本文主要是介绍TFLite JNI 接口实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
JNI is a C interface, which is not object-oriented. It does not really pass the objects.
要实现Mace JNI 接口,先研究下TFLite的 JNI接口实现
Java Code Examples for org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor
Java Code Examples for org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor![]() https://www.programcreek.com/java-api-examples/?api=org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor学习 java-api的网址 如ByteBuffer
https://www.programcreek.com/java-api-examples/?api=org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor学习 java-api的网址 如ByteBuffer
Java Code Examples for java.nio.ByteBuffer![]() https://www.programcreek.com/java-api-examples/?api=java.nio.ByteBuffer
https://www.programcreek.com/java-api-examples/?api=java.nio.ByteBuffer
Tensor数据类型判断
org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor.dataTypeOf java code examples | Tabnine![]() https://www.tabnine.com/code/java/methods/org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor/dataTypeOfjava/org/tensorflow/lite/Tensor.java
https://www.tabnine.com/code/java/methods/org.tensorflow.lite.Tensor/dataTypeOfjava/org/tensorflow/lite/Tensor.java
TFLite基础知识 - VitoYeah - 博客园tensorflow lite基本知识https://www.cnblogs.com/vitoyeah/p/10273299.html
How to run a Tensorflow-Lite inference in (Android Studio) NDK (C / C++ API)? - Stack Overflowhttps://stackoverflow.com/questions/61523713/how-to-run-a-tensorflow-lite-inference-in-android-studio-ndk-c-c-api
How do I declare and initialize an array in Java?
How do I declare and initialize an array in Java? - Stack Overflowhttps://stackoverflow.com/questions/1200621/how-do-i-declare-and-initialize-an-array-in-java
int[] myIntArray = new int[3];
int[] myIntArray = {1, 2, 3};
int[] myIntArray = new int[]{1, 2, 3};
// Since Java 8. Doc of IntStream:
// https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/stream/IntStream.html
int [] myIntArray = IntStream.range(0, 100).toArray(); // From 0 to 99
int [] myIntArray = IntStream.rangeClosed(0, 100).toArray(); // From 0 to 100
int [] myIntArray = IntStream.of(12,25,36,85,28,96,47).toArray(); // The order is preserved.
int [] myIntArray = IntStream.of(12,25,36,85,28,96,47).sorted().toArray(); // Sort
For classes, for example String, it's the same:
String[] myStringArray = new String[3];
String[] myStringArray = {"a", "b", "c"};
String[] myStringArray = new String[]{"a", "b", "c"};
// String对象创建后是不可变的如需改变使用StringBuilder
Syntax with values given (variable/field initialization):
int[] num = {1,2,3,4,5};
Or (less preferred) 但这是C/C++的用法
int num[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
java 基本数据类型和引用
float f1;
boolean b1 = f1.getClass().isPrimitive();
Test.java:12: error: float cannot be dereferenced
boolean b1 = f1.getClass().isPrimitive();
如果使用float的wrapper class,就可使用函数getClass了, 这样说明了基本类型和对象的区别
Float Arr = new Float(1.0); // java 里创建对象和C++还是不同的, class A a(xx) 这应该是在栈里创建而java 没有这种写法
基本类型的数组是个对象
int[] Arr = new int[5];
Class arrClass = Arr.getClass();
System.out.println("name myClass isPrimitive: "
+ arrClass.isPrimitive());
System.out.println("name myClass isArray: "
+ arrClass.isArray());
System.out.println("name myClass: "
+ arrClass.getName());
// Get the ComponentType of arrClass
// using getComponentType() method
System.out.println("ComponentType of myClass: "
+ arrClass.getComponentType());
java 对象类型判断
java判断对象是什么数据类型的方法 - 编程语言 - 亿速云这篇文章将为大家详细讲解有关java判断对象是什么数据类型的方法,小编觉得挺实用的,因此分享给大家做个参考,希望大家阅读完这篇文章后可以有所收获。1、insta...https://www.yisu.com/zixun/130629.html
java 字节序和native字节序
Java中的大端和小端 - 阿提说说 - OSCHINA - 中文开源技术交流社区Java整型的字节序是() A.Little-Endian(小端) B.Big-Endian(大端) C.由运行程序的CPU决定 D.由编译程序的CPU决定 对于大小端,我估计肯定有很多开发人员跟我一样都没听过 由于Java是跨平台的,JVM为我们屏蔽了...https://my.oschina.net/itsaysay/blog/4299422import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JVMEndianTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteOrder byteOrder = ByteOrder.nativeOrder();
//LITTLE_ENDIAN,CPU是Intel的
System.out.println(byteOrder);
int x = 0x01020304;
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.wrap(new byte[4]);
bb.asIntBuffer().put(x);
String ss_before = Arrays.toString(bb.array());
System.out.println("默认字节序 " + bb.order().toString() + "," + " 内存数据 " + ss_before);
bb.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
bb.asIntBuffer().put(x);
String ss_after = Arrays.toString(bb.array());
System.out.println("修改字节序 " + bb.order().toString() + "," + " 内存数据 " + ss_after);
}
}
native order 也就是CPU决定的 order和 java oder的区别
上面代码打印出的log:
LITTLE_ENDIAN (ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
默认字节序 BIG_ENDIAN, 内存数据 [1, 2, 3, 4] (0x01020304 大端存储: 低位0x04, 低地址0x01)
修改字节序 LITTLE_ENDIAN, 内存数据 [4, 3, 2, 1] (0x01020304 小端存储: 低位0x04, 低地址0x04)
java中大小端问题研究 - 掘金一篇简单明了的工具类生成文章![]() https://juejin.cn/post/6844903591963000846关于大小端,java提供了对应的函数
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903591963000846关于大小端,java提供了对应的函数
public static short littleByteToShort(byte[] data) {
if (data.length != 2) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("the byte length is not 2");
}
return ByteBuffer.allocate(data.length).order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN).put(data).getShort(0);
}
public static byte[] shortToLittleByte(short data) {
return ByteBuffer.allocate(2).order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN).putShort(data).array();
}
如果不做处理,通过JNI传输的值有问题吗?
写代码验证了下, 基本数据类型 int/float, int array是没有问题的
但如果是
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
Log.i(TAG, "Default java endian: "+buf.order().toString());
buf.putInt(0x2);
byte[] result = buf.array();
Log.i(TAG, "bytes: " + result[0]);
printBytes(result);
ByteBuffer buf1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
buf1.order(ByteOrder.LITTLE_ENDIAN);
buf1.putInt(0x2);
Log.i(TAG, "now java endian: "+buf1.order().toString());
result = buf1.array();
Log.i(TAG, "bytes: " + result[0]);
printBytes(result);
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: Default java endian: BIG_ENDIAN
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: bytes: 0
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: 0 0 0 2
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: now java endian: LITTLE_ENDIAN
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: bytes: 2
01-01 01:15:44.734 8954 8954 I little_big_edian: 2 0 0 0
为什么要使用FloatBuffer替代float[]
The main reason is performance: ByteBuffers and the other NIO classes enable accelerated operations when interfacing with native code (typically by avoiding the need to copy data into a temporary buffer).
This is pretty important if you are doing a lot of OpenGL rendering calls for example.
The reason for creating a ByteBuffer first is that you want to use the allocateDirect call to create a direct byte buffer, which benefits from the accelerated operations. You then create a FloatBuffer from this that shares the same memory. The FloatBuffer doesn't itself have an allocateDirect method for some reason, which is why you have to go via ByteBuffer.
Java Code Examples of java.nio.FloatBufferThis page provides Java code examples for java.nio.FloatBuffer. The examples are extracted from open source Java projects from GitHub.![]() http://www.javased.com/?api=java.nio.FloatBuffer
http://www.javased.com/?api=java.nio.FloatBuffer
colorValues = new int[FINAL_SIZE * FINAL_SIZE];
float[] floatValues = new float[FINAL_SIZE * FINAL_SIZE * 3];
floatBuffer = FloatBuffer.wrap(floatValues, 0, FINAL_SIZE * FINAL_SIZE * 3);
floatBuffer.rewind(); // The position is set to zero and the mark is discarded
floatBuffer.put(xx);
floatBuffer.array();
FloatBuffer (Java SE 9 & JDK 9 )![]() https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/nio/FloatBuffer.html#rewind--
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/nio/FloatBuffer.html#rewind--
157 // set input tensors
158 for (int i = 0; i < inputs.length; ++i) {
159 getInputTensor(i).setTo(inputs[i]);
160 }
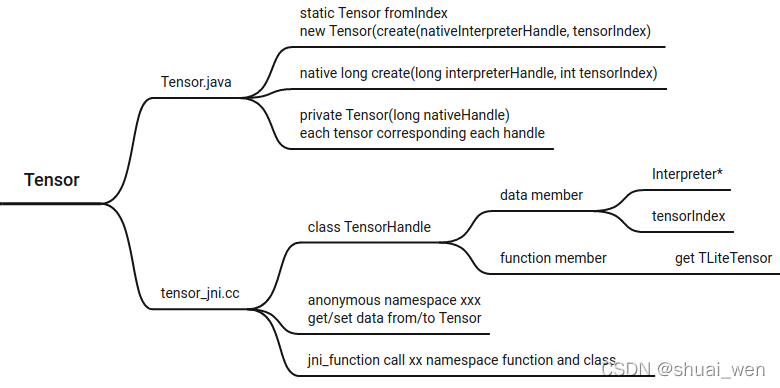
295 * Gets the input {@link Tensor} for the provided input index.
296 *
297 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the input index is invalid.
298 */
299 Tensor getInputTensor(int index) {
300 if (index < 0 || index >= inputTensors.length) {
301 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid input Tensor index: " + index);
302 }
303 Tensor inputTensor = inputTensors[index];
304 if (inputTensor == null) {
305 inputTensor =
306 inputTensors[index] =
307 Tensor.fromIndex(interpreterHandle, getInputTensorIndex(interpreterHandle, index));
308 }
309 return inputTensor;
310 }
170 /**
171 * Copies the contents of the provided {@code src} object to the Tensor.
172 *
173 * <p>The {@code src} should either be a (multi-dimensional) array with a shape matching that of
174 * this tensor, a {@link ByteByffer} of compatible primitive type with a matching flat size, or
175 * {@code null} iff the tensor has an underlying delegate buffer handle.
176 *
177 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the tensor is a scalar or if {@code src} is not compatible
178 * with the tensor (for example, mismatched data types or shapes).
179 */
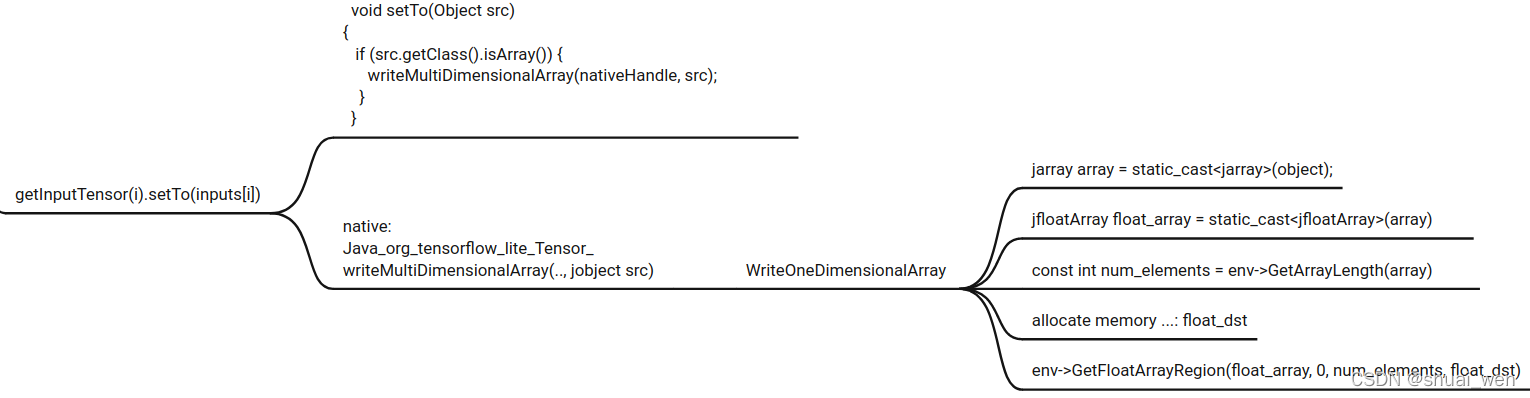
180 void setTo(Object src) {
181 if (src == null) {
182 if (hasDelegateBufferHandle(nativeHandle)) {
183 return;
184 }
185 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
186 "Null inputs are allowed only if the Tensor is bound to a buffer handle.");
187 }
188 throwIfTypeIsIncompatible(src);
189 throwIfSrcShapeIsIncompatible(src);
190 if (isBuffer(src)) {
191 setTo((Buffer) src);
192 } else if (src.getClass().isArray()) {
193 writeMultiDimensionalArray(nativeHandle, src);
194 } else {
195 writeScalar(nativeHandle, src);
196 }
197 }
164 size_t WriteOneDimensionalArray(JNIEnv* env, TfLiteType data_type,
165 const void* src, size_t src_size, jarray dst) {
166 const int len = env->GetArrayLength(dst);
167 const size_t size = len * ElementByteSize(data_type);
168 if (size > src_size) {
169 ThrowException(
170 env, kIllegalStateException,
171 "Internal error: cannot fill a Java array of %d bytes with a Tensor of "
172 "%d bytes",
173 size, src_size);
174 return 0;
175 }
176 switch (data_type) {
177 case kTfLiteFloat32: {
178 jfloatArray float_array = static_cast<jfloatArray>(dst);
179 env->SetFloatArrayRegion(float_array, 0, len,
180 static_cast<const jfloat*>(src));
181 return size;
182 }
183 case kTfLiteInt32: {
184 jintArray int_array = static_cast<jintArray>(dst);
185 env->SetIntArrayRegion(int_array, 0, len, static_cast<const jint*>(src));
186 return size;
187 }
188 case kTfLiteInt64: {
189 jlongArray long_array = static_cast<jlongArray>(dst);
190 env->SetLongArrayRegion(long_array, 0, len,
191 static_cast<const jlong*>(src));
192 return size;
193 }
322 Tensor getOutputTensor(int index) {
323 if (index < 0 || index >= outputTensors.length) {
324 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid output Tensor index: " + index);
325 }
326 Tensor outputTensor = outputTensors[index];
327 if (outputTensor == null) {
328 outputTensor =
329 outputTensors[index] =
330 Tensor.fromIndex(interpreterHandle, getOutputTensorIndex(interpreterHandle, index));
331 }
332 return outputTensor;
333 }
235 /**
236 * Copies the contents of the tensor to {@code dst} and returns {@code dst}.
237 *
238 * @param dst the destination buffer, either an explicitly-typed array, a {@link ByteBuffer} or
239 * {@code null} iff the tensor has an underlying delegate buffer handle.
240 * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code dst} is not compatible with the tensor (for example,
241 * mismatched data types or shapes).
242 */
243 Object copyTo(Object dst) {
244 if (dst == null) {
245 if (hasDelegateBufferHandle(nativeHandle)) {
246 return dst;
247 }
248 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
249 "Null outputs are allowed only if the Tensor is bound to a buffer handle.");
250 }
251 throwIfTypeIsIncompatible(dst);
252 throwIfDstShapeIsIncompatible(dst);
253 if (isBuffer(dst)) {
254 copyTo((Buffer) dst);
255 } else {
256 readMultiDimensionalArray(nativeHandle, dst);
257 }
258 return dst;
259 }
260
JNI Functions![]() https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/jni/spec/functions.html
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/jni/spec/functions.html
https://jefflin1982.medium.com/android-jni%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%8F%96%E5%BE%97java-object%E7%9A%84%E5%80%BC-96b10631f0a![]() https://jefflin1982.medium.com/android-jni%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%8F%96%E5%BE%97java-object%E7%9A%84%E5%80%BC-96b10631f0a
https://jefflin1982.medium.com/android-jni%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E5%8F%96%E5%BE%97java-object%E7%9A%84%E5%80%BC-96b10631f0a
TFLite Java Interface implement
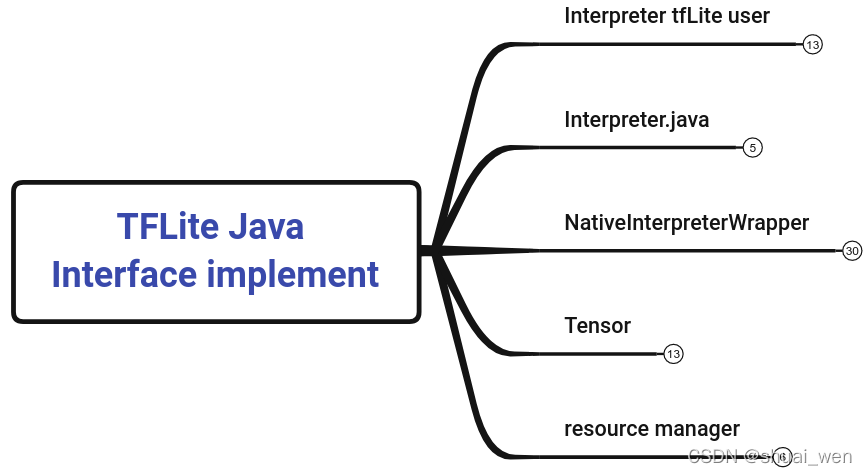


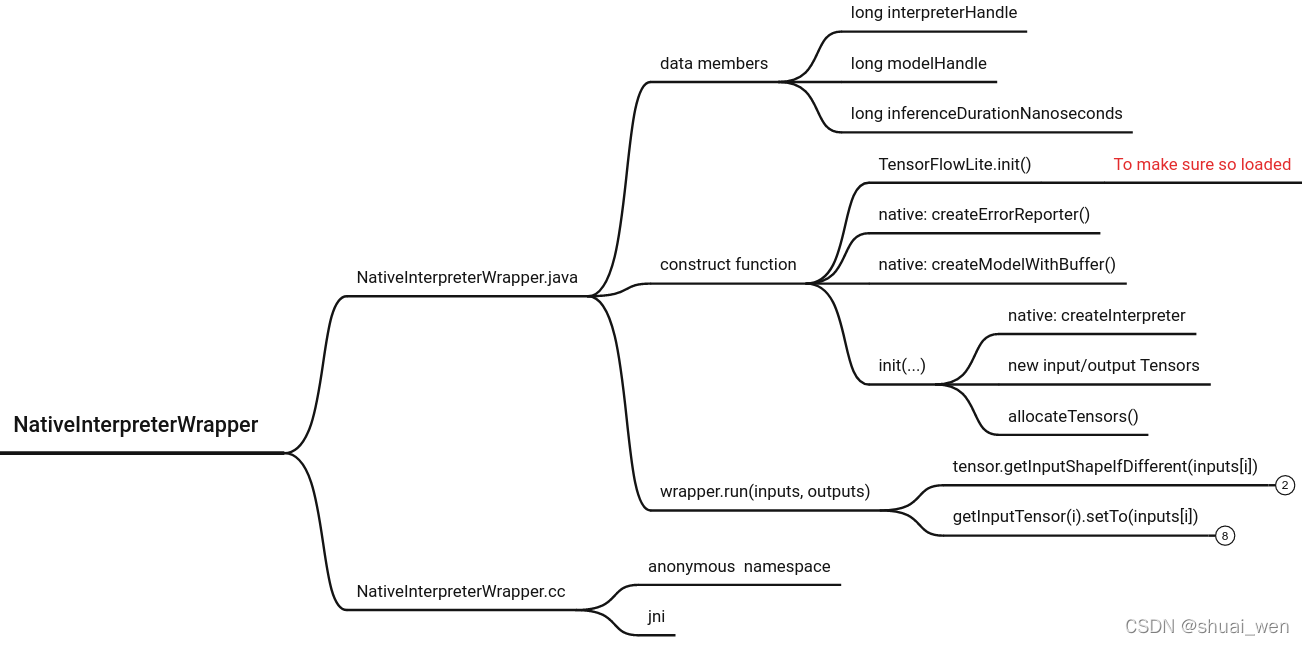
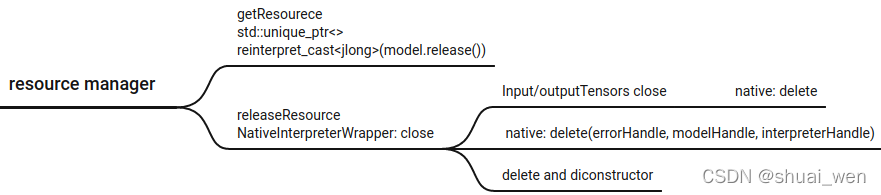
JNI 函数对应关系和命名方法
The naming convention for the C function is Java_{package_and_classname}_{function_name}(JNI_arguments). The dot in package name is replaced by underscore.
含packageName
package com.xiaomi.mace;
public class JniMaceUtils {
public static native float[] maceMobilenetClassify(Object[] input);
}
JNIEXPORT jfloatArray JNICALL
Java_com_xiaomi_mace_JniMaceUtils_maceMobilenetClassify(
JNIEnv *env, jclass thisObj, jobjectArray input_array) {
}
Java_packageName_className_functionName 这个命名格式
不含packageName
public class HelloJNI {// A native method that receives nothing and returns voidprivate native void sayHello();
}
对应的Native function name
Java_HelloJNI_sayHello: Java_className_functionName这个命名格式
JNI 怎样传参一个object and return an object
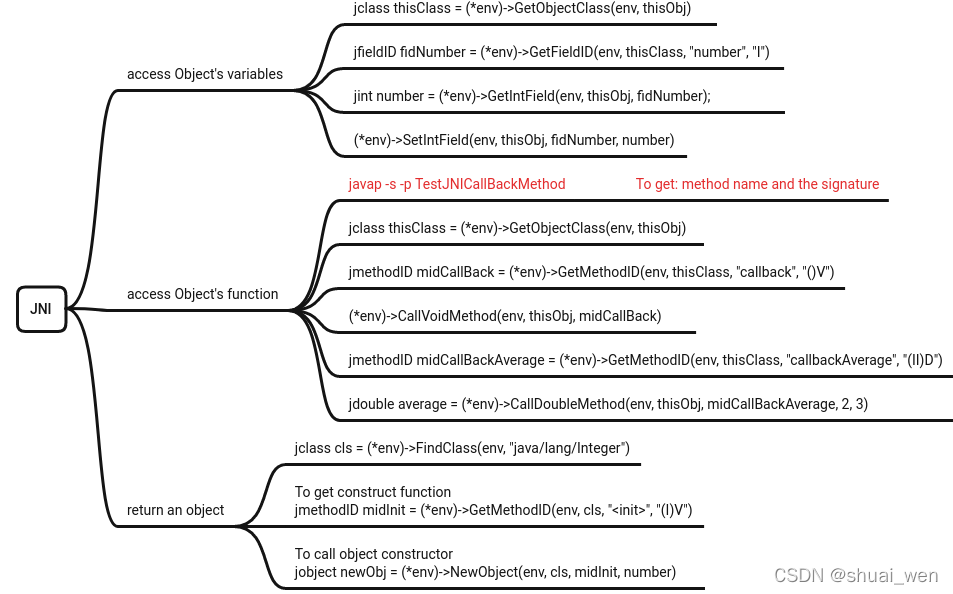
类似java 中的反射方法,通过访问class 对象得到methodID 对创建对象而言就是构造函数的 methodID, 调用构造函数,得到对象
Java Native Interface (JNI) - Java Programming Tutorial
这篇关于TFLite JNI 接口实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!


