本文主要是介绍Struts2系统结构及运行原理(1),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
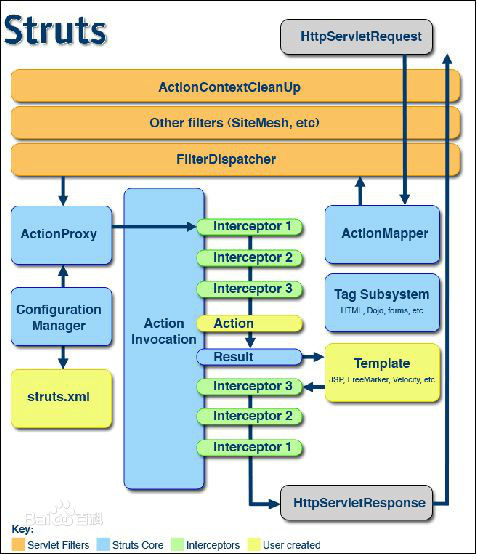
一、架构图
下边是一张Struts2的官方文档中的Struts2的构架图
二、各模块的简要分析
(1)橙色是Servlet Filters,过滤连,所有的请求都要经过Filter的处理;
(2)浅蓝色是Struts Core,是Struts的核心部分,Struts2中已经做好的功能,在实际的开发中不需要动他们;
(3)浅绿色是Interceptor,Struts2的拦截器。Struts2提供了很多默认的拦截器,时刻完成日常开发中的绝大部分工作,当然,也可以自定义拦截器,来实现具体的功能;
(4)浅黄色的是User Creates,即是开发人员完成的工作,包括struts.xml、Action、Template等由开发人员确定。
三、各模块详细说明
(1)FilterDispatcher
FilterDispatcher的四个主要功能:
Master filter for Struts that handles four distinct responsibilities:
1.Executing actions 执行action
2.Cleaning up the ActionContext 清理ActionContext
3.Serving static content 为静态的content提供服务
4.Kicking off XWork's interceptor chain for the request lifecycle 逆转request生命周期中的拦截器过滤链1.)Executing actions 执行action
This filter executes actions by consulting(咨询) the ActionMapper and determining(决定) if the requested URL should
invoke an action. If the mapper indicates it should, the rest of the filter chain is stopped and the action is invoked. This is important, as it means that filters like the SiteMesh filter must be placed before this filter or they will not be able to decorate the output of actions.是整个Struts2的调度中心,根据ActionMapper的结果来决定是否处理请求,如果ActionMapper指出该URL应该被Struts2处理,那么它将会执行Action处理,并停止过滤器链上还没有执行的过滤器。上边提到如果有SiteMesh这类的过滤器的话应该放在FilterDispatcher之前(放到FilterDispatcher大家应该知道,它是不会被执行的)。
2.)Cleaning up the link ActionContext
This filter will also automatically(自动) clean up the ActionContext(The ActionContext is the context in which an Action is executed) for you, ensuring that no memory leaks(泄漏)
take place(确保不会有内存泄露发生). However, this can sometimes cause problems integrating with(使一体化) other products like SiteMesh.下边是FilterDispatcher的一段代码:主要是执行filter
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();String timerKey = "FilterDispatcher_doFilter: ";try {// FIXME: this should be refactored better to not duplicate work with the action invocationValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();ActionContext ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());ActionContext.setContext(ctx);UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);ActionMapping mapping;try {mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());} catch (Exception ex) {log.error("error getting ActionMapping", ex);dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);return;}if (mapping == null) {// there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);if ("".equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();}if (staticResourceLoader.canHandle(resourcePath)) {staticResourceLoader.findStaticResource(resourcePath, request, response);} else {// this is a normal request, let it pass throughchain.doFilter(request, response);}// The framework did its job herereturn;}dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);} finally {dispatcher.cleanUpRequest(request);try {ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);} finally {UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);}devModeOverride.remove();}}可以看到有这一句:
mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());我们可以看到这里边的一个映射关系,是通过ActionMapper获取的,下边会说到ActionMapper,getMapping需要的两个参数,一个是request另一个就是我们通过struts.xml配置的信息,下边都会有说。
if (mapping == null) {}这个判断语句可以看出来如果mapping为空,就是根据判断之后的mapping是一个空值,意思就是这个请求是一个普通的请求,然后下边的操作就是为其提供静态的资源。
(2)ActionMapper
上边已经提到过,ActionMapper提供了HTTP请求与action执行之间的映射,简单的说,ActionMapper会判断这个请求是否应该被Struts2处理,如果需要Struts2处理的话,ActionMapper会返回一个对象来描述请求对应的ActionInvocation的信息。
官方文档解释:The ActionMapper interface provides a mapping between HTTP requests and action invocation requests and vice-versa(反之亦然).
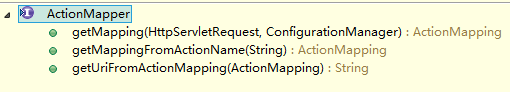
下边是接口的API
public interface ActionMapper {/*** Expose the ActionMapping for the current request* 暴露ActionMapping给当前的request* @param request The servlet request* @param configManager The current configuration manager* @return The appropriate action mapping*/ActionMapping getMapping(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigurationManager configManager);/*** Expose the ActionMapping for the specified action name** @param actionName The name of the action that may have other information embedded in it* @return The appropriate action mapping* @since 2.1.1*/ActionMapping getMappingFromActionName(String actionName);/*** Convert an ActionMapping into a URI string** @param mapping The action mapping* @return The URI string that represents this mapping*/String getUriFromActionMapping(ActionMapping mapping);
}
这里的getMapping(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigurationManager configManager) 就是我们在(1)中提到过的。
(3)ActionProxy
是一个特别的中间层,位于Action和xwork之间,使得在将来有机会引入更多的实现方式,比如通过WebService来实现等。
(4)ConfigurationManager
是xwork配置的管理中心,通俗地讲,可以把它看做是struts.xml这个配置文件在内存中的对应,在服务器启动的时候可以理解为是ConfigurationManager讲struts.xml文件加载到内存中去的。
(5)struts.xml
是struts2的应用配置文件,负责注入URL与Action之间映射的配置,以及执行后页面跳转的Result配置等。
(6)ActionInvocation
真正调用并执行Action,他拥有一个Action实例和这个Action所依赖的拦截器实例。ActionInvocation会执行这些拦截器,Action以及相应的Result,ActionInvocation对象描述了Action运行的整个过程。
(7)Interceptor
拦截器是一些无状态的类,拦截器可以自动拦截Action,他们给开发者提供了在Action运行之前或Resule运行之后来执行一些功能代码的机会,类似于我们熟悉的filter。
(8)Action
动作类是Struts2中的动作执行单元。用来处理用户的请求,并封装业务所需要的数据。
(9)Result
就是不同视图类型的抽象封装模型,不同的视图类型会对应不同的Result实现。
Struts2的运行流程
请参见下一篇文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/xlgen157387/article/details/45845691
这篇关于Struts2系统结构及运行原理(1)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!