDIO bus信息
/sys/class/mdio_bus/fixed-0/
/sys/bus/platform/devices/Fixed\ MDIO\ bus.0/
4.4 通过设备树节点“fixed-link”指定物理链路的状态
4.4.1 设备树“fixed-link”节点的属性
"full-duplex"
"speed"
"pause"
"asym-pause"
“link-gpios”
含义如下(Documentation/devicetree/bindings/net/ethernet-controller.yaml)
properties:speed:allOf:- $ref: /schemas/types.yaml#definitions/uint32- enum: [10, 100, 1000]description:Link speed.full-duplex:$ref: /schemas/types.yaml#definitions/flagdescription:Indicates that full-duplex is used. When absent, halfduplex is assumed.asym-pause:$ref: /schemas/types.yaml#definitions/flagdescription:Indicates that asym_pause should be enabled.link-gpios:maxItems: 1description:GPIO to determine if the link is up
4.4.2 对应的数据结构
struct fixed_phy_status {int link;int speed;int duplex;int pause;int asym_pause;
};4.4.3 获取设备树中“fixed-link”内容的代码
of_phy_register_fixed_link();-> fixed_phy_register();-> __fixed_phy_register();4.5 通过ethtool命令设置物理链路状态
例如:ethtool -s enp0s31f6 speed 100 duplex full autoneg off
内核中对应的代码:struct ethtool_ops->set_link_ksettings();
4.6 查看网络物理链路的状态信息
方法一、ethtool enp0s31f6
方法二、
/sys/class/net/<net_dev>/duplex
/sys/class/net/<net_dev>/speed
这篇关于Linux内核下网卡硬件 MAC 和PHY分析笔记的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







