本文主要是介绍C++—DAY4,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在Complex类的基础上,完成^,<<,>>,~运算符的重载
#include <iostream>using namespace std;
class Complex
{int rel;int vir;
public:Complex(){}Complex(int rel,int vir):rel(rel),vir(vir){}void show(){cout << this->rel << "+" << this->vir << "i" << endl;}//成员函数实现+运算符重载Complex operator+(const Complex c1);Complex operator*(const Complex c1);friend Complex operator-(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);friend Complex operator/(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);friend Complex operator%(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);bool operator>(const Complex c1);friend bool operator>=(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);friend bool operator&&(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);Complex operator--();friend Complex operator--(Complex &c1,int);friend istream &operator>>(istream &in,Complex &c1);friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,Complex c1);friend Complex operator^(const Complex c1,const Complex c2);Complex operator~();};
Complex Complex::operator+(const Complex c1)
{//实例化一个temp类对象,并调用有参构造Complex temp;temp.rel=this->rel+c1.rel;temp.vir=this->vir+c1.vir;return temp;
}
Complex Complex::operator*(const Complex c1)
{//实例化一个temp类对象,并调用有参构造Complex temp;temp.rel=this->rel*c1.rel;temp.vir=this->vir*c1.vir;return temp;
}
//全局函数版
Complex operator-(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{Complex temp;temp.rel=c1.rel-c2.rel;temp.vir=c1.vir-c2.vir;return temp;
}
Complex operator/(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{Complex temp;temp.rel=c1.rel/c2.rel;temp.vir=c1.vir/c2.vir;return temp;
}
Complex operator%(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{Complex temp;temp.rel=c1.rel%c2.rel;temp.vir=c1.vir%c2.vir;return temp;
}
bool Complex::operator>(const Complex c1)
{return this->rel>c1.rel;
}
bool operator>=(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{return c1.rel>=c2.rel;
}
bool operator&&(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{return ((c1.rel&&c2.rel)&&(c1.vir&&c2.vir));
}
Complex Complex::operator--()
{--this->rel;--this->vir;return *this;
}
Complex operator--(Complex &c1,int)
{Complex temp(c1.rel--,c1.vir--);return temp;
}istream &operator>>(istream &in,Complex &c1)
{in >> c1.rel >> c1.vir;return in;
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,Complex c1)
{out << c1.rel << "+" << c1.vir << "i" <<endl;return out;
}
Complex operator^(const Complex c1,const Complex c2)
{Complex temp;temp.rel=c1.rel^c2.rel;temp.vir=c1.vir^c2.vir;return temp;
}
Complex Complex::operator~()
{Complex temp;temp.rel=~this->rel;temp.vir=~this->vir;return temp;
}
int main()
{Complex c1(2,5),c2(3,4);Complex c3=c1+c2;c3.show();Complex c4=c1.operator*(c2);c4.show();Complex c5=operator-(c1,c2);c5.show();Complex c6=operator/(c1,c2);c6.show();Complex c7=operator%(c1,c2);c7.show();cout << operator>=(c1,c2) << endl;Complex c8(0,1),c9(1,1);cout << operator&&(c8,c9) << endl;Complex c10=c9--;c10.show();Complex c11=--c8;c11.show();return 0;
}
在昨天作业myString类的基础上,完成+、关系运算符、逻辑运算符、输入输出运算符的重载
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
char c = '\0';
class myString
{private:char *str; //记录c风格的字符串int size; //记录字符串的实际长度public://无参构造myString():str(new char),size(0){}//有参构造myString(char *p,int size):str(new char[size+1]),size(size){strcpy(str,p);}myString(string s1):str(new char[s1.size()+1]),size(s1.length()){strcpy(str,s1.c_str());}//拷贝构造myString(const myString &other):str(new char[other.size+1]),size(size){strcpy(str,other.str);}//拷贝赋值函数myString &operator=(const myString &other){//提前把申请的空间释放,重新申请空间,为了防止原有的空间不够存下新的内容if(&other!=this){delete []str;str = new char[other.size+1];strcpy(str,other.str);this->size = other.size;}return *this;}//析构函数~myString(){delete []str;}//判空函数bool empty(){return size==0;}//size函数int size_(){return size;}//c_str函数const char *c_str(){return str;}//at函数char &at(int pos){//判断位置合理性if(pos<0||pos>=size){cout << "位置不合理" << endl;return c;}return str[pos];}myString operator+(const myString m1);friend bool operator==(const myString m1,const myString m2);friend bool operator||(const myString m1,const myString M2);friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,myString m1);friend istream &operator>>(istream &in,myString &m1);
};
myString myString::operator+(const myString m1)
{myString temp;temp.str=strcat(this->str,m1.str);temp.size=this->size+m1.size;return temp;
}
bool operator==(const myString m1,const myString m2)
{return (strcmp(m1.str,m2.str)&&(m1.size==m2.size));
}
bool operator||(const myString m1,const myString m2)
{return ((m1.str!=0||m2.str!=0)||(m1.size!=0||m2.size!=0));
}
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,myString m1)
{out << m1.str << "\t" << m1.size;return out;
}
istream &operator>>(istream &in,myString &m1)
{in >> m1.str >> m1.size;return in;
}
int main()
{char str[]="hello";myString str1(str,5);cout << str1.empty() << endl;cout << str1.size_() << endl;cout << str1.at(3) << endl;str1.at(3) = '9';cout << str1.at(3) << endl;return 0;
}思维导图
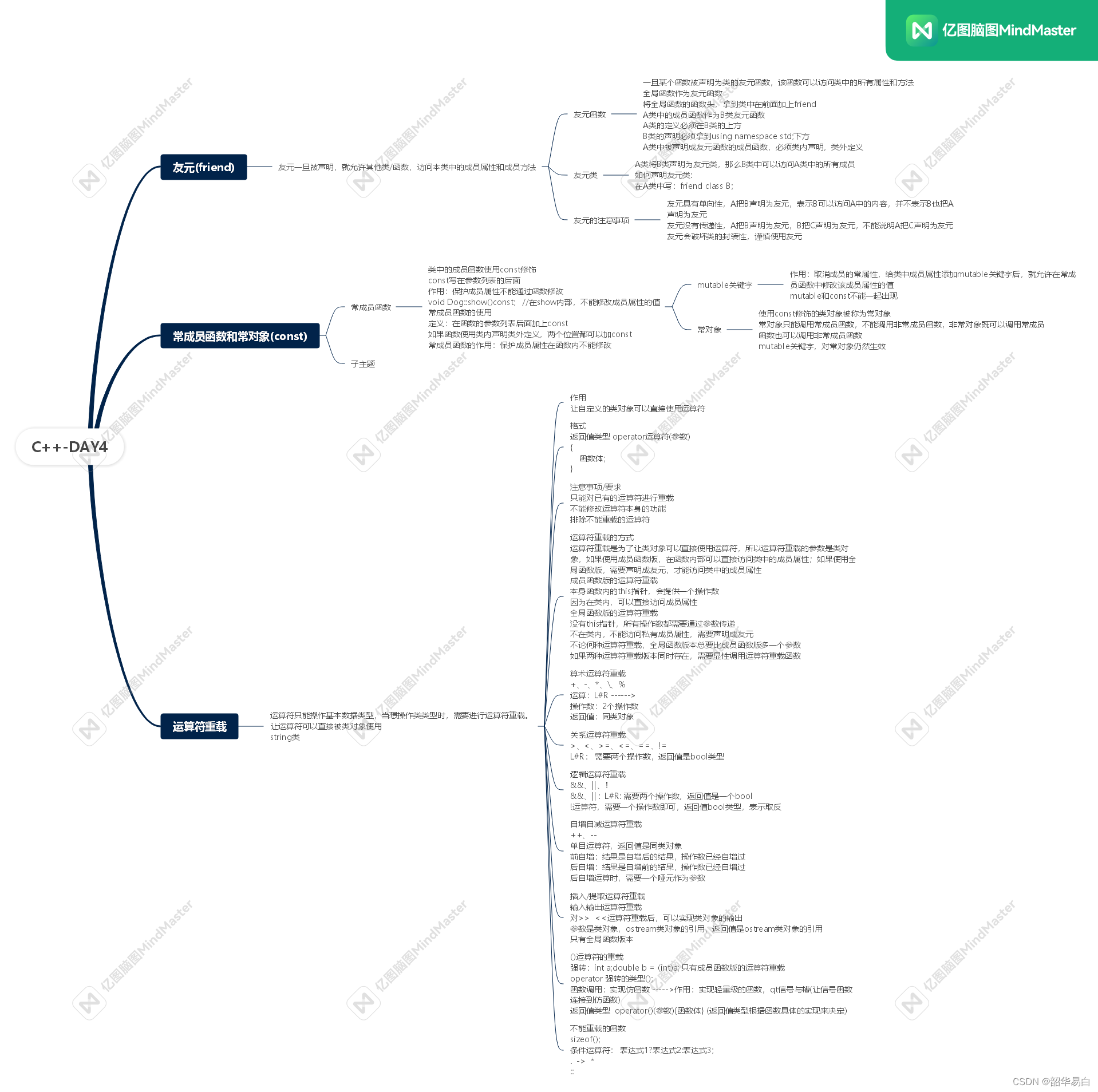
这篇关于C++—DAY4的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





