本文主要是介绍SQL内连接、外连接、交叉连接; Linq内连接、外连接、交叉连接,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
SQL内连接、外连接、交叉连接
转自: http://blog.csdn.net/jiuqiyuliang/article/details/10474221
什么是连接查询呢?
概念:根据两个表或多个表的列之间的关系,从这些表中查询数据。
目的:实现多个表查询操作。
知道了连接查询的概念之后,什么时候用连接查询呢?
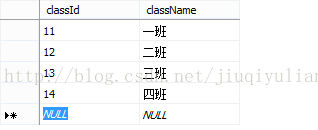
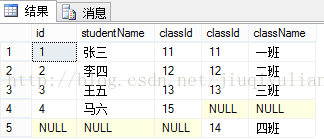
一般是用作关联两张或两张以上的数据表时用的。看起来有点抽象,我们举个例子,做两张表:学生表(T_student)和班级表(T_class)。
T_student T_class
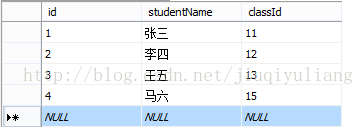
连接标准语法格式:
SQL-92标准所定义的FROM子句的连接语法格式为:
FROM join_table join_type join_table[ON (join_condition)]
其中join_table指出参与连接操作的表名,连接可以对同一个表操作,也可以对多表操作,对同一个表操作的连接又称做自连接。join_type 指出连接类型。join_condition指连接条件。
连接类型:
连接分为三种:内连接、外连接、交叉连接。
内连接(INNER JOIN)
使用比较运算符(包括=、>、<、<>、>=、<=、!>和!<)进行表间的比较操作,查询与连接条件相匹配的数据。根据比较运算符不同,内连接分为等值连接和不等连接两种。
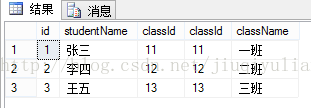
1、等值连接
概念:在连接条件中使用等于号(=)运算符,其查询结果中列出被连接表中的所有列,包括其中的重复列。
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select * from T_student s,T_class c where s.classId = c.classId
- 等于
- select * from T_student s inner join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
2、不等连接
概念:在连接条件中使用除等于号之外运算符(>、<、<>、>=、<=、!>和!<)
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select * from T_student s inner join T_class c on s.classId <> c.classId</span></span>
外连接
外连接分为左连接(LEFT JOIN)或左外连接(LEFT OUTER JOIN)、右连接(RIGHT JOIN)或右外连接(RIGHT OUTER JOIN)、全连接(FULL JOIN)或全外连接(FULL OUTER JOIN)。我们就简单的叫:左连接、右连接和全连接。
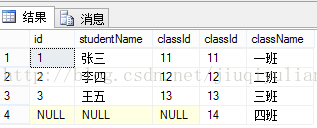
1、左连接:
概念:返回左表中的所有行,如果左表中行在右表中没有匹配行,则结果中右表中的列返回空值。
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select * from T_student s left join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
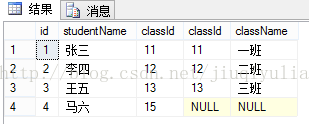
总结:左连接显示左表全部行,和右表与左表相同行。
2、右连接:
概念:恰与左连接相反,返回右表中的所有行,如果右表中行在左表中没有匹配行,则结果中左表中的列返回空值。
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select * from T_student s right join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
总结:右连接恰与左连接相反,显示右表全部行,和左表与右表相同行。
3、全连接:
概念:返回左表和右表中的所有行。当某行在另一表中没有匹配行,则另一表中的列返回空值
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select * from T_student s full join T_class c on s.classId = c.classId</span></span>
总结:返回左表和右表中的所有行。
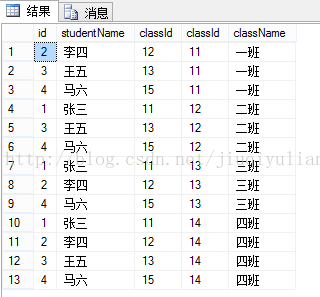
交叉连接(CROSS JOIN):也称迪卡尔积
概念:不带WHERE条件子句,它将会返回被连接的两个表的笛卡尔积,返回结果的行数等于两个表行数的乘积(例如:T_student和T_class,返回4*4=16条记录),如果带where,返回或显示的是匹配的行数。
1、不带where:
- <span style="font-size:18px;"><span style="font-family:System;">
- select *from T_student cross join T_class
- ‘等于
- select *from T_student, T_class</span></span>
结果是:
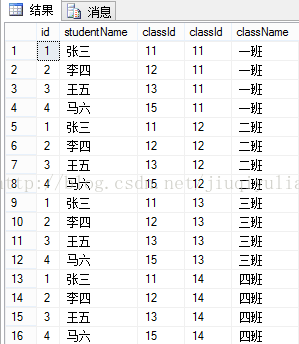
总结:相当与笛卡尔积,左表和右表组合。
2、有where子句,往往会先生成两个表行数乘积的数据表,然后才根据where条件从中选择。
- select * from T_student s cross join T_class c where s.classId = c.classId
- (注:cross join后加条件只能用where,不能用on)
Linq的内连接、外连接、交叉连接:
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/scottckt/archive/2010/08/11/1797716.html
Linq中连接主要有组连接、内连接、左外连接、交叉连接四种。各个用法如下。
注:本文内容主要来自《Linq实战》,本例中用到的对象请见文章底部。
1、 组连接
组连接是与分组查询是一样的。即根据分组得到结果。 如下例,根据publisther分组得到结果。
使用组连接的查询语句如下:
var GroupQuery = from publisher in SampleData.Publishers
join book in SampleData.Books
on publisher equals book.Publisher into publisherBooks
select new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
Books = publisherBooks
};
与上边等同的GroupBy语句如下:
var QueryByGroup = from book in SampleData.Books
group book by book.Publisher into grouping
select new
{
PublisherName = grouping.Key.Name,
Books = grouping
};
2、内连接
内连接与SqL中inner join一样,即找出两个序列的交集。如下例找出book中的Publisher存在于SampleData.Publishers的资料。
内连接查询语句如下:
var joinQuery = from publisher in SampleData.Publishers
join book in SampleData.Books
on publisher equals book.Publisher
select new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = book.Title
};
与上边等同的查询操作符语句如下:
SampleData.Publishers.Join(
SampleData.Books, // join 对象
publisher => publisher, // 外部的key
book => book.Publisher, // 内部的key
(publisher, book) => new // 结果
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = book.Title
});
3、左外连接
左外连接与SqL中left join一样。如下例找出根据publisher中找出SampleData.Publishers中所有资料和book中存在于publisher的资料。
左外连接查询语句如下:
var leftJoinQuerybyDefault = from publisher in SampleData.Publishers
join book in SampleData.Books
on publisher equals book.Publisher into publisherBooks
from book in publisherBooks.DefaultIfEmpty()
select new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = (book == default (Book)) ? " no book " : book.Title
};
注:上例中使用了DefaultIfEmpty操作符,它能够为实序列提供一个默认的元素。DefaultIfEmpty使用了泛型中的default关键字。default关键字对于引用类型将返回null,而对于值类型则返回0。对于结构体类型,则会根据其成员类型将它们相应地初始化为null(引用类型)或0(值类型)。
我们可以不使用default关键字,但在要DefaultIfEmpty中给定当空时的默认对象值。语句如下:
var leftJoinQuery = from publisher in SampleData.Publishers
join book in SampleData.Books
on publisher equals book.Publisher into publisherBooks
from book in publisherBooks.DefaultIfEmpty(
new Book { Title = "" } // 设置为空时的默认值
)
select new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = book.Title
};
4、交叉连接
交叉连接与SqL中Cross join一样。如下例中找出SampleData.Publishers与SampleData.Books的交叉连接。
交叉连接查询语句:
from book in SampleData.Books
select new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = book.Title
};
查询操作符语句:
SampleData.Publishers.SelectMany(publisher => SampleData.Books.Select(
book => new
{
PublisherName = publisher.Name,
BookName = book.Title
}
));
这篇关于SQL内连接、外连接、交叉连接; Linq内连接、外连接、交叉连接的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!