本文主要是介绍iOS ------自动布局之Masonry的使用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
============基本用法
#import "ViewController.h"
// 解决 mas_
//define this constant if you want to use Masonry without the 'mas_' prefix
#define MAS_SHORTHAND
// 解决对数据的自动装箱
//define this constant if you want to enable auto-boxing for default syntax
#define MAS_SHORTHAND_GLOBALS
#warning 宏定义一定要放到导入头文件之前 ,不然会影响编译
// 导入头文件
#import "Masonry.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[superviewDidLoad];
#warning Mansory 会自动的帮我们把autoresizing给关闭
UIView *redView = [[UIViewalloc]init];
redView.backgroundColor = [UIColorredColor];
[self.viewaddSubview:redView];
/**
第一种写法
[redView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
// make 在这里就代表被约束的view
// 顶部
make.top.equalTo(self.view.mas_top).offset(20);
// 设置左侧
make.left.equalTo(self.view.mas_left).offset(20);
// 设置右侧
make.right.equalTo(self.view.mas_right).offset(-20);
// 设置高度 ,这里使用的时候:装箱
make.height.mas_equalTo(40);
}];
*/
/**
第二种写法
如果被约束view的属性和参照view的属性相同的话可以省略掉
[redView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(20);
make.left.equalTo(self.view).offset(20);
make.right.equalTo(self.view).offset(-20);
make.height.mas_equalTo(40);
}];
*/
// 如果想要省略掉 mas_ 导入 #define MAS_SHORTHAND
// [redView makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
// make.top.equalTo(self.view).offset(20);
// make.left.equalTo(self.view).offset(20);
// make.right.equalTo(self.view).offset(-20);
// make.height.equalTo(40);
// }];
/**
如果,被约束view两个属性的值是相同的,可以连写
[redView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.left.equalTo(self.view).offset(20);
make.right.equalTo(self.view).offset(-20);
make.height.mas_equalTo(40);//自己的高度
}];
*/
/**相对于父view设置UIEdgeInset---就是相对于父view的四条边的距离
[redView mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.edges.mas_equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(20, 20, 20, 20));//相当于
make.edges.equalTo(self.view).with.insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(20, 20, 20, 20));这里的with可以省略掉;
}];
*/
// 默认的参照view 就是自己的父view
[redView makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.left.offset(20);//相对于父view的上边,左边都偏移20;
make.right.offset(-20);
make.height.equalTo(40);
}];
// 蓝色的view
UIView *blueView = [[UIViewalloc]init];
blueView.backgroundColor = [UIColorblueColor];
[self.viewaddSubview:blueView];
[blueView makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(redView.bottom).offset(20);//blueview的上边等于redview的上边偏移20;
make.right.equalTo(redView).offset(0);//blueview的右边等于redview的右边偏移0;
make.height.equalTo(redView);//blueview和redview的高度一样;
make.width.equalTo(redView).multipliedBy(0.5);//blueView的宽度是redview宽度的一半;
}];
/**
更新约束 ,在原有的基础上 ,对要更新的约束进行修改
如果使用 makeConstraints就会造成约束冲突
[redView updateConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.height.equalTo(80);
}];
*/
/**
重新设置约束
把原有的约束都清空掉,然后设置新的
[redView remakeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.height.equalTo(50);
}];
*/
}
UIEdgeInsets padding = UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 10, 10, 10);[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {make.top.equalTo(superview.mas_top).with.offset(padding.top); //view1的top相对于父 view的top偏移多少,这里with也可以省略掉; make.left.equalTo(superview.mas_left).with.offset(padding.left); make.bottom.equalTo(superview.mas_bottom).with.offset(-padding.bottom);make.right.equalTo(superview.mas_right).with.offset(-padding.right);
}];
=======================高级用法
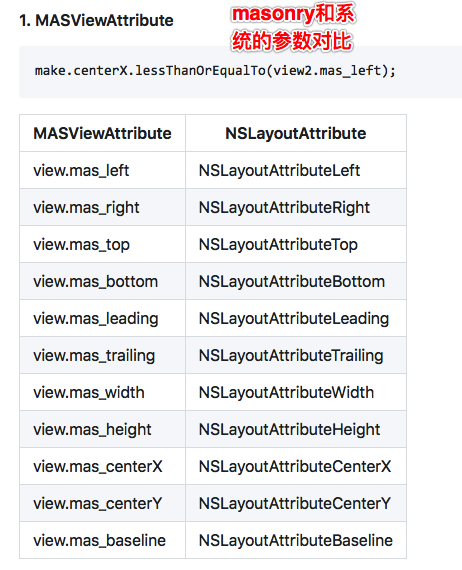
2. UIView/NSView
if you want view.left to be greater than or equal to label.left :
//these two constraints are exactly the same
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label);
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left);3. NSNumber----设置区间
Auto Layout allows width and height to be set to constant values. if you want to set view to have a minimum and maximum width you could pass a number to the equality blocks:
//width >= 200 && width <= 400
make.width.greaterThanOrEqualTo(@200);
make.width.lessThanOrEqualTo(@400)However Auto Layout does not allow alignment attributes such as left, right, centerY etc to be set to constant values. So if you pass a NSNumber for these attributes Masonry will turn these into constraints relative to the view’s superview ie:
//creates view.left = view.superview.left + 10
make.left.lessThanOrEqualTo(@10)Instead of using NSNumber, you can use primitives and structs to build your constraints, like so:
make.top.mas_equalTo(42);
make.height.mas_equalTo(20);
make.size.mas_equalTo(CGSizeMake(50, 100));
make.edges.mas_equalTo(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 0, 10, 0));
make.left.mas_equalTo(view).mas_offset(UIEdgeInsetsMake(10, 0, 10, 0));By default, macros which support autoboxing are prefixed with mas_. Unprefixed versions are available by defining MAS_SHORTHAND_GLOBALS before importing Masonry.
4. NSArray
An array of a mixture of any of the previous types
make.height.equalTo(@[view1.mas_height, view2.mas_height]);
make.height.equalTo(@[view1, view2]);
make.left.equalTo(@[view1, @100, view3.right]);
Learn to prioritize----设置优先级
.priorityallows you to specify an exact priority
.priorityHighequivalent to UILayoutPriorityDefaultHigh
.priorityMediumis half way between high and low
.priorityLowequivalent to UILayoutPriorityDefaultLow
Priorities are can be tacked on to the end of a constraint chain like so:
make.left.greaterThanOrEqualTo(label.mas_left).with.priorityLow();make.top.equalTo(label.mas_top).with.priority(600);Composition, composition, composition
Masonry also gives you a few convenience methods which create multiple constraints at the same time. These are called MASCompositeConstraints
edges---------设置内边距来约束,一般只针对父 view;
// make top, left, bottom, right equal view2
make.edges.equalTo(view2);// make top = superview.top + 5, left = superview.left + 10,
// bottom = superview.bottom - 15, right = superview.right - 20
make.edges.equalTo(superview).insets(UIEdgeInsetsMake(5, 10, 15, 20))size-----根据
// make width and height greater than or equal to titleLabel
make.size.greaterThanOrEqualTo(titleLabel)// make width = superview.width + 100, height = superview.height - 50
make.size.equalTo(superview).sizeOffset(CGSizeMake(100, -50));//对相应的宽和高作加减;center-------根据中心来设置
// make centerX and centerY = button1
make.center.equalTo(button1)// make centerX = superview.centerX - 5, centerY = superview.centerY + 10
make.center.equalTo(superview).centerOffset(CGPointMake(-5, 10));//对中心点作偏移You can chain view attributes for increased readability:
// All edges but the top should equal those of the superview
make.left.right.and.bottom.equalTo(superview);//如果几个值都一样可以连写。
make.top.equalTo(otherView);
******报错:
'couldn't find a common superview for 出现这个错误的原因是,你所设置约束的这个控件和所依赖的控件没有共同的父视图。因为没有共同的视图作为参照,frame 就不能转换到一个相同的坐标系。这个问题经常会出现在,我们创建了要设置约束的视图,而没有将它添加到父控件中,又或者,要设置约束的这个视图和所依赖的视图没有共同的父视图,也就是你遇到的这种情况。
这篇关于iOS ------自动布局之Masonry的使用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!