本文主要是介绍同构树的判断 poj 1635,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目的描述比较长,总的意思就是给出两棵有根树,判断它们是不是同构树。
所谓的同构树,定义我也不太知道 。按字面上的意思就是两棵结构相同的树。
。按字面上的意思就是两棵结构相同的树。
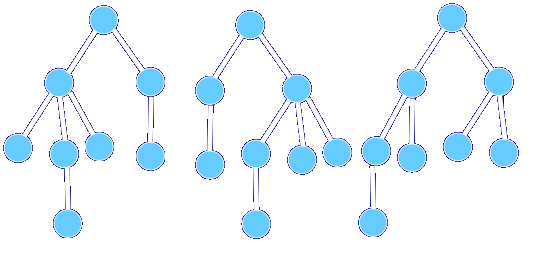
如第一棵树和第二棵树就是同构树,它们和第三棵树不是同构树:
并且,同构树它们有一一对应的点。
对于任意一棵有根树,都可以用括号表示法来表示,可以去http://www.byvoid.com/blog/directed-tree-bracket-sequence/看看。
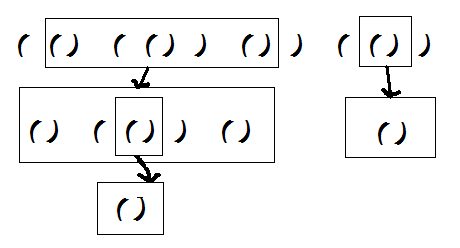
如上面的第一棵树,既可以表示成(()(())())(()),也可以表示成(())((())()()),有很多的表示方法,为了判断,我们要用最小表示法,就是字典序最小的一个。第一种括号可以分解成:
每一层都排一下序就可以找到字典树最小的一个啦 。
。
其实原题就是这样的一个括号序列,0代表左括号,1代表右括号。这样问题就很简单了,把这读入的两个字符串当做括号处理,如果它们的最小表示法是一样的,那么就是同构树啦。
但是,我们要对字符串进行分解,分解完了还要排序,不仅时间复杂度不乐观,空间处理也比较麻烦。所以,我们可以用哈希,把一个括号序列哈希掉。合并的时候将哈希值从小到大排序,再合成当前的哈希值。可以去看看《杨弋<Hash在信息学竞赛中的一类应用>》这篇文章。
我看到网上有一种方法,判断每一层的节点数是否相等,且相同层数子树大小经过排序后对应相等,那么就是同构。我不知道这种方法对不对,网上有的说这是错的。我写了一下,还真的过了,求证明。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <time.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int n, P[3007];
bool d[6007];// 这样读入会快些??
int read(int i) {char ch = '*';do ch = getchar(); while (ch < '0' || ch > '1');for (; ch == '0' || ch == '1'; ch = getchar()) d[i ++] = ch == '1';return i;
}// 字符串的[L, R)的哈希值
int GetHash(int L, int R) {if (L >= R) return 1;// 只能用vector??我想不到更好的办法 vector<int> t;t.clear();int f = 0, cnt = 0;for (int i = L; i < R; i ++) {if (d[i]) f --; else f ++;// 当括号匹配时就可以分解了 if (f == 0) {t.push_back(GetHash(L + 1, i)), cnt ++;L = i + 1;}}// 排序 sort(t.begin(), t.end());// 求出当前哈希值 int res = 1;// 这要找个好的哈希函数,// 一开始我写得不好,有很多重复// 后来在网上看到如下的方法 for (int i = 0; i < cnt; i ++)res = (res ^ t[i]) * P[i] % 15237;return res;
}int main() {freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout);srand((int)time(0));for (int i = 0; i < 3000; i ++) P[i] = rand() % 15237;int T;scanf("%d\n", &T);while (T --) {int n = read(0);int m = read(n);if (GetHash(0, n) == GetHash(n, m)) printf("same\n");else printf("different\n");}return 0;
}
奇怪的方法(代码有点烂, 其实不用构图的):
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;const int N = 3007;struct Tree {int n;int father[N], head[N], to[N], next[N], cnt;struct data {int depth, size;bool operator < (data const &o) const {if (depth != o.depth) return depth < o.depth;return size < o.size;}bool operator == (data const &o) const {return depth == o.depth && size == o.size;}}d[N];void Insert(int u, int v) {to[++ cnt] = v;next[cnt] = head[u];head[u] = cnt;}int Q[N];void Build(char *s) {cnt = 0;memset(head, 0, sizeof(head));int len = strlen(s);n = 1;int cur = 1;for (int i = 0; i < len; i ++)if (s[i] == '0') {Insert(cur, ++ n);father[n]= cur;cur = n;}else cur = father[cur];d[1].depth = 1;int lo = 0, hi = 0;Q[0] = 1;for (; lo <= hi; lo ++) {int u = Q[lo];for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e]) {int v = to[e];d[v].depth = d[u].depth + 1;Q[++ hi] = v;}}for (; hi >= 0; hi --) {int u = Q[hi];d[u].size = 1;for (int e = head[u]; e; e = next[e]) d[u].size += d[to[e]].size;}sort(d + 1, d + 1 + n);}bool operator == (Tree const &o) const {if (n != o.n) return false;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)if (!(d[i] == o.d[i])) return false;return true;}
}a, b;char dat[N];int main() {int T;scanf("%d\n", &T);while (T --) {scanf("%s\n", dat);a.Build(dat);scanf("%s\n", dat);b.Build(dat);if (a == b) printf("same\n");else printf("different\n");}return 0;
}这篇关于同构树的判断 poj 1635的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!