本文主要是介绍Android 电池管理系统架构总结 Android power and battery management architecture summaries,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1 整体架构
- 2 设计构架
- 2.1 driver
- 2.1.1 Charger.ko
- 2.1.2 Battery.ko
- 2.2 power supply
- 2.2.1 基础架构
- 2.2.2 代码分析
- 2.3 healthd
- 2.3.1 基础架构
- 2.3.2 init
- 2.3.4 update
- 2.4 framework
- 3 总结
- 参考
1 整体架构
Android的电池架构包括从顶层用户使用App需要调用的电池相关的Android sdk api到最底层的硬件驱动,分别涉及到Android Framework、Android HAL和Linux Kernel Driver这几个部分。
本文基于基于Android 8.1系统,Rockchip平台进行分析,其中,对于硬件平台的电源驱动移植或者电源驱动编写,其主要关心的部分还是Linux Kernel Driver,这个部分,通常需要实现charger单元和电量计这两个部分的功能。整体的架构简单整理了一下如下图所示;
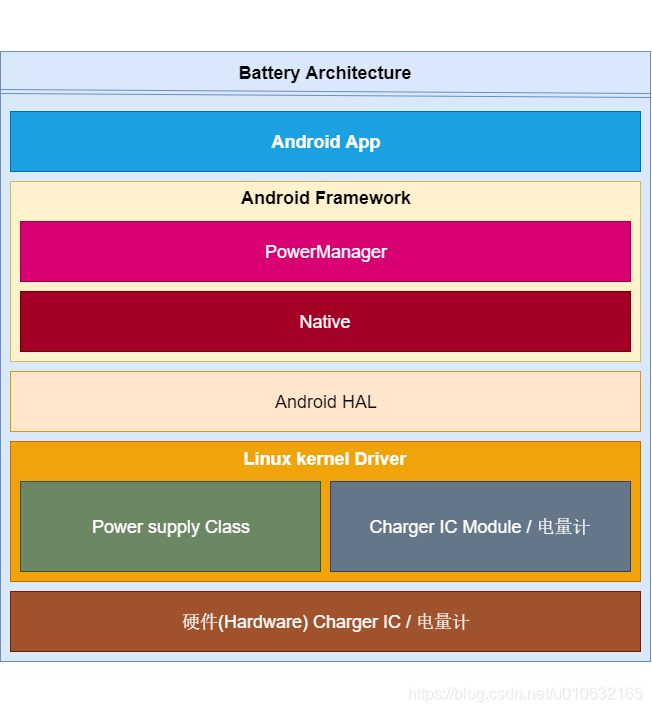
2 设计构架
这节大致介绍一下,电池的各种状态以及充电的状态信息如何从内核空间上报到用户空间。通俗的讲就是如何从内核驱动将各种状态数据上报到Android层。Android系统与传统Linux不同,对于内核空间和用户空间的数据交互,并不再使用udev的机制,而是使用了uevent的方式 ①,当电池状态发生变化,可以实时更新到用户空间,具体的数据架构如下图所示;

2.1 driver
内核需要注册充电IC驱动和电量计驱动,分别为Charger.ko和Battery.ko,当然,驱动的名字可以自定义命名,并不是不固定为Charger.ko和Battery.ko。这两个驱动主要完成设备的电源插入拔出检测,电池充放电,电池电量检测,然后通过注册power supply class将各个数据通过uevent的方式上传到用户空间。下面简单介绍一下驱动需要完成的工作,详细内容可以参考具体的驱动源码分析。
2.1.1 Charger.ko
Charger 驱动需要完成以下几个工作,并上报给用户空间:
-
Charger IC的初始化; -
设备电源的插入和拔出检测;
-
设备电源类型的检测:
ac(dcp),dc,usb(cdp,sdp) -
充放电电流的设置;
- 充电四个阶段:涓流,恒流,恒压,截止
- 放电:过放检测,NTC补偿等等;
-
当前充电状态的查询,包括未充电,充电,充满等等,这个需要预留接口,电量计驱动会使用到;
-
注册
ac,usb这两个power supply类用于数据上报;在这里,Charger在实际工作中还需要完成的任务还有很多,这里暂时不一一列举了,详细参考Charger 驱动源码解析 。
2.1.2 Battery.ko
电量计驱动需要完成很大一部分的工作,电量计实现比较复杂,这里简单列举一下:
- 充电曲线平滑算法;
- 放电曲线平滑算法;
- 电池基本信息上报,包括电池容量,充放电状态,电池百分比等等;
2.2 power supply
power supply framework在kernel/drivers/power/下。内核抽象出来power supply子系统为驱动提供了统一的框架。功能包括:
- 抽象PSY设备的共性,向用户空间提供统一的API;
- 为底层PSY驱动的编写,提供简单、统一的方式。同事封装并实现公共逻辑
2.2.1 基础架构
power supply class位于drivers/power/目录中,主要由3部分组成(可参考下图的软件架构):
power supply core,用于抽象核心数据结构、实现公共逻辑。位于drivers/power/power_supply_core.c中。power supply sysfs,实现sysfs以及uevent功能。位于drivers/power/power_supply_sysfs.c中。power supply leds,基于linux led class,提供PSY设备状态指示的通用实现。位于drivers/power/power_suppply_leds.c中。
根据以上的结构并在内核成功注册之后,会在sysfs系统中注册以下节点ac,battery,usb,如下图所示:

进入battery路径下可以发现很多文件,如下图所示:

这里是系统为了方便调试,可以读取这些文件的内容,这些大多数内容可以在Linux内核源码/kernel/include/power_supply.h中查阅到,下面做个简单介绍:
- capacity:当前电池容量
- charge_full:充满电的电池容量
- temp:电池温度
- uevent:上报
uevent需要用到的数据 - charge_counter:充电次数
- current_now:当前充电电流
- health status:电池健康状态,包括
cold,hot,Good等 - technology:电池类型,包括锂电池,镍铬电池等等
- voltage_now:当前电池电压
2.2.2 代码分析
这里拿ac作为例子来解释一下如何进行power_supply的注册,总共分为四个部分:
- 根据硬件特定的情况,确定psy设备具备哪些特性,哪些数据需要上报,并把他们和
enum power_supply_property对应; - 根据实际的情况,去实现这些
properties的get/set的接口,具体参考bq24296_charge_usb_get_property函数的实现; - 定义一个
struct power_supply_desc变量,并初始化必要成员后,调用devm_power_supply_register将其注册到kernel中; - 根据实际情况,启动设备属性变化的监控函数,可以使用中断,轮询等,并在发生改变时,调用power_supply_changed,通知power suopply core,具体可以参考
bq24296_charge_set_chrg_param。
下面是相应的代码实现;
static enum power_supply_property bq24296_usb_props[] = {POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_ONLINE,POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_STATUS,POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_VOLTAGE_MAX,POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_CURRENT_MAX,
};static int bq24296_charge_usb_get_property(struct power_supply *psy,enum power_supply_property psp,union power_supply_propval *val){struct bq24296_device_info *charge = power_supply_get_drvdata(psy);int ret = 0;switch (psp) {case POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_ONLINE:val->intval = charge->usb_in;break;case POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_STATUS: val->intval = charge->prop_status; break;case POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_VOLTAGE_MAX:val->intval = charge->max_chrg_voltage;break;case POWER_SUPPLY_PROP_CURRENT_MAX:val->intval = charge->max_chrg_current;break;default:ret = -EINVAL;break;}return ret;
}static const struct power_supply_desc bq24296_usb_desc = {.name = "usb",.type = POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB,.properties = bq24296_usb_props,.num_properties = ARRAY_SIZE(bq24296_usb_props),.get_property = bq24296_charge_usb_get_property,
};static int bq24296_charge_init_power_supply(struct bq24296_device_info *charge){struct power_supply_config psy_cfg = { .drv_data = charge, };charge->usb_psy = devm_power_supply_register(charge->dev,&bq24296_usb_desc,&psy_cfg);if (IS_ERR(charge->usb_psy)) {dev_err(charge->dev, "register usb power supply fail\n");return PTR_ERR(charge->usb_psy);}
}static void bq24296_charge_set_chrg_param(struct bq24296_device_info *charge, enum charger_t charger, int det_pin)
{switch (charger) {case USB_TYPE_NONE_CHARGER:charge->usb_in = 0;charge->ac_in = 0;if (charge->dc_in == 0) {charge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_DISCHARGING;// 2}power_supply_changed(charge->usb_psy);power_supply_changed(charge->ac_psy);break;case USB_TYPE_USB_CHARGER:case USB_TYPE_CDP_CHARGER:charge->usb_in = 1;charge->ac_in = 0;if (det_pin)bq24296_set_prop_status(charge);elsecharge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_CHARGING;power_supply_changed(charge->usb_psy);power_supply_changed(charge->ac_psy);break;case USB_TYPE_AC_CHARGER:charge->ac_in = 1;charge->usb_in = 0;if (det_pin)bq24296_set_prop_status(charge);elsecharge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_CHARGING;power_supply_changed(charge->usb_psy);power_supply_changed(charge->ac_psy);break;case DC_TYPE_DC_CHARGER:charge->dc_in = 1;if (det_pin)bq24296_set_prop_status(charge);elsecharge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_CHARGING;power_supply_changed(charge->usb_psy);power_supply_changed(charge->ac_psy);break;case DC_TYPE_NONE_CHARGER:charge->dc_in = 0;charge->ac_in = 0;charge->usb_in = 0;charge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_DISCHARGING;power_supply_changed(charge->usb_psy);power_supply_changed(charge->ac_psy);break;default:charge->prop_status = POWER_SUPPLY_STATUS_DISCHARGING;break;}
}2.3 healthd
healthd是android4.4之后提出来的一种中介模型,安卓源码路径下system/core/healthd,有兴趣可以分析一下源码,healthd已经属于Android层面的进程了,参考了资料上和代码中隐约看到了通过binder机制去调用healthd监听底层的上报的信息,篇幅有限,需要单独参考源码进行分析。
2.3.1 基础架构
首先看到安卓源码路径下的health,文件列表如下所示;
/home/AndroidSource/system/core/healthd# tree
.
├── Android.mk
├── animation.h
├── AnimationParser.cpp
├── AnimationParser.h
├── BatteryMonitor.cpp
├── BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.cpp
├── BatteryPropertiesRegistrar.h
├── charger.cpp
├── healthd_common.cpp
├── healthd.cpp
├── healthd_draw.cpp
├── healthd_draw.h
├── healthd_mode_android.cpp
├── healthd_mode_charger.cpp
可以看到文件比较多,主要是通过BatteryMonitor.cpp中的bool BatteryMonitor::update(void)函数上报信息,其中,内核首先会更新数据到/sys/class/power_supply/battery节点下各个属性,这个在上一个小节有做解释,先来看一下整体的架构,后面再来深入到代码中去分析;具体图片(该图片来自互联网,因为被转载较多,已经不知道出处),具体的流程整理的很清楚,如下所示;
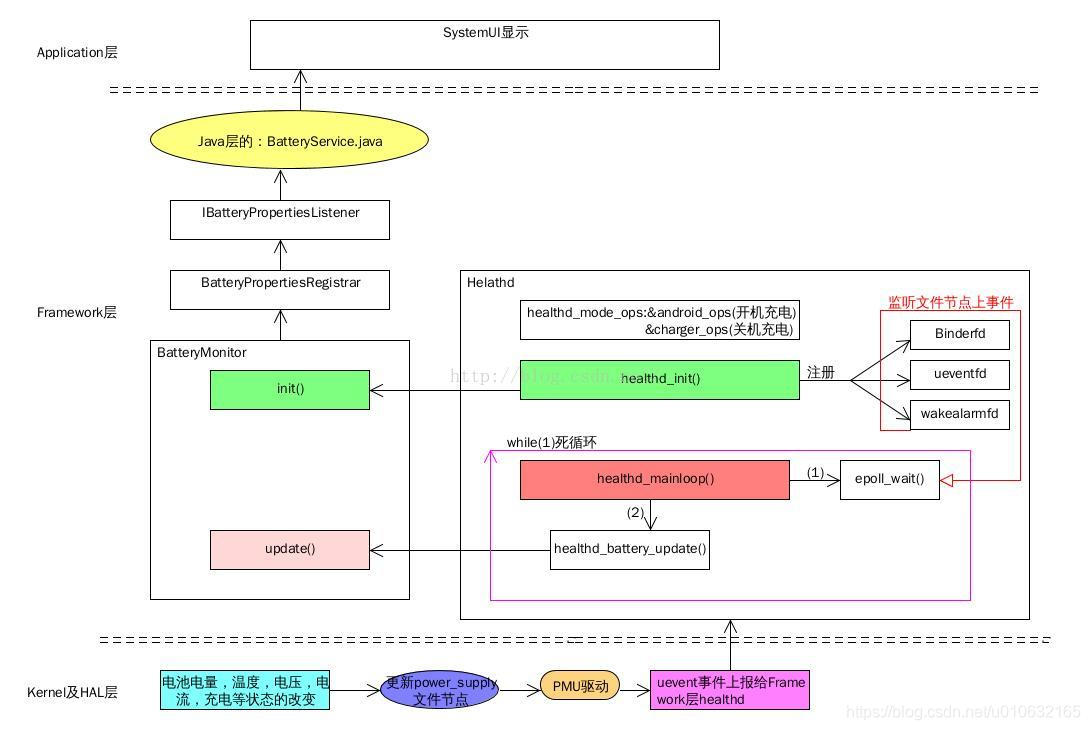
这幅图片再一次把整体的数据走向具体化,可以看到主要负责工作的是BatteryMonitor,主要分析一下该文件中的init和update就可以搞清楚大部分的问题。
2.3.2 init
下面是init()函数的具体实现;
void BatteryMonitor::init(struct healthd_config *hc) {String8 path;char pval[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];mHealthdConfig = hc;std::unique_ptr<DIR, decltype(&closedir)> dir(opendir(POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH), closedir);if (dir == NULL) {KLOG_ERROR(LOG_TAG, "Could not open %s\n", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH);} else {struct dirent* entry;while ((entry = readdir(dir.get()))) {const char* name = entry->d_name;if (!strcmp(name, ".") || !strcmp(name, ".."))continue;// Look for "type" file in each subdirectorypath.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0)mChargerNames.add(String8(name));break;case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_BATTERY:mBatteryDevicePresent = true;if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/status", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/health", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/present", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/capacity", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/voltage_now",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath = path;} else {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/batt_vol",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath = path;}}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_full",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_now",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/cycle_count",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_avg",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentAvgPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/charge_counter",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath = path;}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/temp", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) {mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath = path;} else {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/batt_temp",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath = path;}}if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty()) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/technology",POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH, name);if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath = path;}break;case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_UNKNOWN:break;}}}// Typically the case for devices which do not have a battery and// and are always plugged into AC mains.if (!mBatteryDevicePresent) {KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "No battery devices found\n");hc->periodic_chores_interval_fast = -1;hc->periodic_chores_interval_slow = -1;mBatteryFixedCapacity = ALWAYS_PLUGGED_CAPACITY;mBatteryFixedTemperature = FAKE_BATTERY_TEMPERATURE;mAlwaysPluggedDevice = true;} else {if (mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryStatusPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryHealthPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryPresentPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCapacityPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryVoltagePath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTemperaturePath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryTechnologyPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCurrentNowPath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryFullChargePath not found\n");if (mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty())KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "BatteryCycleCountPath not found\n");}if (property_get("ro.boot.fake_battery", pval, NULL) > 0&& strtol(pval, NULL, 10) != 0) {mBatteryFixedCapacity = FAKE_BATTERY_CAPACITY;mBatteryFixedTemperature = FAKE_BATTERY_TEMPERATURE;}
}在这个函数中,我们可以清楚地看到,对于battery下每一个属性,在init函数中都会提前获取到相应的路径,然后再去读取属性值去做对应的更新,这里通过update函数进行上报。
2.3.4 update
update函数具体实现如下;
bool BatteryMonitor::update(void) {bool logthis;initBatteryProperties(&props);if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath.isEmpty())props.batteryPresent = getBooleanField(mHealthdConfig->batteryPresentPath);elseprops.batteryPresent = mBatteryDevicePresent;props.batteryLevel = mBatteryFixedCapacity ?mBatteryFixedCapacity :getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCapacityPath);props.batteryVoltage = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryVoltagePath) / 1000;if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty())props.batteryCurrent = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath) / 1000;if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty())props.batteryFullCharge = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath);if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty())props.batteryCycleCount = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath);if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath.isEmpty())props.batteryChargeCounter = getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryChargeCounterPath);props.batteryTemperature = mBatteryFixedTemperature ?mBatteryFixedTemperature :getIntField(mHealthdConfig->batteryTemperaturePath);// For devices which do not have battery and are always plugged// into power souce.if (mAlwaysPluggedDevice) {props.chargerAcOnline = true;props.batteryPresent = true;props.batteryStatus = BATTERY_STATUS_CHARGING;props.batteryHealth = BATTERY_HEALTH_GOOD;}std::string buf;if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryStatusPath, &buf) > 0)props.batteryStatus = getBatteryStatus(buf.c_str());if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryHealthPath, &buf) > 0)props.batteryHealth = getBatteryHealth(buf.c_str());if (readFromFile(mHealthdConfig->batteryTechnologyPath, &buf) > 0)props.batteryTechnology = String8(buf.c_str());unsigned int i;double MaxPower = 0;for (i = 0; i < mChargerNames.size(); i++) {String8 path;path.appendFormat("%s/%s/online", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,mChargerNames[i].string());if (getIntField(path)) {path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/type", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,mChargerNames[i].string());switch(readPowerSupplyType(path)) {case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_AC:props.chargerAcOnline = true;break;case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_USB:props.chargerUsbOnline = true;break;case ANDROID_POWER_SUPPLY_TYPE_WIRELESS:props.chargerWirelessOnline = true;break;default:KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "%s: Unknown power supply type\n",mChargerNames[i].string());}path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/current_max", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,mChargerNames[i].string());int ChargingCurrent =(access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0) ? getIntField(path) : 0;path.clear();path.appendFormat("%s/%s/voltage_max", POWER_SUPPLY_SYSFS_PATH,mChargerNames[i].string());int ChargingVoltage =(access(path.string(), R_OK) == 0) ? getIntField(path) :DEFAULT_VBUS_VOLTAGE;double power = ((double)ChargingCurrent / MILLION) *((double)ChargingVoltage / MILLION);if (MaxPower < power) {props.maxChargingCurrent = ChargingCurrent;props.maxChargingVoltage = ChargingVoltage;MaxPower = power;}}}logthis = !healthd_board_battery_update(&props);if (logthis) {char dmesgline[256];size_t len;if (props.batteryPresent) {snprintf(dmesgline, sizeof(dmesgline),"battery l=%d v=%d t=%s%d.%d h=%d st=%d",props.batteryLevel, props.batteryVoltage,props.batteryTemperature < 0 ? "-" : "",abs(props.batteryTemperature / 10),abs(props.batteryTemperature % 10), props.batteryHealth,props.batteryStatus);len = strlen(dmesgline);if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCurrentNowPath.isEmpty()) {len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len," c=%d", props.batteryCurrent);}if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryFullChargePath.isEmpty()) {len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len," fc=%d", props.batteryFullCharge);}if (!mHealthdConfig->batteryCycleCountPath.isEmpty()) {len += snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len," cc=%d", props.batteryCycleCount);}} else {len = snprintf(dmesgline, sizeof(dmesgline),"battery none");}snprintf(dmesgline + len, sizeof(dmesgline) - len, " chg=%s%s%s",props.chargerAcOnline ? "a" : "",props.chargerUsbOnline ? "u" : "",props.chargerWirelessOnline ? "w" : "");KLOG_WARNING(LOG_TAG, "%s\n", dmesgline);}healthd_mode_ops->battery_update(&props);return props.chargerAcOnline | props.chargerUsbOnline |props.chargerWirelessOnline;
}2.4 framework
对于Framework的分析,暂时还没有深入到代码去做研究,这里网上资料比较多,但是有必要再去debug一下代码,这样才能知己知彼,百战不殆,可以参考这篇文章5,下面顺便贴一下文章中的一张图片,感觉瞬间把思路都理清楚了。

3 总结
Android的电源管理涉及到的东西比较杂乱,单纯进行硬件驱动的开发只需要关心power supply类的注册和具体的驱动实现,本文大概分成两个部分进行展开说明,一,整体架构的实现包括软件的分层;二,设计上的架构,包括驱动的设计以及设备数据如何上报的用户空间,这里还有一个问题没有阐述清楚,就是healthd的数据提交的具体实现过程,后面有时间再更新。由于水平有限,难免存在纰漏,错误之处,希望斧正。
参考
[1]:Android Uevent 分析,从kernel到framework
[2]:linux设备驱动uevent详解,高通平台battery上报电量实例
[3]:Linux uevent机制
[4]:Android 电池(三):android电池系统
[5]:android-power-and-battery-management-a-look-underneath-the-hood
[6]:power_management
这篇关于Android 电池管理系统架构总结 Android power and battery management architecture summaries的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






