本文主要是介绍FFmpeg———encode_video(学习),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 前言
- 源码
- 函数
- 最终效果
前言
encode_video:实现了对图片使用指定编码进行编码,生成可播放的视频流,编译时出现了一些错误,做了一些调整。
基本流程:
1、获取指定的编码器
2、编码器内存申请
3、编码器上下文内容参数设置
4、打开编码器
5、申请数据帧内存
6、模拟图片
7、编码
源码
测试代码,做了部分修改
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>extern"C"
{
#include "libavcodec/avcodec.h"
#include "libavutil/opt.h"
#include "libavutil/imgutils.h"
#include "libavutil/error.h"
}static void encode(AVCodecContext* enc_ctx, AVFrame* frame, AVPacket* pkt,FILE* outfile)
{int ret;/* send the frame to the encoder */if (frame)printf("Send frame %lld\n", frame->pts); //修改 lld 替换 PRId64/*avcodec_send_frame 与 avcodec_receive_packet 配合使用*/ret = avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame);if (ret < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Error sending a frame for encoding\n");exit(1);}while (ret >= 0) {ret = avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, pkt);if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN) || ret == AVERROR_EOF)return;else if (ret < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Error during encoding\n");exit(1);}printf("Write packet %lld (size=%d)\n", pkt->pts, pkt->size); //修改 lld 替换 PRId64fwrite(pkt->data, 1, pkt->size, outfile);av_packet_unref(pkt); //清空数据压缩包}
}int main()
{const char* filename;const AVCodec* codec;AVCodecContext* c = NULL; // 编码器上下文int i, ret, x, y;FILE* f;AVFrame* frame; // 音视频数据帧结构体AVPacket* pkt;uint8_t endcode[] = { 0, 0, 1, 0xb7 };filename = "text_264";/* find the mpeg1video encoder */codec = avcodec_find_encoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);if (!codec) {fprintf(stderr, "Codec not found\n");exit(1);}// 为编码器申请空间并设置初始值c = avcodec_alloc_context3(codec);if (!c) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video codec context\n");exit(1);}pkt = av_packet_alloc();if (!pkt)exit(1);/* put sample parameters */c->bit_rate = 400000;/* 分辨率 为2的倍数 */c->width = 352;c->height = 288;/* frames per second */c->time_base.num = 1;c->time_base.den = 25;//帧率c->framerate.num = 25;c->framerate.den = 1;/* emit one intra frame every ten frames* check frame pict_type before passing frame* to encoder, if frame->pict_type is AV_PICTURE_TYPE_I* then gop_size is ignored and the output of encoder* will always be I frame irrespective to gop_size*/c->gop_size = 10;c->max_b_frames = 1; //非B帧之间的最大的B帧数c->pix_fmt = AV_PIX_FMT_YUV420P; //像素格式if (codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264)av_opt_set(c->priv_data, "preset", "slow", 0); //设置属性/* open it */ret = avcodec_open2(c, codec, NULL);if (ret < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not open codec: %s\n", av_err2str(ret));exit(1);}f = fopen(filename, "wb");if (!f) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not open %s\n", filename);exit(1);}frame = av_frame_alloc();if (!frame) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate video frame\n");exit(1);}frame->format = c->pix_fmt;frame->width = c->width;frame->height = c->height;ret = av_frame_get_buffer(frame, 0); //申请数据帧缓冲区if (ret < 0) {fprintf(stderr, "Could not allocate the video frame data\n");exit(1);}/* encode 1 second of video */for (i = 0; i < 25; i++) {fflush(stdout);/* Make sure the frame data is writable.On the first round, the frame is fresh from av_frame_get_buffer()and therefore we know it is writable.But on the next rounds, encode() will have calledavcodec_send_frame(), and the codec may have kept a reference tothe frame in its internal structures, that makes the frameunwritable.av_frame_make_writable() checks that and allocates a new bufferfor the frame only if necessary.*/ret = av_frame_make_writable(frame); //确保数据帧是可写if (ret < 0)exit(1);/* 模拟图片数据*//* Y */for (y = 0; y < c->height; y++) {for (x = 0; x < c->width; x++) {frame->data[0][y * frame->linesize[0] + x] = x + y + i * 3;}}/* Cb and Cr */for (y = 0; y < c->height / 2; y++) {for (x = 0; x < c->width / 2; x++) {frame->data[1][y * frame->linesize[1] + x] = 128 + y + i * 2;frame->data[2][y * frame->linesize[2] + x] = 64 + x + i * 5;}}frame->pts = i;/* encode the image */encode(c, frame, pkt, f);}/* flush the encoder */encode(c, NULL, pkt, f);/* Add sequence end code to have a real MPEG file.It makes only sense because this tiny examples writes packetsdirectly. This is called "elementary stream" and only works for somecodecs. To create a valid file, you usually need to write packetsinto a proper file format or protocol; see mux.c.*/if (codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG1VIDEO || codec->id == AV_CODEC_ID_MPEG2VIDEO)fwrite(endcode, 1, sizeof(endcode), f);fclose(f);avcodec_free_context(&c);av_frame_free(&frame);av_packet_free(&pkt);return 0;
}函数
1、int avcodec_send_frame(AVCodecContext *avctx, const AVFrame *frame);
向编码器发送音频或视频的数据包与
int avcodec_receive_packet(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVPacket *avpkt);配合使用
成功返回0
2、av_err2str(errnum)
编译会报错
修改:
char av_error[AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE] = { 0 };
#define av_err2str(errnum) \av_make_error_string(av_error, AV_ERROR_MAX_STRING_SIZE, errnum)
最终效果
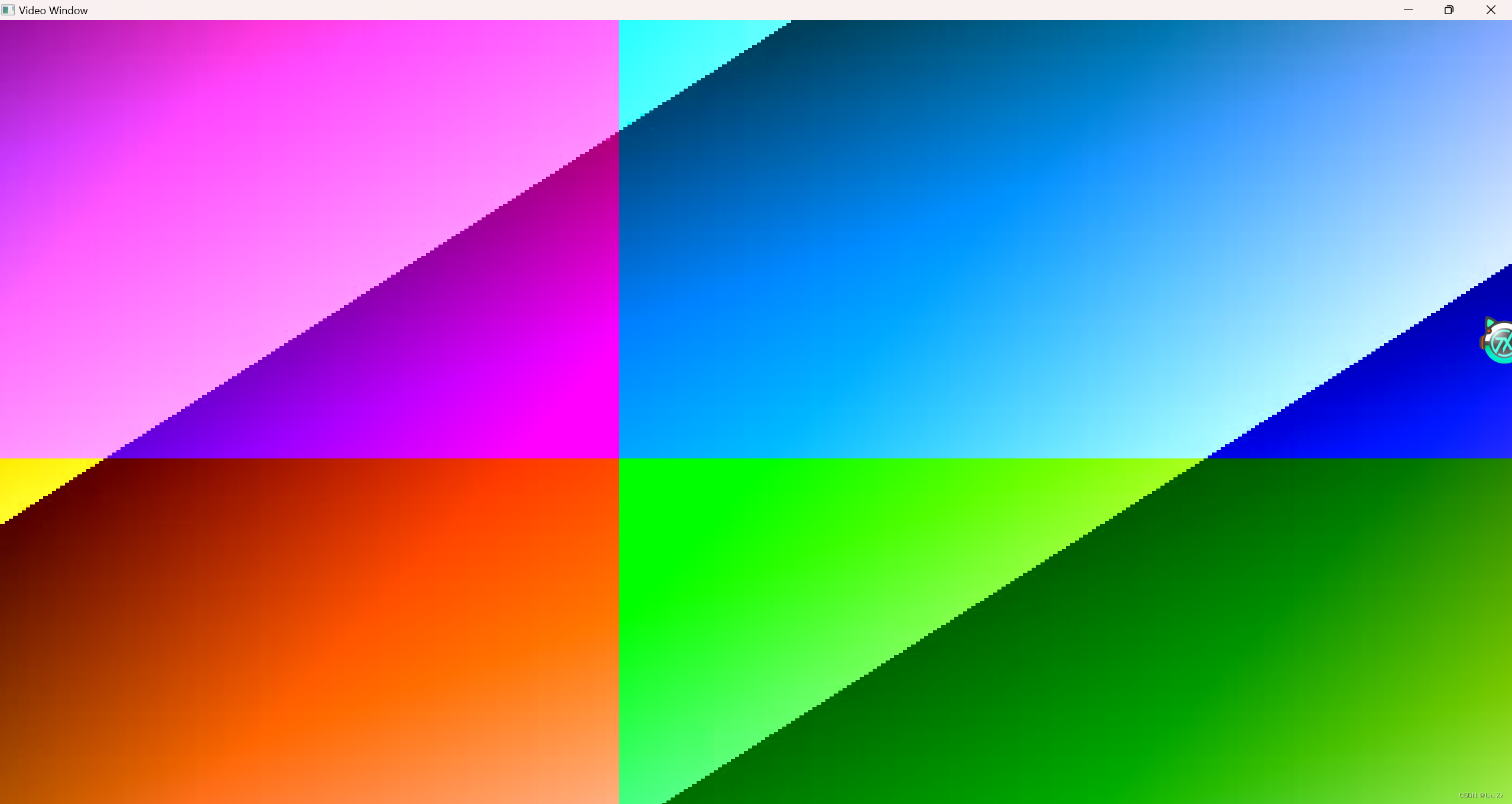
这篇关于FFmpeg———encode_video(学习)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






