本文主要是介绍Android测试系列之三 - 构建仪器单元测试,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Android测试系列之一 - 测试分类(节选)
Android测试系列之二 - 构建本地单元测试
Android测试系列之三 - 构建仪器单元测试
仪器单元测试,它是运行真机或者模拟器上进行测试,它有一个好处就是它们可以调用Android framework层的APIs以及
supporting APIs,比如:Android Testing Support Library。如果你需要去访问仪器的相关信息(比如目标app的Context)
或者它们需要Android framework层组件的实体(比如Parcelable或者SharedPreferences对象)。
使用仪器单元测试可以让其省去 编写和维护mock 部分的代码。当然,如果你想要的话,你仍然可以继续去使用模拟框架
去模拟任何依赖关系。
搭建测试环境
在Android Studio工程中,你必须将你的仪器测试的源文件放入到 module-name/src/androidTests/java/目录下。
在开始之前,你需要 download the Android Testing Support Library Setup ,它提供了一些APIs,能够让你的
app很快地构建和运行仪器测试代码。The Testing Support Library 包含了一个JUnit 4 test runner (AndroidJUnitRunner)
以及用于UI测试的API (Espresso 和 UI Automator )
为了能够在你的工程中使用 The Testing Support Library 提供的 the test runner 和 APIs,你需要配置一下Android 测试
的依赖。为了简化测试的开发,你还应该把 Hamcrest 库包含进来,通过使用the Hamcrest matcher APIs,它能够
让你编写出更加灵活的断言。
在你app的build.gradle文件中,你需要指定以下这些库作为一种依赖:
dependencies {androidTestCompile 'com.android.support:support-annotations:24.0.0'androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:runner:0.5'androidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test:rules:0.5'// Optional -- Hamcrest libraryandroidTestCompile 'org.hamcrest:hamcrest-library:1.3'// Optional -- UI testing with EspressoandroidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2'// Optional -- UI testing with UI AutomatorandroidTestCompile 'com.android.support.test.uiautomator:uiautomator-v18:2.1.2' }
注意:
如果你的编译配置文件中,因为support-annotations库包含进了一个compile 的依赖,又因为 espresso-core库
包含进了一个androidTestCompile 依赖,那么,你编译时就有可能会出错,因为依赖发生了冲突。那么,此时这个
问题的解决办法就是:将espresso-core 库的依赖升级如下:
androidTestCompile('com.android.support.test.espresso:espresso-core:2.2.2', {exclude group: 'com.android.support', module: 'support-annotations' })为了使用 JUnit 4测试类,在你的工程中,你需要在app module的build.gradle文件中进行如下设置,去指定
AndroidJUnitRunner
作为一个默认的test instrumentation runner :
android {defaultConfig {testInstrumentationRunner "android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnitRunner"} }
创建一个仪器单元测试类
你的仪器单元测试类应该被写为一个 JUnit 4 测试类,为了了解更多关于如何创建 JUnit 4 测试类以及如何使用JUnit 4
断言和注释,可以参考Create a Local Unit Test Class.
为了创建一个JUnit 4 测试类,你要在测试类定义的开头添加 @RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) 注释。你还需要
去指定Android Testing Support Library提供的 AndroidJUnitRunner类作为你默认的 test runner。在 Getting Started with Testing
可以看到更多关于这一步的详细信息。
下面这个示例展示了如何编写一个仪器单元测试去测试关于LogHistory类的Parcelable接口是否被正确地予以实现:
import android.os.Parcel; import android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnit4; import android.util.Pair; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import java.util.List; import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is; import static org.junit.Assert.assertThat;@RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) @SmallTest public class LogHistoryAndroidUnitTest {public static final String TEST_STRING = "This is a string";public static final long TEST_LONG = 12345678L;private LogHistory mLogHistory;@Beforepublic void createLogHistory() {mLogHistory = new LogHistory();}@Testpublic void logHistory_ParcelableWriteRead() {// Set up the Parcelable object to send and receive.mLogHistory.addEntry(TEST_STRING, TEST_LONG);// Write the data.Parcel parcel = Parcel.obtain();mLogHistory.writeToParcel(parcel, mLogHistory.describeContents());// After you're done with writing, you need to reset the parcel for reading.parcel.setDataPosition(0);// Read the data.LogHistory createdFromParcel = LogHistory.CREATOR.createFromParcel(parcel);List<Pair<String, Long>> createdFromParcelData = createdFromParcel.getData();// Verify that the received data is correct.assertThat(createdFromParcelData.size(), is(1));assertThat(createdFromParcelData.get(0).first, is(TEST_STRING));assertThat(createdFromParcelData.get(0).second, is(TEST_LONG));} }
创建一个测试套件
为了组织多个仪器单元测试的执行,你可以将多个测试类组织在一起,放入一个测试套件中,然后一起运行这些测试类。
测试套件可以嵌套。你的测试套件也可以和其他测试套件组合在一起,然后再一起去运行所有的测试类。
一个测试套件是被包含在一个测试包中,类似于 main application package。按照惯例,这个测试包通常以 .suite作为后缀
(比如:com.example.android.testing.mysample.suite)。
为了在单元测试中创建一个测试套件,需要导入 the JUnit RunWith and Suite 类。在你的测试套件中,还需要
添加 @RunWith(Suite.class) 和 @Suite.SuitClasses() 注释。在 @Suite.SuitClasses() 中列出了单独
的测试类或测试套件作为参数。
下边这个例子展示了如何一个名为UnitTestSuite的套件是如何被实现的,这个套件将CalculatorInstrumentationTest 和
CalculatorAddParameterizedTest 测试类组合在了一起,然后予以运行:
import com.example.android.testing.mysample.CalculatorAddParameterizedTest; import com.example.android.testing.mysample.CalculatorInstrumentationTest; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.junit.runners.Suite;// Runs all unit tests. @RunWith(Suite.class) @Suite.SuiteClasses({CalculatorInstrumentationTest.class,CalculatorAddParameterizedTest.class}) public class UnitTestSuite {}
运行仪器单元测试
为了运行仪器测试,需要遵循以下几个步骤:
1>确保你的工程已通过按钮 Sync Project进行了同步
2>以其中的一种方式去运行你的测试文件
I>运行单个测试,需要打开 Project 窗体,然后右键点击 测试文件,然后 单击 Run
II>测试一个类的所有方法,需要在测试文件中右键点击这个类或方法,然后单击 Run
III>为了运行一个目录下的所有测试,右键单击这个目录,然后选择 Run tests
参考:
《Building Instrumented Unit Tests》
附加的测试示例:
在需要获取应用的上下文信息时,大家可以通过 InstrumentationRegistry.getTargetContext() 获取的应用的上下文,示例如下:
package com.example.administrator.safecenter; import android.support.test.InstrumentationRegistry; import android.support.test.runner.AndroidJUnit4; import com.example.administrator.safecenter.db_dao.BlackNumberDao; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals; /** * * 版权:XXX公司 版权所有 * * 作者:will smith * * 版本:1.0 * * 创建日期:2016/9/10 * * 描述: * * 修订历史: * */ @RunWith(AndroidJUnit4.class) public class DatabaseTest {/*** * InstrumentationRegistry.getTargetContext()去获取上下文; * * BlackNumberDao:是自己用来测试的一个数据库操作的类; */ @Test public void test(){BlackNumberDao dao = new BlackNumberDao(InstrumentationRegistry.getTargetContext()); dao.add("12345678902","2"); assertEquals(String.valueOf(1), dao.findNumberMode("12345678902")); }}
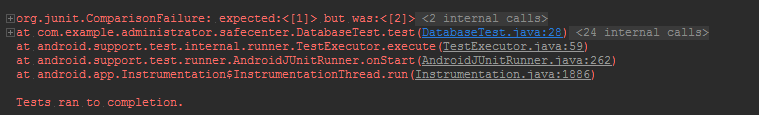
运行结果:
分析:
在代码中,我们用字符串“1”与我们插入的数据库中的模式位字符串“2”进行比较,
从测试报错信息:expected:<[1]> but was:<[2]> 可以看出,我们数据库添加的操作是没有问题的;
这篇关于Android测试系列之三 - 构建仪器单元测试的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!