本文主要是介绍RabbitMQ(二)七种工作模式,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 概述:工作模式(七种)
- 1. "Hello World!"
- 2. Work Queues(工作队列模式)
- 3. Publish/Subscribe(发布订阅模式)
- 4. Routing
- 5. Topics
- 6. RPC
- 7. Publisher Confirms
- 详细
- 1. "Hello World!"
- 2. Work Queues(工作队列模式)
- 3. Publish/Subscribe(发布订阅模式)
- 4. Routing
- 5. Topics
- 6. RPC
- 7. Publisher Confirms
- 小结
概述:工作模式(七种)
官网链接
https://www.rabbitmq.com/tutorials
1. “Hello World!”
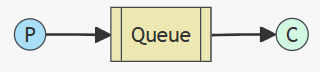
2. Work Queues(工作队列模式)
多个消费者消费同一队列

3. Publish/Subscribe(发布订阅模式)
通过exchange广播到多个queue中

4. Routing
通过route key发布到指定queue

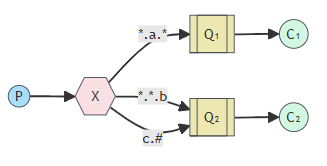
5. Topics
通过pattern匹配一个或者多个queue
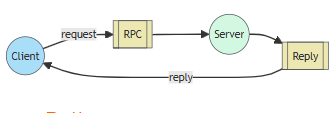
6. RPC
同步调用
7. Publisher Confirms
可靠性投递
详细
// rabbitMQ版本:3.13-management
<dependency><groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId><artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId><version>5.20.0</version>
</dependency>
1. “Hello World!”
2. Work Queues(工作队列模式)

多个消费者监听同一个队列,则各消费者之间对同一个消息是竞争的关系。
Work Queues工作模式适用于任务较重或任务较多的情况,多消费者分摊任务
可以提高消息处理的效率。
//生产者import com.atguigu.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection; public class Producer { public static final String QUEUE_NAME = "work_queue"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null); for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { String body = i+"hello rabbitmq~~~"; channel.basicPublish("",QUEUE_NAME,null,body.getBytes()); } channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
//消费者1public class Consumer1 { static final String QUEUE_NAME = "work_queue"; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("Consumer1 body:"+new String(body)); } }; channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME,true,consumer); } }
//消费者2
public class Consumer2 {static final String QUEUE_NAME = "work_queue";public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME,true,false,false,null);Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {System.out.println("Consumer2 body:"+new String(body));}};channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME,true,consumer);}}
3. Publish/Subscribe(发布订阅模式)
交换机概念
- 生产者不是把消息直接发送到队列,而是发送到交换机
- 交换机接收消息,而如何处理消息取决于交换机的类型
交换机有如下3种常见类型
- Fanout:广播,将消息发送给所有绑定到交换机的队列
- Direct:定向,把消息交给符合指定routing key的队列
- Topic:通配符,把消息交给符合routing pattern(路由模式)的队列
注意:Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因
此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那
么消息会丢失!

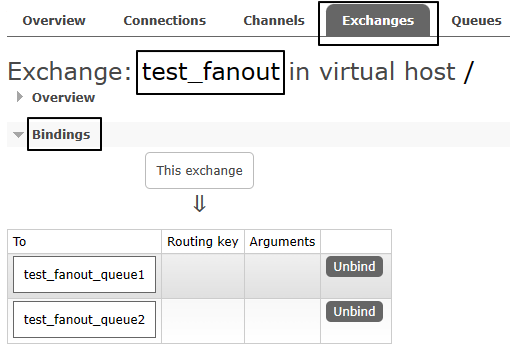
交换机需要与队列进行绑定,绑定之后;一个消息可以被多个消费者都收到。
发布订阅模式与工作队列模式的区别:
- 工作队列模式本质上是绑定默认交换机
- 发布订阅模式绑定指定交换机
- 监听同一个队列的消费端程序彼此之间是竞争关系
- 绑定同一个交换机的多个队列在发布订阅模式下,消息是广播的,每个队列都能接收到消息
//生产者import com.atguigu.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.BuiltinExchangeType;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory; public class Producer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1、获取连接Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); // 2、创建频道Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); // 参数1. exchange:交换机名称// 参数2. type:交换机类型// DIRECT("direct"):定向// FANOUT("fanout"):扇形(广播),发送消息到每一个与之绑定队列。 // TOPIC("topic"):通配符的方式 // HEADERS("headers"):参数匹配 // 参数3. durable:是否持久化 // 参数4. autoDelete:自动删除 // 参数5. internal:内部使用。一般false // 参数6. arguments:其它参数 String exchangeName = "test_fanout"; // 3、创建交换机channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, BuiltinExchangeType.FANOUT,true,false,false,null); // 4、创建队列String queue1Name = "test_fanout_queue1"; String queue2Name = "test_fanout_queue2"; channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name,true,false,false,null); channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null); // 5、绑定队列和交换机// 参数1. queue:队列名称 // 参数2. exchange:交换机名称 // 参数3. routingKey:路由键,绑定规则// 如果交换机的类型为fanout,routingKey设置为"" channel.queueBind(queue1Name,exchangeName,""); channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,""); String body = "日志信息:张三调用了findAll方法...日志级别:info..."; // 6、发送消息channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"",null,body.getBytes()); // 7、释放资源channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
//消费者1import com.atguigu.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); String queue1Name = "test_fanout_queue1"; channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name,true,false,false,null); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("body:"+new String(body)); System.out.println("队列 1 消费者 1 将日志信息打印到控制台....."); } }; channel.basicConsume(queue1Name,true,consumer); } }//消费者2
import com.atguigu.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException; public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); String queue2Name = "test_fanout_queue2"; channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("body:"+new String(body)); System.out.println("队列 2 消费者 2 将日志信息打印到控制台....."); } }; channel.basicConsume(queue2Name,true,consumer); } }
4. Routing

路由key相当于交叉路口指示牌根据不同指示牌走不同的路
通过『路由绑定』的方式,把交换机和队列关联起来
- 交换机和队列通过路由键进行绑定
- 生产者发送消息时不仅要指定交换机,还要指定路由键
- 交换机接收到消息会发送到路由键绑定的队列
- 在编码上与 Publish/Subscribe发布与订阅模式的区别:
- 交换机的类型为:
Direct - 队列绑定交换机的时候需要指定
routing key。
- 交换机的类型为:
//生产者public class Producer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); String exchangeName = "test_direct"; // 创建交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName,BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT,true,false,false,null); // 创建队列 String queue1Name = "test_direct_queue1"; String queue2Name = "test_direct_queue2"; // 声明(创建)队列 channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name,true,false,false,null); channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null); // 队列绑定交换机 // 队列1绑定error channel.queueBind(queue1Name,exchangeName,"error"); // 队列2绑定info error warning channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"info"); channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"error"); channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"warning"); String message = "日志信息:张三调用了delete方法.错误了,日志级别error";// 发送消息 channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"error",null,message.getBytes());System.out.println(message); // 释放资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }
//消费者1public class Producer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); String exchangeName = "test_direct"; // 创建交换机 channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName,BuiltinExchangeType.DIRECT,true,false,false,null); // 创建队列 String queue1Name = "test_direct_queue1"; String queue2Name = "test_direct_queue2"; // 声明(创建)队列 channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name,true,false,false,null); channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null); // 队列绑定交换机 // 队列1绑定error channel.queueBind(queue1Name,exchangeName,"error"); // 队列2绑定info error warning channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"info"); channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"error"); channel.queueBind(queue2Name,exchangeName,"warning"); String message = "日志信息:张三调用了delete方法.错误了,日志级别error";// 发送消息 channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"error",null,message.getBytes());System.out.println(message); // 释放资源 channel.close(); connection.close(); } }//消费者2
public class Consumer2 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); String queue2Name = "test_direct_queue2"; channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name,true,false,false,null); Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel){ @Override public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException { System.out.println("body:"+new String(body)); System.out.println("Consumer2 将日志信息存储到数据库....."); } }; channel.basicConsume(queue2Name,true,consumer); } }
5. Topics

- Topic类型与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队
列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定Routing key的时候使用
通配符 - Routingkey一般都是由一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以“.”分割,
例如:item.insert - 通配符规则:
- #:匹配零个或多个词
- *:匹配一个词
//生产者public class Producer {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();String exchangeName = "test_topic";channel.exchangeDeclare(exchangeName, BuiltinExchangeType.TOPIC, true, false, false, null);String queue1Name = "test_topic_queue1";String queue2Name = "test_topic_queue2";channel.queueDeclare(queue1Name, true, false, false, null);channel.queueDeclare(queue2Name, true, false, false, null);// 绑定队列和交换机// 参数1. queue:队列名称// 参数2. exchange:交换机名称// 参数3. routingKey:路由键,绑定规则// 如果交换机的类型为fanout ,routingKey设置为""// routing key 常用格式:系统的名称.日志的级别。// 需求: 所有error级别的日志存入数据库,所有order系统的日志存入数据库channel.queueBind(queue1Name, exchangeName, "#.error");channel.queueBind(queue1Name, exchangeName, "order.*");channel.queueBind(queue2Name, exchangeName, "*.*");// 分别发送消息到队列:order.info、goods.info、goods.errorString body = "[所在系统:order][日志级别:info][日志内容:订单生成,保存成功]";
// channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"order.info",null,body.getBytes());// body = "[所在系统:goods][日志级别:info][日志内容:商品发布成功]";
// channel.basicPublish(exchangeName,"goods.info",null,body.getBytes());body = "[所在系统:goods][日志级别:error][日志内容:商品发布失败]";channel.basicPublish(exchangeName, "goods.error", null, body.getBytes());channel.close();connection.close();}}
//消费者public class Consumer1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();String QUEUE_NAME = "test_topic_queue1";channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {System.out.println("body:" + new String(body));}};channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);}}//消费者2
public class Consumer2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();Channel channel = connection.createChannel();String QUEUE_NAME = "test_topic_queue2";channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, true, false, false, null);Consumer consumer = new DefaultConsumer(channel) {@Overridepublic void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {System.out.println("body:" + new String(body));}};channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, consumer);}}
6. RPC

远程过程调用,本质上是同步调用,和我们使用OpenFeign调用远程接口一
样
7. Publisher Confirms
发送端消息确认
小结
直接发送到队列:底层使用了默认交换机
- 经过交换机发送到队列
- Fanout:没有Routing key直接绑定队列
- Direct:通过Routing key绑定队列,消息发送到绑定的队列上
- 一个交换机绑定一个队列:定点发送
- 一个交换机绑定多个队列:广播发送
- Topic:针对Routing key使用通配符
这篇关于RabbitMQ(二)七种工作模式的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







