本文主要是介绍CF E. Vanya and Brackets(添加一对括号使得表达式的值最大),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Vanya is doing his maths homework. He has an expression of form 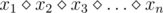 , where x1, x2, ..., xn are digits from 1 to 9, and sign
, where x1, x2, ..., xn are digits from 1 to 9, and sign  represents either a plus '+' or the multiplication sign '*'. Vanya needs to add one pair of brackets in this expression so that to maximize the value of the resulting expression.
represents either a plus '+' or the multiplication sign '*'. Vanya needs to add one pair of brackets in this expression so that to maximize the value of the resulting expression.
The first line contains expression s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 5001, |s| is odd), its odd positions only contain digits from 1 to 9, and even positions only contain signs + and * .
The number of signs * doesn't exceed 15.
In the first line print the maximum possible value of an expression.
3+5*7+8*4
303
2+3*5
25
3*4*5
60
Note to the first sample test. 3 + 5 * (7 + 8) * 4 = 303.
Note to the second sample test. (2 + 3) * 5 = 25.
Note to the third sample test. (3 * 4) * 5 = 60 (also many other variants are valid, for instance, (3) * 4 * 5 = 60).
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5005;
#define LL __int64char fh[N],s[N]; //����ջ�����ʽ
LL num[N]; //����ջ
int ftop,ntop ,slen; //����ջ��������ջ��
void calculate(){if(fh[ftop]=='+')num[ntop-1]+=num[ntop],ntop--;else if(fh[ftop]=='-')num[ntop-1]-=num[ntop],ntop--;else if(fh[ftop]=='*')num[ntop-1]*=num[ntop],ntop--;else if(fh[ftop]=='/')num[ntop-1]/=num[ntop],ntop--;ftop--;
}
void countfuction(int l,int r){ftop=0;ntop=0;int flagNum=0;LL ans=0;for(int i=0; i<=slen; ++i){if(i!=slen&&(s[i]>='0'&&s[i]<='9')){ans=ans*10+s[i]-'0';flagNum=1;}else{if(flagNum)num[++ntop]=ans; flagNum=0; ans=0;if(i==slen)break;if(s[i]=='+'||s[i]=='-'){while(ftop&&fh[ftop]!='(') calculate();fh[++ftop]=s[i];}else if(s[i]=='*'&&i==r){while(ftop&&fh[ftop]!='(') calculate(); ftop--;while(ftop&&(fh[ftop]=='*'||fh[ftop]=='/')) calculate();fh[++ftop]=s[i];//printf("# ");}else if(s[i]=='*'||i==l){while(ftop&&(fh[ftop]=='*'||fh[ftop]=='/')) calculate();fh[++ftop]=s[i];if(i==l)fh[++ftop]='(';}}}while(ftop) calculate();}
int main(){while(scanf("%s",s)>0){LL ans=0;int id[20],k=0;for(int i=strlen(s); i>=0; i--)s[i+2]=s[i];s[0]='1'; s[1]='*';slen=strlen(s);s[slen]='*'; s[slen+1]='1'; s[slen+2]='\0';slen=strlen(s);for(int i=0; i<slen; i++)if(s[i]=='*')id[k++]=i;for(int i=0; i<k-1; i++)for(int j=i+1; j<k; j++){countfuction(id[i],id[j]);if(num[1]>ans)ans=num[1];}printf("%I64d\n",ans);}
}这篇关于CF E. Vanya and Brackets(添加一对括号使得表达式的值最大)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





