本文主要是介绍Go 语言 ORM 框架之 xorm,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、xorm
1.1、xorm 简介
xorm 是一个简单而强大的Go语言ORM库. 通过它可以使数据库操作非常简便。
特性
- 支持 struct 和数据库表之间的灵活映射,并支持自动同步
- 事务支持
- 同时支持原始SQL语句和ORM操作的混合执行
- 使用连写来简化调用
- 支持使用ID, In, Where, Limit, Join, Having, Table, SQL, Cols等函数和结构体等方式作为条件
1.2、安装环境
go get xorm.io/xorm
1.3、快速开始
基本的连接信息
var (username string = "root"password string = "xxxxxx"ip string = "127.0.0.1"port int = 3306dbName = "go_web"charset string = "utf8mb4")dataSource := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:%d)/%s?charset=%s",username ,password,ip ,port ,dbName ,charset )
1.3.1、同步结构体到数据库
1. 创建引擎
// 1. 创建引擎engine, err := xorm.NewEngine("mysql", dataSource)if err!=nil {println("连接失败")}2. 创建结构体
结构体中的每个字段都将对应一个表的字段,我们可以通过标签来告诉 xorm 同步到数据库或使用什么数据类型:
// 2. 创建结构体type User struct {Id int64Name stringAge intPassword string `xorm:"varchar(200)"`Created time.Time `xorm:"created"`Updated time.Time `xorm:"updated"`}3. 同步结构体
// 3. 同步结构体err = engine.Sync(new(User))if err!=nil {println("创建表格失败")}同步结构体这个操作可以执行多次,如果我们删除了字段,只需要重新同步即可。但是如果修改了字段,就会把修改后的字段作为一个新的字段,所以一定要注意。
1.3.1、单条数据的插入
插入数据需要使用 Insert 方法,这个方法需要传入一个对象的指针,因为我们知道,方法中的参数是形参,而且结构体类型是值类型,所以进入 Insert 方法后会拷贝一份,而不是操作我们的实参。
我们可以试着打印插入前后,我们实参的变化:
// 1. 插入单条数据user1 := User{ Id: 2, Name: "李大喜", Age: 22, Password: "123456",}fmt.Println(user1)res,err := engine.InsertOne(&user1)if err != nil {println("插入失败",err)}else {fmt.Printf("成功插入 %d 条数据\n",res)}fmt.Println(user1)运行结果:
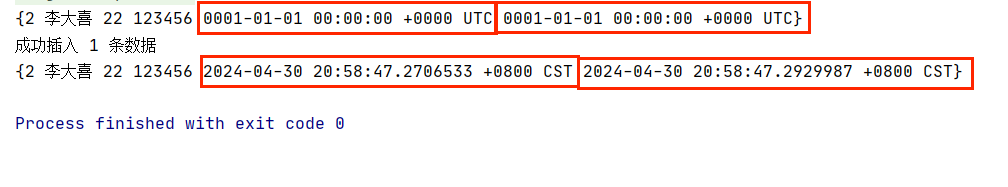
可以看到,对象未进入 insert 方法之前,它的两个 time 类型的字段是默认值,但是进入 insert 方法后,被赋值为当前时间。
1.3.2、多条数据的插入
1. 传入多个结构体对象插入
// 1. 插入多条数据user1 := User{ Id: 3, Name: "刘能", Age: 52, Password: "123456",}user2 := User{ Id: 4, Name: "赵四", Age: 52, Password: "123456",}res,err := engine.Insert(&user1,&user2)if err != nil {println("插入失败",err)}else {fmt.Printf("成功插入 %d 条数据\n",res)}2. 通过切片插入
users := make([]User,2)user1 := User{ Id: 3, Name: "刘能", Age: 52, Password: "123456",}user2 := User{ Id: 4, Name: "赵四", Age: 52, Password: "123456",}users[0] = user1users[2] = user2res,err := engine.Insert(&users)if err != nil {println("插入失败",err)}else {fmt.Printf("成功插入 %d 条数据\n",res)}虽然Go语言中的切片是引用类型,但在我们这里仍然需要传入切片的地址(指针)。
这是因为xorm的Insert方法在处理切片时,如果接收到的是切片的指针,它能够通过该指针获取到切片的实时长度信息。这个长度信息对于数据库的批量插入操作是非常重要的,因为它可以帮助xorm确定一次性能插入多少条记录,从而提高效率。
1.3.3、更新与删除
更新数据
// 修改用户user := User{Name: "谢永强"}res,_ := engine.ID(1).Update(&user)fmt.Println(res)删除数据
// 1. 删除单条数据user := User{Name: "谢永强"}res,_ := engine.ID(1).Delete(&user)fmt.Println(res)执行 SQL
// 1. 执行 SQLres,_ := engine.Exec("UPDATE user SET name = '刘海柱' WHERE id = ?",1)fmt.Println(res)
1.3.4、查询与遍历
1. SQL 查询(不常用)
- Query 最原始的也支持SQL语句查询,返回的结果类型为 []map[string][]byte。
- QueryString 返回 []map[string]string, QueryInterface 返回 []map[string]interface{}。
res1,_ := engine.Query("SELECT * FROM user");fmt.Println(res1)res2,_ := engine.QueryString("SELECT * FROM user");fmt.Println(res2)res3,_ := engine.QueryInterface("SELECT * FROM user");fmt.Println(res3)运行结果:
[map[age:[50 50] created:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 48 58 53 53 58 51 53] id:[49] name:[229 136 152 230 181 183 230 159 177] password:[49 50 51 52 53 54] updated:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 49 58 49 52 58 50 57]] map[age:[50 50] created:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 48 58 53 56 58 52 55] id:[50] name:[230 157 142 229 164 167 229 150 156] password:[49 50 51 52 53 54] updated:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 48 58 53 56 58 52 55]] map[age:[53 50] created:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 49 58 48 52 58 49 49] id:[51] name:[229 136 152 232 131 189] password:[49 50 51 52 53 54] updated:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 49 58 48 52 58 49 49]] map[age:[53 50] created:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 49 58 48 52 58 49 49] id:[52] name:[232 181 181 229 155 155] password:[49 50 51 52 53 54] updated:[50 48 50 52 45 48 52 45 51 48 32 50 49 58 48 52 58 49 49]]]
[map[age:22 created:2024-04-30 20:55:35 id:1 name:刘海柱 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:14:29] map[age:22 created:2024-04-30 20:58:47 id:2 name:李大喜 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 20:58:47] map[age:52 created:2024-04-30 21:04:11 id:3 name:刘能 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:04:11] map[age:52 created:2024-04-30 21:04:11 id:4 name:赵四 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:04:11]]
[map[age:22 created:2024-04-30 20:55:35 id:1 name:刘海柱 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:14:29] map[age:22 created:2024-04-30 20:58:47 id:2 name:李大喜 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 20:58:47] map[age:52 created:2024-04-30 21:04:11 id:3 name:刘能 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:04:11] map[age:52 created:2024-04-30 21:04:11 id:4 name:赵四 password:123456 updated:2024-04-30 21:04:11]]2. GET 查询(单行查询)
// GET 查询user := User{}engine.Get(&user) // 默认查询第一条数据fmt.Println(user) // {1 刘海柱 22 123456 2024-04-30 20:55:35 +0800 CST 2024-04-30 21:14:29 +0800 CST}
指定条件来查询
user := User{Name: "刘海柱"}// 查询指定用户名 且 根据id降序后的第一条数据engine.Where("name=?",user.Name).Desc("id").Get(&user)fmt.Println(user)查询指定字段:
// 获取指定字段值user := User{}var name string// Table(&user) 代表表结构和结构体 User 相同engine.Table(&user).Where("id = 1").Cols("name").Get(&name)fmt.Println(name)3. Find 查询(多行查询)
var users []Userengine.Where("id < 5").And("password = 123456").Limit(10).Find(&users)for i := 0; i < len(users);i++ {fmt.Println(users[i])}// 或者使用 range 遍历切片for _,user := range users{fmt.Println(user)}运行结果:
{1 刘海柱 22 123456 2024-04-30 20:55:35 +0800 CST 2024-04-30 21:14:29 +0800 CST}
{2 李大喜 22 123456 2024-04-30 20:58:47 +0800 CST 2024-04-30 20:58:47 +0800 CST}
{3 刘能 52 123456 2024-04-30 21:04:11 +0800 CST 2024-04-30 21:04:11 +0800 CST}
{4 赵四 52 123456 2024-04-30 21:04:11 +0800 CST 2024-04-30 21:04:11 +0800 CST}4. Count 查询
// 查询所有 password="123456" 的用户user := User{Password: "123456"}count,_ := engine.Count(&user)fmt.Println(count) // 45. Iterate 迭代查询
Iterate 方法有两个参数:
- 查询条件(哪个结构体对应的表以及过滤条件)
- 匿名函数(第一个参数代表查询到的当前元素的索引,第二个参数代表当前元素对象)
engine.Iterate(&User{Password: "123456"}, func(idx int, bean interface{}) error {// 类型断言user := bean.(*User)fmt.Println(user)return nil})
6. Rows 迭代查询
rows,_ := engine.Rows(&User{Password: "123456"})defer rows.Close()user := new(User) // 传递指针给userfor rows.Next(){rows.Scan(user)fmt.Println(user)}
这里的 Scan 方法需要一个指针,所以我们上面使用 new(User) 来初始化一个指针给 user,我们也可以通过下面的方法,都是一样的:
rows,_ := engine.Rows(&User{Password: "123456"})defer rows.Close()user := User{}for rows.Next(){rows.Scan(&user)fmt.Println(user)}1.3.5、事务
要使用事务的话,必须使用 session 类进行数据的增删改,并结合 panic 和 recover 来进行异常的处理,一旦出现异常就回滚所有事务:
session := engine.NewSession()defer session.Close()// 通过 panic 和 recover 进行异常的处理defer func() {err := recover()if err != nil {fmt.Println("Rollback")session.Rollback()}else {session.Commit()}}()session.Begin() // 开启事务user := User{Id: 5,Name: "王老七",Age: 40}if _,err := session.Insert(&user);err!=nil{panic(err)}
这篇关于Go 语言 ORM 框架之 xorm的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





