本文主要是介绍【鸿蒙开发】第二十四章 IPC与RPC进程间通讯服务,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1 IPC与RPC通信概述
IPC(Inter-Process Communication)与RPC(Remote Procedure Call)用于实现跨进程通信,不同的是前者使用Binder驱动,用于设备内的跨进程通信,后者使用软总线驱动,用于跨设备跨进程通信。需要跨进程通信的原因是因为每个进程都有自己独立的资源和内存空间,其他进程不能随意访问不同进程的内存和资源,IPC/RPC便是为了突破这一点。
- IPC(Inter-Process Communication):使用
Binder驱动,用于设备内的跨进程通信 - RPC(Remote Procedure Call):使用
软总线驱动,用于跨设备跨进程通信
说明:
Stage模型不能直接使用本文介绍的IPC和RPC,需要通过以下能力实现相关业务场景:
- IPC典型使用场景在后台服务,应用的后台服务通过IPC机制提供跨进程的服务调用能力。
- RPC典型使用场景在多端协同,多端协同通过RPC机制提供远端接口调用与数据传递能力。
2 实现原理
IPC和RPC通常采用客户端-服务器(Client-Server)模型,在使用时,请求服务的(Client)一端进程可获取提供服务(Server)一端所在进程的代理(Proxy),并通过此代理读写数据来实现进程间的数据通信,更具体的讲,首先请求服务的(Client)一端会建立一个服务提供端(Server)的代理对象,这个代理对象具备和服务提供端(Server)一样的功能,若想访问服务提供端(Server)中的某一个方法,以下步骤:
- 访问
代理对象中对应的方法即可,代理对象会将请求发送给服务提供端(Server); - 然后服务提供端(Server)处理接受到的请求,处理完之后通过驱动返回处理结果给代理对象;
- 最后代理对象将请求结果进一步返回给请求服务端(Client)。
通常,Server会先注册系统能力(System Ability)到系统能力管理者(System Ability Manager,缩写SAMgr)中,SAMgr负责管理这些SA并向Client提供相关的接口。Client要和某个具体的SA通信,必须先从SAMgr中获取该SA的代理,然后使用代理和SA通信。下文直接使用Proxy表示服务请求方,Stub表示服务提供方。
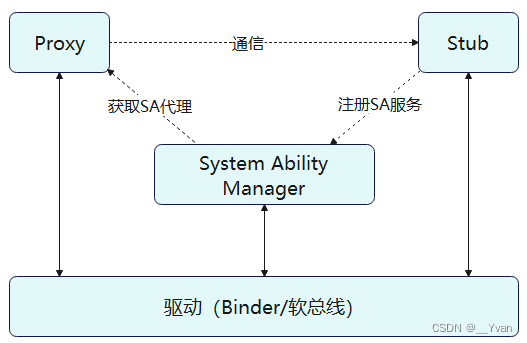
3 约束与限制
- 单个设备上跨进程通信时,传输的数据量最大约为
1MB,过大的数据量请使用匿名共享内存。 - 不支持在
RPC中订阅匿名Stub对象(没有向SAMgr注册Stub对象)的死亡通知。 - 不支持把跨设备的
Proxy对象传递回该Proxy对象所指向的Stub对象所在的设备,即指向远端设备Stub的Proxy对象不能在本设备内进行二次跨进程传递。
4 使用场景
IPC/RPC的主要工作是让运行在不同进程的Proxy和Stub互相通信,包括Proxy和Stub运行在不同设备的情况。
表1 Native侧IPC接口
| 接口名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sptr AsObject() | 返回通信对象。Stub端返回RemoteObject对象本身,Proxy端返回代理对象。 |
| virtual int OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) | 请求处理方法,派生类需要重写该方法用来处理Proxy的请求并返回结果。 |
| IRemoteProxy | Remote()->SendRequest(code, data, reply, option) |
5 开发步骤
5.1 Native侧开发步骤
- 添加依赖
#SDK依赖:
#ipc场景
external_deps = ["ipc:ipc_single",
]#rpc场景
external_deps = ["ipc:ipc_core",
]#此外, IPC/RPC依赖的refbase实现在公共基础库下,请增加对utils的依赖:
external_deps = ["c_utils:utils",
]
- 定义IPC接口ITestAbility
SA接口继承IPC基类接口IRemoteBroker,接口里定义描述符、业务函数和消息码,其中业务函数在Proxy端和Stub端都需要实现。
#include "iremote_broker.h"//定义消息码
const int TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY = 5;const std::string DESCRIPTOR = "test.ITestAbility";class ITestAbility : public IRemoteBroker {
public:// DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR是必需的,入参需使用std::u16string;DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(to_utf16(DESCRIPTOR));virtual int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) = 0; // 定义业务函数
};- 定义和实现服务端TestAbilityStub
该类是和IPC框架相关的实现,需要继承IRemoteStub<ITestAbility>。Stub端作为接收请求的一端,需重写OnRemoteRequest方法用于接收客户端调用。
#include "iability_test.h"
#include "iremote_stub.h"class TestAbilityStub : public IRemoteStub<ITestAbility> {
public:virtual int OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option) override;int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) override;};int TestAbilityStub::OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code,MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option)
{switch (code) {case TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY: {std::u16string dummy = data.ReadString16();int result = TestPingAbility(dummy);reply.WriteInt32(result);return 0;}default:return IPCObjectStub::OnRemoteRequest(code, data, reply, option);}
}- 定义服务端业务函数具体实现类
TestAbility
#include "iability_server_test.h"class TestAbility : public TestAbilityStub {
public:int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy);
}int TestAbility::TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) {return 0;
}- 定义和实现客户端 TestAbilityProxy
该类是Proxy端实现,继承IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility>,调用SendRequest接口向Stub端发送请求,对外暴露服务端提供的能力。
#include "iability_test.h"
#include "iremote_proxy.h"
#include "iremote_object.h"class TestAbilityProxy : public IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility> {
public:explicit TestAbilityProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl);int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) override;
private:static inline BrokerDelegator<TestAbilityProxy> delegator_; // 方便后续使用iface_cast宏
}TestAbilityProxy::TestAbilityProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl): IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility>(impl)
{
}int TestAbilityProxy::TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy){MessageOption option;MessageParcel dataParcel, replyParcel;dataParcel.WriteString16(dummy);int error = Remote()->SendRequest(TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY, dataParcel, replyParcel, option);int result = (error == ERR_NONE) ? replyParcel.ReadInt32() : -1;return result;
}- SA注册与启动
SA需要将自己的TestAbilityStub实例通过AddSystemAbility接口注册到SystemAbilityManager,设备内与分布式的注册参数不同。
// 注册到本设备内
auto samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
samgr->AddSystemAbility(saId, new TestAbility());// 在组网场景下,会被同步到其他设备上
auto samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
ISystemAbilityManager::SAExtraProp saExtra;
saExtra.isDistributed = true; // 设置为分布式SA
int result = samgr->AddSystemAbility(saId, new TestAbility(), saExtra);- SA获取与调用
通过SystemAbilityManager的GetSystemAbility方法可获取到对应SA的代理IRemoteObject,然后构造TestAbilityProxy即可。
// 获取本设备内注册的SA的proxy
sptr<ISystemAbilityManager> samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteObject = samgr->GetSystemAbility(saId);
sptr<ITestAbility> testAbility = iface_cast<ITestAbility>(remoteObject); // 使用iface_cast宏转换成具体类型// 获取其他设备注册的SA的proxy
sptr<ISystemAbilityManager> samgr = SystemAbilityManagerClient::GetInstance().GetSystemAbilityManager();// networkId是组网场景下对应设备的标识符,可以通过GetLocalNodeDeviceInfo获取
sptr<IRemoteObject> remoteObject = samgr->GetSystemAbility(saId, networkId);
sptr<TestAbilityProxy> proxy(new TestAbilityProxy(remoteObject)); // 直接构造具体Proxy
5.2 ArkTS侧开发步骤
- 添加依赖
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';// 仅FA模型需要导入@ohos.ability.featureAbility// import featureAbility from '@ohos.ability.featureAbility';
Stage模型需要获取context
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';
import AbilityConstant from '@ohos.app.ability.AbilityConstant';
import window from '@ohos.window';export default class MainAbility extends UIAbility {onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onCreate');let context = this.context;}onDestroy() {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onDestroy');}onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {// Main window is created, set main page for this abilityhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onWindowStageCreate');}onWindowStageDestroy() {// Main window is destroyed, release UI related resourceshilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onWindowStageDestroy');}onForeground() {// Ability has brought to foregroundhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onForeground');}onBackground() {// Ability has back to backgroundhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onBackground');}
}- 绑定Ability
首先,构造变量want,指定要绑定的Ability所在应用的包名、组件名,如果是跨设备的场景,还需要绑定目标设备NetworkId(组网场景下对应设备的标识符,可以使用deviceManager获取目标设备的NetworkId);然后,构造变量connect,指定绑定成功、绑定失败、断开连接时的回调函数;最后,FA模型使用featureAbility提供的接口绑定Ability,Stage模型通过context获取服务后用提供的接口绑定Ability。
// 仅FA模型需要导入@ohos.ability.featureAbility// import featureAbility from "@ohos.ability.featureAbility";import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';import deviceManager from '@ohos.distributedDeviceManager';import { BusinessError } from '@ohos.base';let dmInstance: deviceManager.DeviceManager | undefined;let proxy: rpc.IRemoteObject | undefined;let connectId: number;// 单个设备绑定Abilitylet want: Want = {// 包名和组件名写实际的值bundleName: "ohos.rpc.test.server",abilityName: "ohos.rpc.test.server.ServiceAbility",};let connect: common.ConnectOptions = {onConnect: (elementName, remoteProxy) => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: js onConnect called');proxy = remoteProxy;},onDisconnect: (elementName) => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: onDisconnect');},onFailed: () => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: onFailed');}};// FA模型使用此方法连接服务// connectId = featureAbility.connectAbility(want, connect);connectId = this.context.connectServiceExtensionAbility(want,connect);// 跨设备绑定 try{dmInstance = deviceManager.createDeviceManager("ohos.rpc.test");} catch(error) {let err: BusinessError = error as BusinessError;hilog.error(0x0000, 'testTag', 'createDeviceManager errCode:' + err.code + ', errMessage:' + err.message);}// 使用deviceManager获取目标设备NetworkIdif (dmInstance != undefined) {let deviceList = dmInstance.getAvailableDeviceListSync();let networkId = deviceList[0].networkId;let want: Want = {bundleName: "ohos.rpc.test.server",abilityName: "ohos.rpc.test.service.ServiceAbility",deviceId: networkId,flags: 256};// 建立连接后返回的Id需要保存下来,在断开连接时需要作为参数传入// FA模型使用此方法连接服务// connectId = featureAbility.connectAbility(want, connect);// 第一个参数是本应用的包名,第二个参数是接收deviceManager的回调函数connectId = this.context.connectServiceExtensionAbility(want,connect);}- 服务端处理客户端请求
服务端被绑定的Ability在onConnect方法里返回继承自rpc.RemoteObject的对象,该对象需要实现onRemoteMessageRequest方法,处理客户端的请求。
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';class Stub extends rpc.RemoteObject {constructor(descriptor: string) {super(descriptor);}onRemoteMessageRequest(code: number, data: rpc.MessageSequence, reply: rpc.MessageSequence, option: rpc.MessageOption): boolean | Promise<boolean> {// 根据code处理客户端的请求return true;}onConnect(want: Want) {const robj: rpc.RemoteObject = new Stub("rpcTestAbility");return robj;}} - 客户端处理服务端响应
客户端在onConnect回调里接收到代理对象,调用sendMessageRequest方法发起请求,在期约(用于表示一个异步操作的最终完成或失败及其结果值)或者回调函数里接收结果。
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';// 使用期约let option = new rpc.MessageOption();let data = rpc.MessageSequence.create();let reply = rpc.MessageSequence.create();// 往data里写入参数let proxy: rpc.IRemoteObject | undefined;if (proxy != undefined) {proxy.sendMessageRequest(1, data, reply, option).then((result: rpc.RequestResult) => {if (result.errCode != 0) {hilog.error(0x0000, 'testTag', 'sendMessageRequest failed, errCode: ' + result.errCode);return;}// 从result.reply里读取结果}).catch((e: Error) => {hilog.error(0x0000, 'testTag', 'sendMessageRequest got exception: ' + e);}).finally(() => {data.reclaim();reply.reclaim();})}// 使用回调函数function sendRequestCallback(err: Error, result: rpc.RequestResult) {try {if (result.errCode != 0) {hilog.error(0x0000, 'testTag', 'sendMessageRequest failed, errCode: ' + result.errCode);return;}// 从result.reply里读取结果} finally {result.data.reclaim();result.reply.reclaim();}}let options = new rpc.MessageOption();let datas = rpc.MessageSequence.create();let replys = rpc.MessageSequence.create();// 往data里写入参数if (proxy != undefined) {proxy.sendMessageRequest(1, datas, replys, options, sendRequestCallback);}- 断开连接
IPC通信结束后,FA模型使用featureAbility的接口断开连接,Stage模型在获取context后用提供的接口断开连接。
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';// 仅FA模型需要导入@ohos.ability.featureAbility// import featureAbility from "@ohos.ability.featureAbility";function disconnectCallback() {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'disconnect ability done');}// FA模型使用此方法断开连接// featureAbility.disconnectAbility(connectId, disconnectCallback);let proxy: rpc.IRemoteObject | undefined;let connectId: number;// 单个设备绑定Abilitylet want: Want = {// 包名和组件名写实际的值bundleName: "ohos.rpc.test.server",abilityName: "ohos.rpc.test.server.ServiceAbility",};let connect: common.ConnectOptions = {onConnect: (elementName, remote) => {proxy = remote;},onDisconnect: (elementName) => {},onFailed: () => {proxy;}};// FA模型使用此方法连接服务// connectId = featureAbility.connectAbility(want, connect);connectId = this.context.connectServiceExtensionAbility(want,connect);this.context.disconnectServiceExtensionAbility(connectId);6 远端状态订阅开发实例
IPC/RPC提供对远端Stub对象状态的订阅机制,在远端Stub对象消亡时,可触发消亡通知告诉本地Proxy对象。这种状态通知订阅需要调用特定接口完成,当不再需要订阅时也需要调用特定接口取消。使用这种订阅机制的用户,需要实现消亡通知接口DeathRecipient并实现onRemoteDied方法清理资源。该方法会在远端Stub对象所在进程消亡或所在设备离开组网时被回调。值得注意的是,调用这些接口有一定的顺序。首先,需要Proxy订阅Stub消亡通知,若在订阅期间Stub状态正常,则在不再需要时取消订阅;若在订阅期间Stub所在进程退出或者所在设备退出组网,则会自动触发Proxy自定义的后续操作。
6.1 使用场景
这种订阅机制适用于本地Proxy对象需要感知远端Stub对象所在进程消亡,或所在设备离开组网的场景。当Proxy感知到Stub端消亡后,可适当清理本地资源。此外,RPC目前不提供匿名Stub对象的消亡通知,即只有向SAMgr注册过的服务才能被订阅消亡通知,IPC则支持匿名对象的消亡通知。
6.1.1 Native侧接口
| 接口名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| bool AddDeathRecipient(const sptr &recipient); | 订阅远端Stub对象状态。 |
| bool RemoveDeathRecipient(const sptr &recipient); | 取消订阅远端Stub对象状态。 |
| void OnRemoteDied(const wptr &object); | 当远端Stub对象死亡时回调。 |
参考代码
#include "iremote_broker.h"
#include "iremote_stub.h"//定义消息码
enum {TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY = 5,TRANS_ID_REVERSED_MONITOR
};const std::string DESCRIPTOR = "test.ITestAbility";class ITestService : public IRemoteBroker {
public:// DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR是必需的,入参需使用std::u16string;DECLARE_INTERFACE_DESCRIPTOR(to_utf16(DESCRIPTOR));virtual int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) = 0; // 定义业务函数
};class TestServiceProxy : public IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility> {
public:explicit TestAbilityProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl);virtual int TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy) override;int TestAnonymousStub();
private:static inline BrokerDelegator<TestAbilityProxy> delegator_; // 方便后续使用iface_cast宏
};TestServiceProxy::TestServiceProxy(const sptr<IRemoteObject> &impl): IRemoteProxy<ITestAbility>(impl)
{
}int TestServiceProxy::TestPingAbility(const std::u16string &dummy){MessageOption option;MessageParcel dataParcel, replyParcel;dataParcel.WriteString16(dummy);int error = PeerHolder::Remote()->SendRequest(TRANS_ID_PING_ABILITY, dataParcel, replyParcel, option);int result = (error == ERR_NONE) ? replyParcel.ReadInt32() : -1;return result;
}#include "iremote_object.h"class TestDeathRecipient : public IRemoteObject::DeathRecipient {
public:virtual void OnRemoteDied(const wptr<IRemoteObject>& remoteObject);
}void TestDeathRecipient::OnRemoteDied(const wptr<IRemoteObject>& remoteObject)
{
}sptr<IPCObjectProxy> object = new IPCObjectProxy(1, to_utf16(DESCRIPTOR));
sptr<IRemoteObject::DeathRecipient> deathRecipient (new TestDeathRecipient()); // 构造一个消亡通知对象
bool result = object->AddDeathRecipient(deathRecipient); // 注册消亡通知
result = object->RemoveDeathRecipient(deathRecipient); // 移除消亡通知6.2 ArkTS侧接口
| 接口名 | 返回值类型 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| registerDeathRecipient | void | 注册用于接收远程对象消亡通知的回调,增加 proxy 对象上的消亡通知。 |
| unregisterDeathRecipient | void | 注销用于接收远程对象消亡通知的回调。 |
| onRemoteDied | void | 在成功添加死亡通知订阅后,当远端对象死亡时,将自动调用本方法。 |
获取context
Stage模型在连接服务前需要先获取context
import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility';
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';
import AbilityConstant from '@ohos.app.ability.AbilityConstant';
import window from '@ohos.window';export default class MainAbility extends UIAbility {onCreate(want: Want, launchParam: AbilityConstant.LaunchParam) {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onCreate');let context = this.context;}onDestroy() {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onDestroy');}onWindowStageCreate(windowStage: window.WindowStage) {// Main window is created, set main page for this abilityhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onWindowStageCreate');}onWindowStageDestroy() {// Main window is destroyed, release UI related resourceshilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onWindowStageDestroy');}onForeground() {// Ability has brought to foregroundhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onForeground');}onBackground() {// Ability has back to backgroundhilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', '%{public}s', 'UIAbility onBackground');}
}参考代码
// 仅FA模型需要导入@ohos.ability.featureAbility
// import FA from "@ohos.ability.featureAbility";
import Want from '@ohos.app.ability.Want';
import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';
import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';let proxy: rpc.IRemoteObject | undefined;
let connect: common.ConnectOptions = {onConnect: (elementName, remoteProxy) => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: js onConnect called.');proxy = remoteProxy;},onDisconnect: (elementName) => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: onDisconnect');},onFailed: () => {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'RpcClient: onFailed');}
};
let want: Want = {bundleName: "com.ohos.server",abilityName: "com.ohos.server.EntryAbility",
};
// FA模型通过此方法连接服务
// FA.connectAbility(want, connect);this.context.connectServiceExtensionAbility(want, connect);上述onConnect回调函数中的proxy对象需要等ability异步连接成功后才会被赋值,然后才可调用proxy对象的unregisterDeathRecipient接口方法注销死亡回调
import rpc from '@ohos.rpc';
import hilog from '@ohos.hilog';class MyDeathRecipient implements rpc.DeathRecipient{onRemoteDied() {hilog.info(0x0000, 'testTag', 'server died');}
}
let deathRecipient = new MyDeathRecipient();
if (proxy != undefined) {proxy.registerDeathRecipient(deathRecipient, 0);proxy.unregisterDeathRecipient(deathRecipient, 0);
}6.3 Stub感知Proxy消亡(匿名Stub的使用)
正向的消亡通知是Proxy感知Stub的状态,若想达到反向的死消亡通知,即Stub感知Proxy的状态,可以巧妙的利用正向消亡通知。如两个进程A(原Stub所在进程)和B(原Proxy所在进程),进程B在获取到进程A的Proxy对象后,在B进程新建一个匿名Stub对象(匿名指未向SAMgr注册),可称之为回调Stub,再通过SendRequest接口将回调Stub传给进程A的原Stub。这样一来,进程A便获取到了进程B的回调Proxy。当进程B消亡或B所在设备离开组网时,回调Stub会消亡,回调Proxy会感知,进而通知给原Stub,便实现了反向消亡通知。
注意:
反向死亡通知仅限设备内跨进程通信使用,不可用于跨设备。
当匿名Stub对象没有被任何一个Proxy指向的时候,内核会自动回收。
参考代码
// Proxy
int TestAbilityProxy::TestAnonymousStub()
{MessageOption option;MessageParcel dataParcel, replyParcel;dataParcel.UpdateDataVersion(Remote());dataParcel.WriteRemoteObject(new TestAbilityStub());int error = Remote()->SendRequest(TRANS_ID_REVERSED_MONITOR,dataParcel, replyParcel, option);int result = (error == ERR_NONE) ? replyParcel.ReadInt32() : -1;return result;
}// Stubint TestAbilityStub::OnRemoteRequest(uint32_t code, MessageParcel &data, MessageParcel &reply, MessageOption &option)
{switch (code) {case TRANS_ID_REVERSED_MONITOR: {sptr<IRemoteObject> obj = data.ReadRemoteObject();if (obj == nullptr) {reply.WriteInt32(ERR_NULL_OBJECT);return ERR_NULL_OBJECT;}bool result = obj->AddDeathRecipient(new TestDeathRecipient());result ? reply.WriteInt32(ERR_NONE) : reply.WriteInt32(-1);break;}default:break;}return ERR_NONE;
}参考文献:
[1]OpenHarmoney应用开发文档
这篇关于【鸿蒙开发】第二十四章 IPC与RPC进程间通讯服务的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





